5 Shocking Truths About Mammary Gland Health You Shouldn’t Ignore
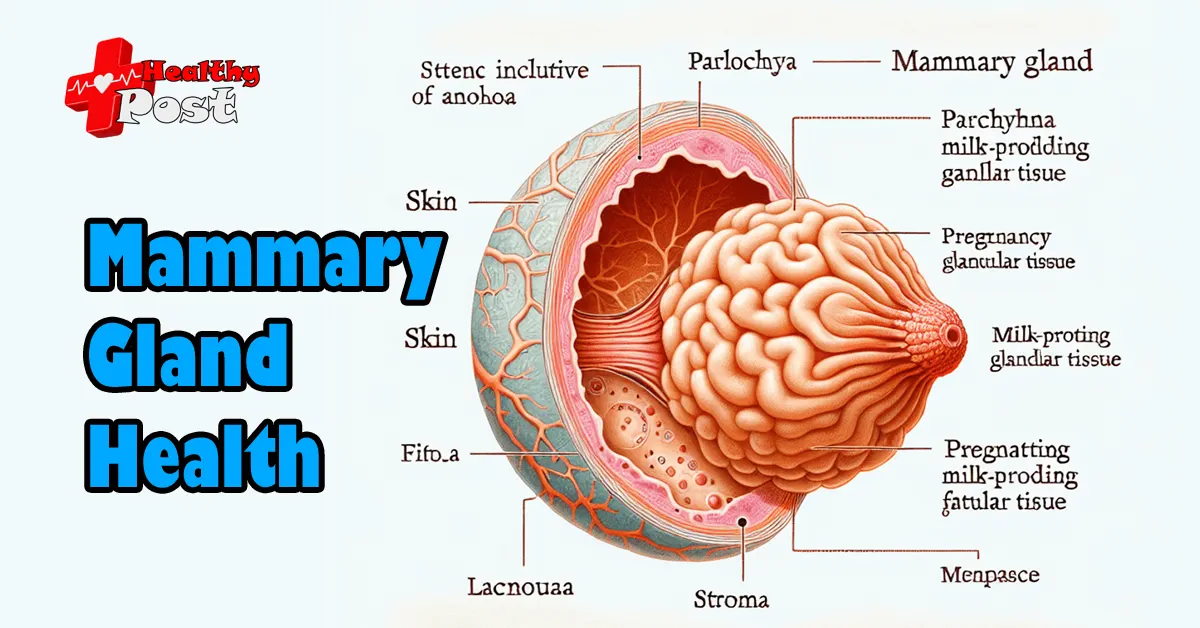
Your body has amazing organs, each with its own purpose. The mammary gland is a perfect example of nature’s intricate design – a specialized organ that can produce life-sustaining milk for newborns.
These complex structures have three main parts:
- Skin (including nipple and areola)
- Parenchyma (milk-producing glandular tissue)
- Stroma (supporting fatty tissue)
The mammary gland is more than just a milk-producing organ. It responds to hormonal changes throughout your life, from puberty to pregnancy, lactation, and menopause.
Recent studies have revealed surprising facts about mammary gland health that challenge common beliefs. Many people think breast health is only about preventing cancer, but the truth is much more complicated.
In this article, we’ll explore these 5 important facts:
- Why men should also care about their mammary glands
- How hormones dramatically affect breast tissue
- Other threats to breast health besides cancer
- Warning signs you might overlook
- Preventive measures that can change your life
By understanding these essential facts about mammary gland health, you’ll be able to make better decisions for your well-being. Knowledge is your best defense against potential health problems.
Let’s dive into these revelations that could transform how you approach breast health.
1. Male Mammary Gland Health: An Overlooked Issue
Understanding Male Mammary Glands
It’s a little-known fact that male mammary glands exist. These structures develop during fetal growth and remain present throughout life, albeit in a rudimentary form. The male breast contains ducts, stroma, and a small amount of glandular tissue – similar to female breast anatomy.
Hormonal Influence on Male Breast Tissue
Men’s breast tissue responds to hormonal changes. Conditions like gynecomastia affect up to 70% of adolescent males during puberty due to hormonal fluctuations. This temporary enlargement typically resolves naturally but highlights the active nature of male breast tissue.
