
Abdominal Bloating ICD 10: The Latest Update You Need to Know
That uncomfortable, swollen sensation in your belly – abdominal bloating affects millions worldwide, impacting daily life and well-being. From mild discomfort to severe distress, this common condition prompts countless medical visits each year.
Medical professionals rely on precise diagnostic codes to document and treat abdominal bloating effectively. The latest update to the ICD-10 coding system brings significant changes, particularly with the R14.0 code designated for abdominal distension.
Starting October 1, 2024, healthcare providers will use these updated codes to:
- Track patient symptoms accurately
- Develop targeted treatment plans
- Process insurance claims efficiently
- Conduct meaningful research studies
The R14.0 code now specifically addresses gaseous abdominal distension, commonly known as bloating. This update reflects the medical community’s growing understanding of digestive health conditions and their impact on patient care.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore:
- Current understanding of abdominal bloating
- The significance of ICD-10 codes in healthcare
- Latest updates to the R14.0 code
- Related diagnostic codes for gastrointestinal symptoms
- Future developments in medical coding
Whether you’re a healthcare provider, researcher, or patient seeking information, these coding updates mark a significant step forward in the diagnosis and treatment of abdominal bloating.
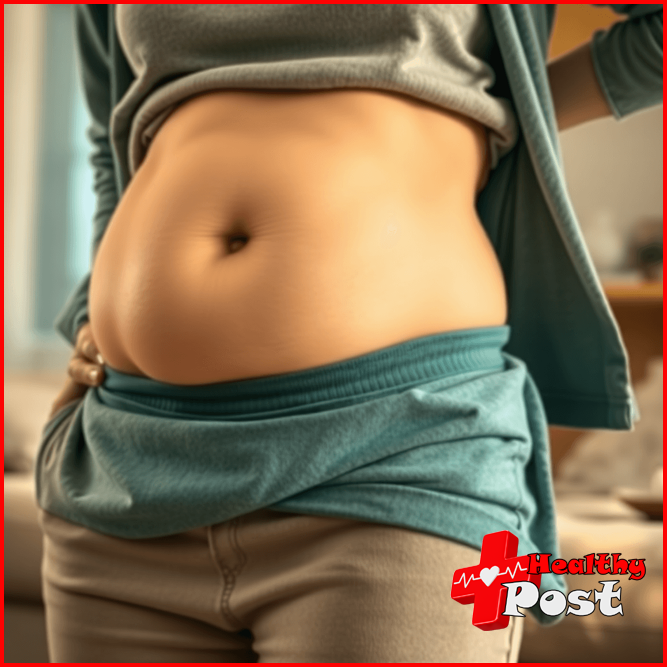

Understanding Abdominal Bloating
That uncomfortable, full sensation in your belly – known as abdominal bloating – affects up to 30% of Americans. This common digestive issue makes your stomach appear larger and feel tight or hard to the touch.
Common Causes of Bloating:
- Food Intolerances: Lactose sensitivity, gluten intolerance, FODMAPs reactions
- Dietary Habits: Eating too quickly, large portion sizes, carbonated beverages, high-sodium foods
- Digestive Issues: Constipation, excess gas production, bacterial imbalances, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)
Key Symptoms to Watch For:
- Physical Changes: Visible stomach distension, tight hard abdomen, stomach gurgling, increased gas passing
- Discomfort Levels: Mild to severe pain, pressure in abdomen, cramping sensations, feeling uncomfortably full
- Associated Symptoms: Changes in bowel movements, loss of appetite, nausea, stomach rumbling
Women experience bloating more frequently than men, with up to 40% reporting regular symptoms. The intensity can range from mild discomfort to severe pain that impacts daily activities. Many people notice their symptoms worsen throughout the day, particularly after meals.
The buildup of gas in your digestive system plays a significant role in bloating. This can happen when you swallow excess air while eating or drinking or when gut bacteria break down certain foods. Your body typically produces between 500-2000ml of gas per day, but various factors can increase this amount and lead to bloating symptoms.
