Osimertinib resistance! Five new therapies worth paying attention
A variety of 4th-generation targeted drugs, antibody-drug conjugates , and combination regimens have been launched… In 2024, patients who are resistant to osimertinib will have more treatment options! More and more lucky EGFR lung cancer patients have benefited from the third-generation targeted drug osimertinib and have successfully survived for 5 or 10 years. However, osimertinib resistance has also become a new survival challenge for lung cancer patients, and many patients are eagerly waiting for a “life-extending” solution to crack osimertinib resistance!
In 2024, these 5 new therapies will bring hope to patients!
1. The 4th-generation targeted drug BBT-176 for lung cancer released updated research data!
BBT-176 is a broad-spectrum, highly effective 4th-generation EGFR targeted drug with enhanced activity against sensitizing and treatment-emergent EGFR mutations, including T790M and C797S. Previous clinical data showed that this drug has observed promising early efficacy signals in multiple patients, including those with EGFR C797S triple mutations, and has the potential to treat or prevent brain metastases, whether for acquired resistance or early treatment.
Updated data on BBT-176, a 4th-generation targeted drug that is highly anticipated by lung cancer patients, was announced at the 2023 World Lung Cancer Conference (WCLC).
As of March 29, 2023, 44 patients with EGFR mutations who had previously received at least one EGFR-targeted therapy (19 patients from the BID cohort) had received BBT-176.
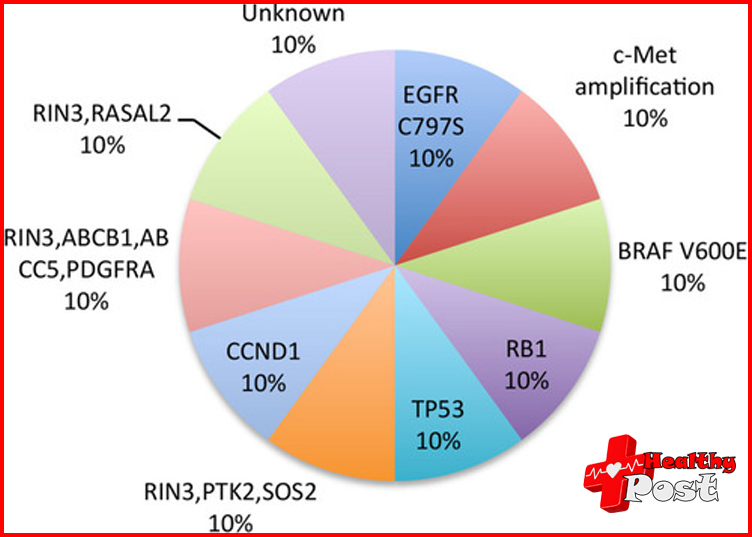
The results show that EGFR triple mutation genes (exon 19 del/T790M/C797S or L858R/T790M/C797S) were detect in the plasma of 11 patients, and early efficacy signals were currently show.
“We believe that BBT-176 has the potential to be a broad-spectrum fourth-generation EGFR TKI and has the ability to further enhance treatment through combination.
2. The 4th-generation “star” targeted drug BLU-945 for lung cancer releases the latest research data!
BLU-945 is a fourth-generation EGFR TKI develop by the famous American company blueprint . Previous studies have shown that BLU-945 can effectively inhibit triple-mutated EGFR carrying activated L858R or exon 19 deletion mutations and acquired T790M and C797S mutations. It can be use as a first-line treatment for patients with EGFR mutant NSCLC, and of course, it can also be use as a second-line treatment for patients with EGFR T790M mutations.
At the 2023 ASCO conference, the results of BLU-945’s earliest study, code-named SYMPHONY, once again brought surprises: BLU-945 showed unprecedented good safety as a monotherapy (n=112) or in combination with osimertinib (n=55) in the treatment of advanced, osimertinib-resistant, EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer .
The results show:
1. Good safety and tolerability. BLU-945 was generally well tolerate when use as a monotherapy or in combination with osimertinib.
2. Strong anti-tumor activity, with significant tumor shrinkage. In heavily pretreated patients, BLU-945 monotherapy or combined with osimertinib showed evidence of clinical activity, and higher doses of BLU-945 had stronger anti-tumor activity.
In the monotherapy group , higher doses of BLU-945 show stronger anti-tumor activity, and two patients have been confirm to have achieve partial remission (PR).
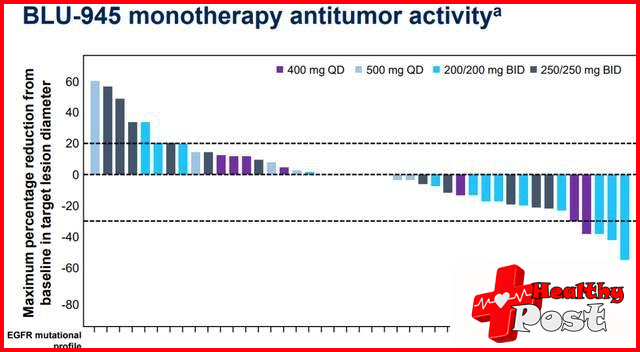
In the BLU-945 combine with osimertinib treatment group, more patients experience tumor shrinkage in patients who use osimertinib as the last treatment regimen, and during the continuous dose escalation process, 10 patients achieved partial response (PR), of which 4 were confirmed.
