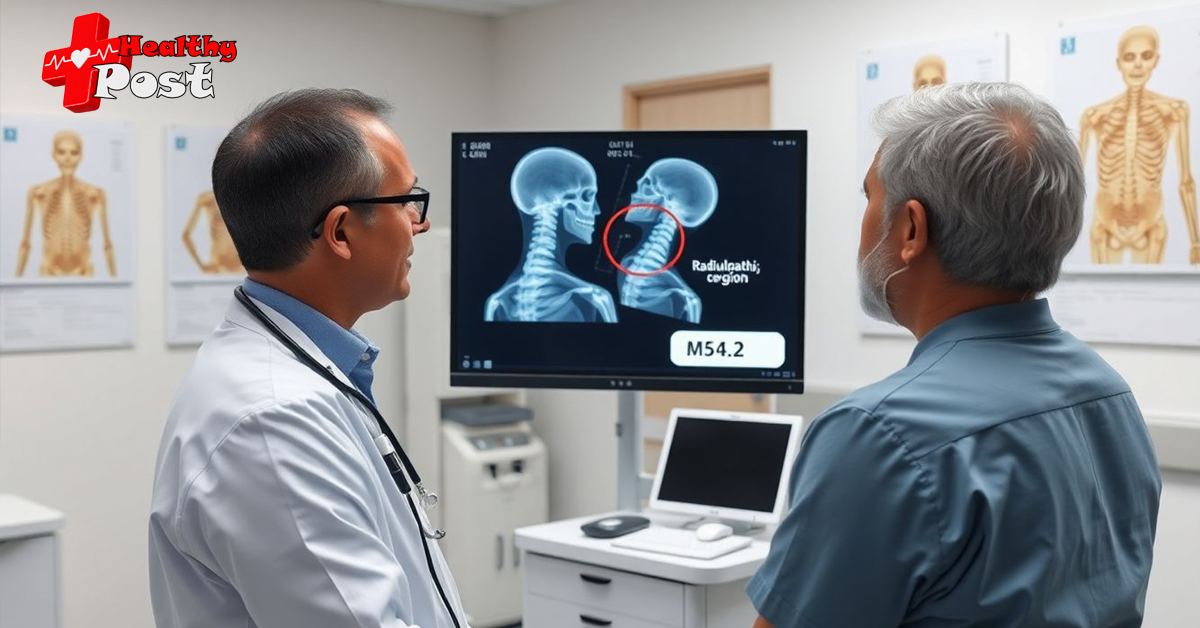
Understanding M54.2 Diagnosing code and Managing Lumbar Radiculopathy
Clear medical coding helps doctors and insurance companies understand your condition. It makes medical records accurate and payments smooth. The code M54.2 (m54.2 diagnosis code) is key for identifying lumbar radiculopathy, a nerve problem in the lower back. Knowing what this code means improves how we treat patients and process claims. Both healthcare providers and patients benefit from understanding the significance of diagnosis codes like M54.2. It guides proper treatment plans and ensures correct billing.
What Is M54.2 and What Does It Cover?
Definition and Clinical Scope
M54.2 is a medical code used to mark lumbar radiculopathy. This condition involves nerve root issues in the lower back. It causes pain that travels from the spine into the legs. It is different from general back pain that doesn’t involve nerve roots. Lumbar radiculopathy often shows up as sciatica—a shooting pain down the leg.
Coding Standards and Medical Classification
M54.2 falls under ICD-10, a global system for classifying diseases. It’s part of broader categories for spine and nerve conditions. Medical coders use M54.2 to specify when nerve roots in the lumbar spine are pinched or irritated. This helps doctors document their findings clearly.
Causes and Risk Factors for Lumbar Radiculopathy (M54.2)
Common Causes
- Herniated discs push into nerve roots.
- Spinal stenosis narrows spaces around nerves.
- Degenerative disc disease wears down discs over time.
Risk Factors
- Older age increases the chance of nerve compression.