The Role of ICD-10 Codes in Healthcare
ICD-10 codes are a standardized system used by healthcare providers worldwide to accurately identify diseases, injuries, and health conditions. These codes consist of alphanumeric characters that precisely define each medical diagnosis. With the use of ICD-10 codes, healthcare professionals can effectively communicate with one another, track disease patterns, support medical research initiatives, and assess the quality of healthcare delivery.
How ICD-10 Codes Benefit Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers rely on ICD-10 codes for various purposes:
- Documenting patient diagnoses accurately
- Monitoring disease outbreaks and tracking patterns
- Supporting medical research initiatives
- Facilitating effective communication between healthcare professionals
- Assessing the quality of healthcare delivery
The Importance of Specificity in ICD-10 Coding
For cases involving abdominal bloating, ICD-10 codes play a crucial role in helping physicians identify specific conditions affecting the digestive system. The detailed structure of these codes enables healthcare providers to distinguish between different types of bloating and associated symptoms, leading to more targeted treatment approaches.
Benefits of Specificity in Medical Billing and Documentation
The specificity offered by ICD-10 coding brings several advantages to medical billing and documentation processes:
- Streamlined Insurance Claims: Precise coding reduces claim denials and processing delays
- Accurate Reimbursement: Specific codes ensure appropriate payment for services rendered
- Data Analysis: Detailed coding supports healthcare trend analysis and resource allocation
- Legal Protection: Proper documentation safeguards both providers and patients
Financial Implications for Healthcare Organizations
The choice of ICD-10 codes used by healthcare providers can have a significant impact on the financial health of their organizations. When providers consistently use accurate and specific codes, they can expect the following benefits:
- Minimized claim rejections
- Reduced administrative burden
- Faster payment processing
- Improved revenue cycle management
By optimizing their coding practices, healthcare organizations can enhance their cash flow and overall financial stability.
Enhancing Documentation for Abdominal Bloating Cases
When it comes to documenting abdominal bloating cases, healthcare providers can leverage ICD-10 codes to capture important details such as severity levels, contributing factors, and related conditions. This comprehensive documentation serves multiple purposes:
- Supporting medical necessity: Insurers often require evidence of medical necessity before approving certain treatments or procedures. By providing thorough documentation that includes specific ICD-10 codes, healthcare providers can strengthen their arguments for why a particular intervention is necessary.
- Establishing care plans: In order to deliver effective care to patients with abdominal bloating issues, it is essential for healthcare professionals to have a clear understanding of the underlying causes and associated factors. The information gathered through detailed coding can inform the development of tailored care plans that address each patient’s unique needs.
Improving Insurance Approval Processes
The specificity offered by ICD-10 coding not only benefits healthcare providers but also has implications for insurance companies involved in the reimbursement process. When insurers receive claims with precise codes that accurately reflect the medical services provided, they are better equipped to evaluate the necessity and appropriateness of those services.
This improved understanding on the part of insurers can lead to faster approval processes for claims related to abdominal bloating treatments or procedures. As a result, both healthcare providers and insurance companies stand to benefit from streamlined operations and reduced administrative overhead.
In summary, ICD-10 codes play a vital role in the healthcare industry by facilitating accurate documentation, supporting effective communication among professionals, enabling data analysis for research purposes, and impacting financial aspects such as claim processing efficiency and revenue management.
Latest Updates on Abdominal Bloating ICD 10 Codes

Healthcare providers need to stay current with the latest ICD-10 code updates for abdominal bloating. The most significant update is the introduction of Diagnosis Code R14.0, effective October 1, 2024. This code specifically addresses abdominal distension with gaseous symptoms.