The Importance of Awareness
The lack of awareness about male mammary gland health creates dangerous delays in diagnosis. Men often dismiss breast changes or feel embarrassed to seek medical attention. This stigma leads to later-stage diagnoses and potentially worse outcomes.
Signs to Watch For
Physical signs men should monitor include:
- Hard lumps beneath the nipple
- Nipple discharge
- Skin dimpling or puckering
- Nipple retraction
- Redness or scaling
- Swelling in the breast area
The Role of Self-Examinations
Medical professionals recommend men perform regular self-examinations, particularly those with high-risk factors. Understanding normal male breast anatomy helps identify concerning changes early.
The Need for Healthcare Provider Involvement
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in male mammary gland health education. Regular physical exams should include breast tissue assessment, especially for men with genetic predispositions or relevant family history.
Rising Rates of Male Breast Cancer
Research shows male breast cancer rates have increased by 25% over the past 25 years. This trend emphasizes the need for greater awareness and proactive health monitoring in men. Male mammary gland health deserves equal attention in medical discussions and public health campaigns.
Male Breast Cancer Statistics:
- 1 in 833 men will develop breast cancer
- 2,710 new cases diagnosed annually in the US
- Average age at diagnosis: 68 years
- 5-year survival rate: 84% when caught early
Risk Factors Specific to Male Breast Cancer:
- BRCA2 gene mutations – men should be screened for these
- Klinefelter syndrome
- Family history
- Liver disease
- Obesity
- Radiation exposure
2. Hormonal Changes Dramatically Influence Mammary Gland Structure and Function
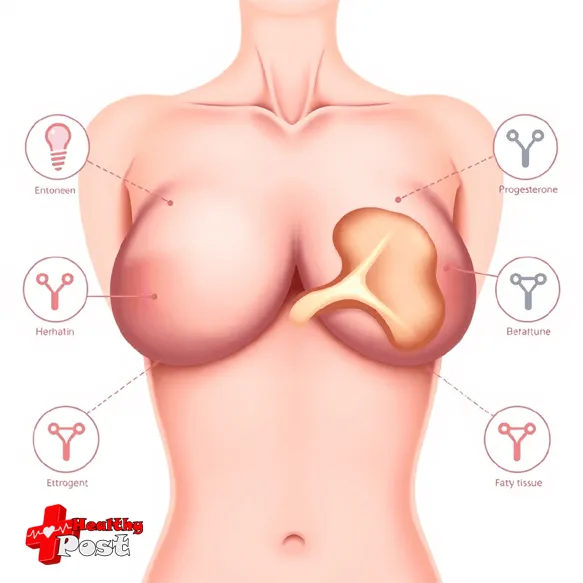
Hormones play a crucial role in shaping the development of mammary glands throughout a person’s life. These chemical messengers bring about significant changes in the structure and function of breast tissue.
Key Hormones and Their Roles
1. Estrogen
- Stimulates ductal growth and branching
- Increases breast size during puberty
- Maintains breast tissue elasticity
2. Progesterone
- Promotes development of milk-producing cells
- Triggers growth of lobules
- Prepares breasts for potential milk production
3. Prolactin
- Initiates milk production
- Maintains lactation
- Regulates milk protein synthesis
4. Human Placental Lactogen (HPL)
- Prepares mammary tissue for breastfeeding
- Enhances breast growth during pregnancy
- Supports milk production development
Life Stage Changes in Breast Tissue
Understanding how breast tissue changes at different stages of life can provide insights into hormonal influences:
1. Puberty
- Rapid breast development begins
- Formation of milk ducts
- Increase in fatty tissue
- Development of glandular structures
2. Pregnancy
- Enhanced blood flow to breast tissue
- Growth of milk-producing cells
- Expansion of ductal system
- Darkening of areola
3. Lactation
- Active milk production starts
- Increased breast size
- Enhanced sensitivity
- Regular milk removal maintains production
4. Menopause
- Reduction in glandular tissue
- Increased fatty tissue ratio
- Decreased breast density
- Changes in breast shape and size
Impact of Hormonal Imbalances
Disruptions in hormone levels can trigger various breast changes:
1. Excess Estrogen
- Breast tenderness
- Fibrocystic changes
- Increased cancer risk
2. Low Progesterone
- Irregular breast changes
- Cyclic breast pain
- Lumpy breast tissue
3. Thyroid Dysfunction
- Changes in breast size
- Altered tissue sensitivity
- Modified milk production capacity
Understanding these hormonal influences helps identify potential health issues early. Regular monitoring
3. Breast Cancer Is Not the Only Threat to Mammary Glands
Many people think that breast health issues only mean cancer. But in reality, there are many other conditions affecting mammary glands that also need attention.
