
The infamous prefrontal lobotomy
The purpose of the lobotomy surgery is to remove nerve fibers in the brain that connect the frontal lobe (the area of the brain responsible for thinking) to other areas of the brain.
Commonly used to treat major depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and schizophrenia .

01. History of lobotomy
In 1935, Portuguese neurologist António Egas Moniz performed the world’s first lobotomy .
His method was to drill a hole in the skull and then inject absolute alcohol into the frontal cortex, essentially destroying the brain tissue.
Moniz believes that disrupting connections between the front of the brain and other parts of the brain could help patients stop “abnormal” behaviors and painful feelings .
This approach was later shown to damage other parts of the brain.
Later, Moniz invented an instrument called a lobotomy , which could remove chunks of brain tissue from the frontal lobes.
Moniz also won the 1949 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for this technology. [1]
Within the next year, American neurologist Walter Freeman and neurosurgeon James Watts performed the first prefrontal lobotomy inspired by the Moniz operation .
But Freeman wanted to develop a faster, more effective, and streamlined surgical procedure.
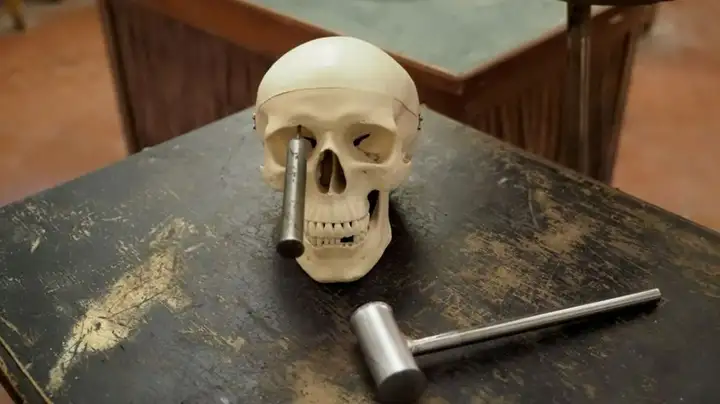

Ten years later, he developed a new method called orbitofrontal lobotomy ,
Rather than drilling holes in the skull to sever the connection to the frontal lobes, as Moniz did, he used a hammer to insert icepicks from the patient’s eye sockets into the brain.
Once the ice pick is in, it begins to move around, severing the connection between the prefrontal cortex and the thalamus.
This adapted procedure is also known as “ice pick therapy . “
A lobotomy usually takes an hour to complete, but Freeman’s “ice pick therapy” only takes 10 minutes or less.
Because the patient does not need to be anesthetized, it can even be done outside the operating room.
02. Famous cases of lobotomy
According to reports, Freeman believes that a lobotomy is only slightly more dangerous than a tooth extraction surgery .
However, this is not the case for most patients.
Brain resection has serious negative effects on the patient’s personality, initiative, consistency, empathy, and ability to be independent .
Here are some examples of people who have had lobotomies:
1.Alice Hood Hammatt
Alice Hood Hammatt , Freeman ‘s first lobotomy patient, had been diagnosed with anxiety-depressive disorder .
When she woke up from the surgery, she said she was “very happy.”
Six days after surgery, Hammatt experienced brief speech difficulties, disorientation, and excessive agitation .
Still, Freeman calls the surgery a success.
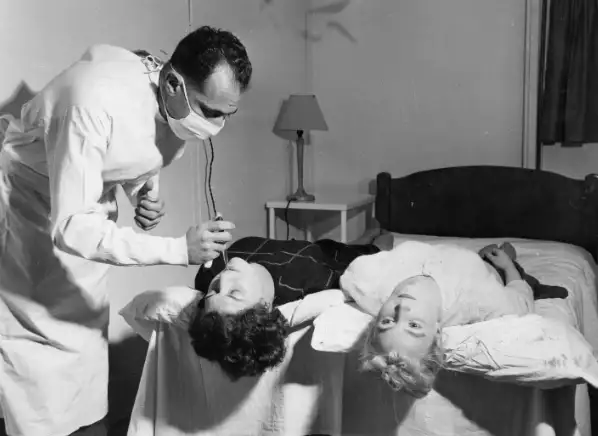
2.Rosemary Kennedy
Rosemary Kennedy is the sister of U.S. President John F. Kennedy and is considered the most famous patient to undergo a lobotomy .
As a teenager, Rosemary suffered from mild developmental delays, which seriously affected her performance in school.
As she grew, Rosemary began to suffer from violent epileptic seizures and would often become angry at those around her.
Seeking treatment to relieve her symptoms and fearing that her behavior would bring bad reputation to the family, Rosemary ‘s father arranged for a lobotomy when she was 23 years old .
It is said that Rosemary remained awake throughout the operation, talking to the doctors and reciting poetry to the nurses.
When she stopped talking, the operation was over.
After the surgery, Rosemary became severely disabled and unable to live independently.
Spent the rest of his life in a mental hospital.