Key Features of R14.0 Code
- Billable Status: R14.0 is a billable/specific code approved for medical diagnosis documentation
- Classification: Falls under R00-R99 category for symptoms and clinical findings
- Clinical Application: Used for documenting tympanites (abdominal/intestinal swelling)
Clinical Terminology and Synonyms
The R14.0 code encompasses several clinical terms healthcare providers commonly use in practice:
- Abdominal bloating
- Gaseous distention
- Tympanites
- Intestinal distension
- Stomach swelling with gas
Associated Diagnostic Related Groups (DRGs)
R14.0 links to specific DRGs that help classify patient conditions:
Major Complications Present:
- Esophagitis with major complications
- Gastroenteritis with severe comorbidities
- Digestive disorders requiring intensive care
Without Major Complications:
- Uncomplicated esophagitis
- Simple gastroenteritis
- Minor digestive system disorders
Documentation Requirements
Healthcare providers must include these elements for proper R14.0 coding:
- Symptom Duration: Acute vs. chronic presentation
- Associated Symptoms: Presence of pain, discomfort, or other related symptoms
- Severity Level: Mild, moderate, or severe
- Contributing Factors: Dietary triggers, medical conditions
- Treatment Response: Effectiveness of interventions
Clinical Coding Guidelines
For accurate R14.0 implementation:
- Document specific location of bloating
- Note any underlying conditions
- Record symptom patterns
- Include diagnostic test results
- Specify treatment protocols
Additional Code Considerations
R14.0 may require supplementary codes for complete documentation:
Additional Relevant Codes for Gastrointestinal Symptoms
The ICD-10 classification system includes specific codes that complement R14.0 when documenting gastrointestinal symptoms. These codes create a comprehensive picture of a patient’s digestive health concerns:
1. R14.1 – Gas Pain
- Captures acute or chronic gas-related discomfort
- Applicable for localized abdominal pain caused by trapped gas
- Used when pain is the primary presenting symptom
- Billable code effective October 1, 2024
2. R14.3 – Flatulence
- Documents excessive gas passage
- Applicable for chronic flatulence conditions
- Includes cases of recurring intestinal gas
- Billable code effective October 1, 2024
Healthcare providers often use these codes in combination to accurately reflect the full spectrum of gastrointestinal symptoms. A patient might present with:
- Abdominal bloating (R14.0)
- Associated gas pain (R14.1)
- Concurrent flatulence (R14.3)
The specificity of these codes helps create detailed medical records that:
- Support accurate diagnosis patterns
- Guide appropriate treatment plans
- Enable precise insurance billing
- Track symptom progression
- Facilitate research studies
Medical practitioners should document the presence or absence of each symptom during patient evaluations. This detailed coding approach helps identify patterns in symptom presentation and supports the development of targeted treatment strategies for gastrointestinal disorders, as highlighted in this research article.
Future Updates in ICD Coding: What to Expect Beyond 2024
The healthcare coding landscape continues to evolve with significant updates planned for late 2024. The introduction of the new R19.00 code marks a substantial advancement in classifying intra-abdominal and pelvic swelling conditions. This addition brings enhanced precision to diagnostic documentation, allowing healthcare providers to differentiate between various types of abdominal distention with greater accuracy.
Key Features of the R19.00 Code
- Expanded Classification Options: The new code provides specific subcategories for different types of swelling
- Improved Diagnostic Precision: Healthcare providers can now document the exact location and nature of abdominal distention
- Better Integration: Seamless connection with existing gastrointestinal condition codes
Implications of Coding Changes on Clinical Practice and Patient Care
The implementation of these new codes brings substantial improvements to clinical practice:
Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
- Precise documentation of symptoms and conditions
- Reduced risk of coding errors
- Better tracking of patient progress over time
Streamlined Treatment Planning
- Clear correlation between symptoms and diagnostic codes
- Improved ability to develop targeted treatment protocols
- Enhanced communication between healthcare providers
Research and Data Analysis Benefits
- More accurate statistical analysis of gastrointestinal conditions
- Better tracking of treatment outcomes
- Improved ability to identify patterns in patient populations
Healthcare practitioners utilizing these revised ICD codes can expect several practical advantages:
- Simplified Documentation Process
- Reduced time spent on administrative tasks
- Clearer guidelines for code selection
- Streamlined billing procedures
- Improved Patient Outcomes
- More accurate diagnosis tracking
- Better coordination of care
- Enhanced ability to monitor treatment effectiveness
- Financial Benefits
- Reduced claim denials
- Faster reimbursement processes
- More accurate billing documentation
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning systems with these new codes creates opportunities for advanced data analysis. Healthcare facilities can now track patterns in patient presentations, treatment responses, and outcomes with unprecedented accuracy. This data-driven approach enables healthcare providers to make more informed decisions about patient care strategies.