Common Benign Breast Conditions
1. Fibrocystic Changes
- Small fluid-filled sacs develop within breast tissue
- Affects up to 60% of women during reproductive years
- Creates tender, lumpy areas that fluctuate with menstrual cycles
2. Fibroadenomas
- Solid, round lumps made of normal breast cells
- Most common in women aged 15-35
- Move freely when touched (“breast mouse”)
- Usually harmless but may require monitoring
Distinguishing Benign vs. Malignant Signs
Benign Characteristics
- Smooth, round edges
- Mobile when touched
- Bilateral symptoms
- Pain that correlates with menstrual cycle
- No skin changes
Malignant Warning Signs
- Irregular, hard edges
- Fixed position
- Usually unilateral
- Persistent pain unrelated to cycle
- Skin dimpling or puckering
Mastitis and Breast Infections
Lactating mothers face unique challenges with mammary gland health. Mastitis affects up to 20% of breastfeeding women.
Common Symptoms
- Breast tenderness
- Redness and swelling
- Fever above 101°F
- Flu-like symptoms
Risk Factors
- Cracked nipples
- Blocked milk ducts
- Poor latch during feeding
- Missed feeding sessions
Other Notable Conditions
Intraductal Papillomas: Small wart-like growths inside milk ducts that cause nipple discharge and may require surgical removal.
Breast Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs common in women aged 35-50 that can appear suddenly and may resolve without treatment.
Understanding these various conditions helps differentiate between serious threats and normal breast changes. Regular breast health monitoring remains crucial for identifying any concerning developments in mammary gland health.
4. Early Symptoms of Mammary Gland Diseases Are Often Subtle But Critical to Recognize
Detecting mammary gland diseases early requires vigilance and attention to subtle changes in breast tissue. Many people miss these warning signs, mistaking them for normal variations. However, recognizing these signs is crucial as it can lead to an earlier diagnosis and significantly improve treatment outcomes, as highlighted in this article on early detection of breast cancer.
Key Warning Signs to Monitor:
- Breast Lumps or Thickening: Hard, immobile lumps with irregular edges; soft, movable masses that feel different from surrounding tissue; changes in breast texture or density; thickened areas under the skin.
- Nipple Changes: Sudden inversion or retraction; clear or bloody discharge without squeezing; crusting or scaling around nipple area; changes in nipple direction or position.
- Skin Alterations: Redness or darkening of breast skin; orange-peel texture (peau d’orange); unusual warmth or swelling; persistent rashes or skin irritation.
- Pain Patterns: New, persistent discomfort; sharp, shooting sensations; burning or tenderness; pain that doesn’t correlate with menstrual cycle.
Regular self-examination plays a crucial role in early detection. The best time for breast self-exams is 7-10 days after the start of menstruation when breast tissue is least swollen.
Proper Self-Examination Technique:
- Visual inspection in mirror: arms at sides, arms raised overhead, hands pressed on hips
- Physical examination: use pad of fingers, apply different pressure levels, check entire breast area, include armpit region
Clinical screenings complement self-exams through professional expertise and advanced imaging. Mammograms can detect abnormalities before they become physically noticeable.
Recommended Screening Schedule:
- Ages 20-39: Clinical breast exam every 3 years
- Ages 40+: Annual mammogram and clinical breast exam
- High-risk individuals: Additional MRI screening
- Personal history: More frequent monitoring as advised
Any unusual changes warrant immediate medical attention.
5. Lifestyle Choices and Preventive Measures Can Significantly Reduce Risks to Mammary Gland Health
Your daily habits shape your mammary gland health. Research shows lifestyle modifications can reduce breast disease risks by up to 30%.