03. The popularity of lobotomies
After completing his first surgery, Freeman began traveling across the United States to promote his “ice pick therapy . “
Although this type of lobotomy was initially used only to treat serious mental health conditions, Freeman later popularized it as a treatment for a variety of conditions including neurodyspepsia.
In the United States, approximately 50,000 people have undergone lobotomies .
Most occurred between 1949 and 1952.
Freeman is said to have performed the procedure on approximately 3,500 people, including 19 children as young as four years old.

04. Effects of lobotomy
Although the purpose of a lobotomy is to relieve a patient’s mental health symptoms and improve their function, the results are often unsatisfactory.
Some patients do improve and are able to live independent lives.
However, many more people are affected by behavioral changes, emotional problems, and lack of impulse control , resulting in loss of function, emotional numbness, and apathy.
In some cases, a lobotomy can also be fatal.
Serious risks include:
- brain infection
- changes in language ability
- cognitive impairment
- Loss of bladder and bowel control
- muscle weakness
- personality changes
Some people report experiencing severe pain during the procedure, while some report no memory of the procedure at all.

05. Why is lobotomy widely promoted?
Lobotomy is considered one of the most barbaric treatments in the history of modern medicine.
Even in the 1940s, lobotomy was a controversial topic.
Although the program is rife with ethical issues, it has gained widespread popularity.
The reasons are as follows:
Lack of effective treatments: Antipsychotic drugs were not available until the mid-1950s, a time when people were eager to treat severe mental symptoms by any means possible.
Overcrowding of mental health institutions: In 1937, 477 mental hospitals housed more than 450,000 patients. Lobotomies are used in unruly patients and are easier to manage.
Media: In the media, lobotomy was described as a “miraculous and heroic” procedure.

06. Alternative treatments to lobotomy
In the mid-1950s, as scientists developed more effective antipsychotics and antidepressants , lobotomies were increasingly rejected .
Today’s treatment of severe mental illness typically focuses on psychotherapy, medication, or a combination of the two .
The specific plan depends on a variety of factors, including the symptoms a person is experiencing, the nature of the diagnosis, and the severity of the symptoms.

1. Psychotherapy
Talk therapy has become a powerful tool in treating mental health issues.
Among them, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is one of the most researched and widely recommended therapies.
Other types of therapy that may be used include: psychodynamic therapy, dialectical behavior therapy, family therapy, or group therapy .
2. Drugs
Medications can also help relieve symptoms of mental disorders.
These include antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, stimulants, and mood stabilizers .
3. Psychosurgery therapy
Although Moniz and Freeman ‘s work was ethically problematic, it also paved the way for other forms of psychosurgery.
Such as anterior cingulotomy, deep brain stimulation and other surgeries.
This has a certain effect in the treatment of severe depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder, as well as neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s disease.
In addition , electroconvulsive (ECT) therapy can be used to treat epileptic seizures in people under anesthesia, and is sometimes used to treat major depression, bipolar disorder, and other mental illnesses .


One thought on “The infamous prefrontal lobotomy”