These coding updates reflect the healthcare industry’s commitment to precision medicine. By leveraging advancements in technology, we can further enhance the accuracy and efficiency of our healthcare delivery system.
Staying Informed: The Importance of Keeping Up with ICD Code Changes
Medical coding standards evolve continuously, making it crucial for healthcare professionals to maintain current knowledge of ICD updates. The recent changes in abdominal bloating ICD-10 codes represent just one example of the dynamic nature of medical documentation.
Practical Methods for Staying Updated
Healthcare providers can stay updated through these practical methods:
- Subscribe to Professional Organizations – Join medical coding societies that provide regular updates and educational resources
- Participate in Continuing Education – Attend workshops, webinars, and training sessions focused on coding updates
- Use Digital Tools – Implement coding software that automatically updates with the latest changes
- Create Internal Update Systems – Establish protocols for regular team reviews of coding modifications
The Impact of Staying Current with ICD Updates
These practices directly impact:
- Patient care quality through accurate diagnosis documentation
- Insurance claim processing efficiency
- Research data accuracy
- Healthcare facility compliance
The Benefits for Medical Coders and Healthcare Providers
Medical coders and healthcare providers who prioritize staying current with ICD updates demonstrate:
- Enhanced professional competency
- Improved documentation accuracy
- Better patient outcomes through precise diagnosis coding
- Reduced claim denials and billing errors
The healthcare landscape demands adaptability, particularly in diagnostic coding. Regular review of coding updates ensures healthcare facilities maintain compliance while delivering optimal patient care through accurate documentation and appropriate treatment planning.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is abdominal bloating and what are its common causes?
Abdominal bloating is a condition characterized by discomfort and distension in the abdomen. It is prevalent among individuals and can be caused by various factors, including dietary choices, gas buildup in the digestive system, and certain medical conditions.
What is the significance of ICD-10 codes in healthcare?
ICD-10 codes play a crucial role in healthcare by providing a standardized system for diagnosing and documenting medical conditions. They facilitate accurate treatment planning and are essential for healthcare billing processes, impacting reimbursement for services rendered.
What is the latest update regarding the R14.0 code for abdominal bloating?
The R14.0 code has been introduced to classify abdominal distension (gaseous) within the ICD-10 classification system. This code is billable and will become effective on October 1, 2024.
Are there additional codes related to gastrointestinal symptoms that should be considered?
Yes, alongside the R14.0 code for abdominal bloating, there are related codes such as R14.1 for gas pain and R14.3 for flatulence. These codes can provide more comprehensive documentation of gastrointestinal symptoms.
What future updates can we expect in ICD coding beyond 2024?
Beyond 2024, an upcoming code R19.00 for intra-abdominal and pelvic swelling is expected to enhance the classification of gastrointestinal conditions. These updates aim to improve clinical practice by allowing for more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment approaches.
Why is it important for healthcare professionals to stay updated with ICD code changes?
Staying informed about ICD code changes is vital for healthcare professionals as it ensures accurate documentation, enhances patient care outcomes, and keeps practitioners aligned with current standards in medical coding practices.

6 thoughts on “Abdominal Bloating ICD 10: The Latest Update You Need to Know”