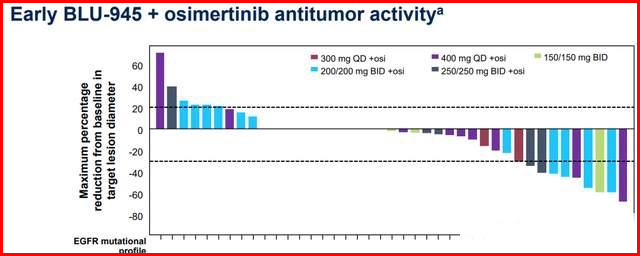
Compared with other fourth-generation EGFR-TKIs under development, BLU-945 is one of the fastest-progressing fourth-generation EGFR-TKIs, and its preclinical data on overcoming drug resistance show highly effective anti-tumor activity.
3. Nearly 50% of patients had significantly reduced tumor size! New drug combination successfully breaks the EGFR resistance dilemma!
After becoming resistant to osimertinib, most patients who undergo genetic re-testing will find that they have a new resistance mutation – MET overexpression and/or amplification. Studies have found that this is one of the most common resistance mechanisms to osimertinib, and there is currently no approved targeted drug. The new drug combination of osimertinib and savotinib breaks through this resistance bottleneck.
In one study, among all lung cancer patients whose disease progressed after osimertinib treatment , 62% of these patients had tumors with MET overexpression and/or amplification, and more than one-third (34%) of these patients had high MET expression.
As of August 2021, the objective response rate (ORR) of the combination therapy was as high as 49% in drug-resistant patients with high MET expression, and the ORR of patients who had not received chemotherapy was as high as 52%. This means that nearly half of the patients had their lesions reduced by more than 30% or even disappeared after receiving osimertinib combined with savotinib! Please see the table below for detailed efficacy data:
4. The “life-extending” therapy Amivantamab combined with chemotherapy has been apply for marketing approval!
Recently, amivantamab-vmjw (Rybrevant), a “star” targeted drug for lung cancer EGFR, has submitted a new indication application to the FDA, seeking approval for the combination of amivantamab and platinum chemotherapy for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 19 deletions. This means that if everything goes well, the first “life-extending” new solution to break the Oxidase resistance that patients have been waiting for is expect to be approve!
Amivantamab is a novel EGFR-MET bispecific antibody that targets activated and resistant EGFR and MET mutations and amplifications. The application for marketing approval is base on a global trial codenamed MARIPOSA-2, in which all patients were enrolled in advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients with osimertinib-resistant EGFR exon 19 deletion or L858R mutation.
The latest research results announced at the 2023 ESMO Congress showed that compared with chemotherapy alone, amivantamab combined with chemotherapy, and amivantamab combined with lazertinib (Leclaza) and chemotherapy, significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS).
The addition of amivantamab and lazertinib to chemotherapy reduced the risk of progression or death by 56% compared with chemotherapy alone ;
Adding amivanta to chemotherapy reduced the risk of progression or death by 52% compared with chemotherapy alone .
5. The disease control rate reaches 70%, and the new drug U3-1402 becomes a ray of hope for the treatment of drug resistance
U3-1402 is a Her3 antibody-drug conjugate develop by Daiichi Sankyo Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. of Japan. The main therapeutic mechanism is that U3-1402 binds to the Her3 protein and then delivers the therapeutic drugs it carries into tumor cells to kill them.
The drug U3-1402 can address multiple drug resistance mechanisms, including drug resistance caused by C797S mutation of the EGFR gene, MET gene amplification, HER2 protein mutation, BRAF gene and PIK3CA gene mutation. Most importantly, it does not matter what gene mutation causes the drug resistance, U3-1402 may work.
Clinical data:
The latest clinical data of U3-1402 was report at the ESMO conference. The patients enrolled were non-small cell lung cancer patients with EGFR gene mutations, and they had previously used targeted drugs and chemotherapy and were resistant. They had used an average of 4 treatment regimens. 90% of the patients had used chemotherapy and an average of 2 EGFR targeted drugs, of which 86% had previously used osimertinib. Nearly half of the patients had brain metastases. The results showed that one patient had complete disappearance of visible lesions, and 13 patients had tumor lesions that shrank by more than 30%, achieving partial remission. The overall treatment response rate was 25% , and the disease control rate was 70% .
This is very valuable for patients who have developed drug resistance after an average of more than 4 lines of treatment. In addition to excellent efficacy, the safety is also controllable.
In addition to the five new therapies mentioned above, there are many drugs around the world that have shown great potential in overcoming osimertinib resistance!
Note: Patients who have undergone genetic testing can take out the report and if there is an EGFR mutation, they can submit the information to the Global Oncology Doctors Network Medical Department to see if there is a chance to receive treatment with new domestic drugs.
A number of clinical studies are also being carry out, and a large number of patients have been successfully enroll and receive treatment through the Global Oncology Physicians Network. Applications are still open.
With the development of these new drugs and new treatments, the cure rate and survival of cancer patients are better than before. Domestic patients have the opportunity to choose better treatments and get better treatment outcomes.