- Trauma or injuries can trigger radiculopathy.
- Genetics and lifestyle choices, such as smoking, may contribute.
Case Examples and Epidemiology
Radiculopathy is common in people aged 30 to 60. Athletes and manual laborers are at higher risk. Studies show that about 3 to 5 out of 100 adults experience lumbar radiculopathy at some point. It impacts quality of life and work productivity.
Clinical Presentation and Symptoms of Lumbar Radiculopathy
Typical Symptoms
People report sharp pain that travels down the leg, often called sciatic pain. They may also feel numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected leg. The symptoms worsen with activity and improve with rest.
Diagnostic Indicators
Doctors look for signs like reduced reflexes or muscle weakness. They perform neurological exams to find nerve involvement. Patient history often reveals pain patterns aligned with nerve roots.
Differentiating from Other Conditions
While back pain can have many causes, M54.2 specifically points to nerve root problems. Distinguishing radiculopathy from muscular pain helps guide proper treatment.
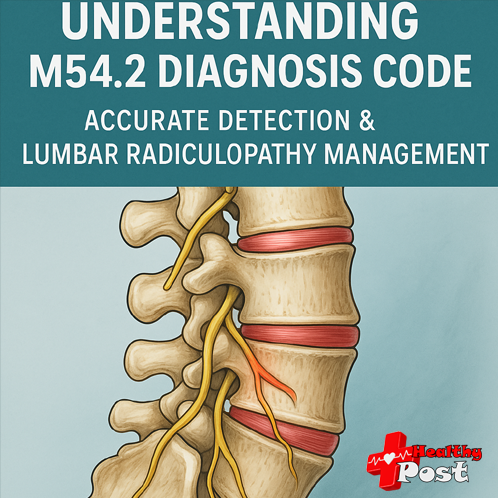
Diagnostic Procedures for M54.2
Imaging Techniques
MRI scans are the best way to see nerve compression and disc herniation. CT scans may help if MRI isn’t available. X-rays show bone changes but not soft tissues effectively.
Electrophysiological Tests
Nerve conduction studies and EMG measure electrical signals in nerves and muscles. Abnormal results confirm nerve damage.
Additional Diagnostic Measures
Along with imaging, doctors review your medical history. They match your symptoms with test results to confirm radiculopathy. Proper diagnosis requires ruling out other issues like tumors or infections.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Conservative Management
Physical therapy exercises can reduce nerve pressure and improve strength. Anti-inflammatory medicines like NSAIDs help ease pain. Corticosteroids may be used for short-term relief.
Interventional Procedures
Epidural steroid injections target inflamed nerves directly. Nerve blocks can provide temporary relief for intense pain.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is considered if conservative treatments fail. Options include discectomy, which removes herniated tissue, or laminectomy, which enlarges spinal canals. Expect some recovery time post-surgery, but outcomes are often good.
Patient Education and Self-Management Tips
Maintaining good posture, avoiding heavy lifting, and staying active help prevent worsening symptoms. Patients should seek medical help if pain worsens or numbness spreads.
Coding and Billing Considerations for M54.2
Accurate Documentation for Reimbursement
Doctors must note specific symptoms and test results related to lumbar radiculopathy. Clear notes help avoid billing errors. Record details like pain location, neurological findings, and imaging results.
Insurance and Claims Processing
Insurance companies look for correct codes like M54.2 for approving treatments. Avoid generic back pain codes when nerve root issues are involved to prevent denial.
Implications of Co-morbidities and Additional Codes
Patients with other conditions, like osteoporosis, might need additional codes. Proper coding impacts the coverage and the patient’s out-of-pocket costs. Always document associated diagnoses if relevant.
Conclusion
M54.2 is a vital code for diagnosing lumbar radiculopathy. Accurate coding improves patient care and makes billing smoother. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options helps both clinicians and patients. When properly documented, this code ensures the right treatment reaches those who need it most. Remember, precise diagnosis coding is the first step toward effective management and better health outcomes.