Key Lifestyle Factors Affecting Breast Health:
1. Alcohol Consumption
- Each daily alcoholic drink increases breast cancer risk by 7-10%
- Limit intake to 1 drink per day or less
- Choose alcohol-free days each week
2. Weight Management
- Post-menopausal weight gain raises breast cancer risk by 20-40%
- Maintain BMI between 18.5-24.9
- Focus on balanced nutrition with plenty of fruits and vegetables
3. Physical Activity
- 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly reduces breast cancer risk by 15-20%
- Include both cardio and strength training
- Simple activities like brisk walking count toward your goal
Smart Hormone Management:
Hormone therapy requires careful consideration and medical supervision:
- Use lowest effective dose
- Limited duration of treatment
- Regular monitoring of breast tissue changes
- Discussion of alternative options with healthcare provider
Preventive Options for High-Risk Individuals:
Risk-reduction medications:
- Selective estrogen receptor modulators
- Aromatase inhibitors
- Regular consultations with breast specialists
Surgical considerations:
- Prophylactic mastectomy for BRCA gene carriers
- Preventive oophorectomy when appropriate
- Reconstruction options discussion
Lifestyle Guidelines for Optimal Breast Health:
- Maintain consistent sleep schedule
- Practice stress management techniques
- Avoid smoking and second-hand smoke exposure
- Choose organic products when possible
- Limit exposure to environmental toxins
Nutritional Support:
Foods that support breast health:
- Cruciferous vegetables
- Omega-3 rich fish
- Whole grains
- Green tea
- Turmeric
- Berries
A proactive approach through lifestyle modifications creates a strong foundation for mammary gland health. These changes work together with regular screenings and medical care to provide comprehensive protection.
Conclusion
Your mammary gland health deserves attention – it’s not just another health concern to push aside.
These 5 Shocking Truths About Mammary Gland Health You Shouldn’t Ignore highlight critical aspects many people overlook:
- Both men and women need mammary gland awareness
- Hormonal influences shape breast health throughout life
- Multiple conditions beyond cancer affect mammary tissue
- Subtle early warning signs require vigilant attention
- Daily choices impact long-term breast health
The power to protect your mammary gland health lies within your daily decisions. Start with these simple steps:
- Schedule regular medical check-ups
- Perform monthly self-examinations
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Stay physically active
- Limit alcohol consumption
Remember: Early intervention saves lives. Don’t wait for obvious symptoms to appear.
Your body sends signals – learn to listen and respond. Make mammary gland health a priority today.
Consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice based on your risk factors and family history.
Take charge of your mammary gland health. Your future self will thank you for the preventive steps you take today.
Schedule a mammogram screening – it could be the most important appointment you make this year.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Why is mammary gland health important for both women and men?
Mammary glands play a vital role in female physiology, but they are also present, though rudimentary, in males. Understanding mammary gland health is crucial for early detection and prevention of diseases, including breast cancer, which can affect men as well. Male mammary gland health is often overlooked but equally important.
How do hormonal changes impact the structure and function of mammary glands?
Key hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, prolactin, and somatomammotropin significantly influence mammary gland development and changes. Life stages like puberty, pregnancy, lactation, and menopause alter breast tissue structurally and functionally. Hormonal imbalances or therapies can also affect mammary gland health.
Are there other threats to mammary glands besides breast cancer?
Yes, benign breast conditions like fibrocystic changes, fibroadenomas, and infections such as mastitis during lactation commonly affect mammary glands. Recognizing signs and symptoms that distinguish benign from malignant conditions is essential for maintaining breast health.
What are the early symptoms of mammary gland diseases that people should recognize?
Early warning signs include lumps or thickened areas under the skin, nipple inversion or unusual discharge, skin peeling or scaling over the breast area, and pain in breast tissue. Regular self-exams and clinical screenings are critical for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
How do lifestyle choices influence the risk of mammary gland diseases?
Lifestyle factors such as alcohol consumption, obesity levels, and physical activity significantly impact the risk profile for mammary gland diseases. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, adhering to guidelines on hormone therapy usage, and considering preventive strategies can reduce risks.
What preventive measures can individuals take to protect their mammary gland health?
Preventive measures include adopting healthy lifestyle habits like balanced diet and exercise, regular self-examinations and clinical screenings for early detection, cautious use of hormone therapies following medical advice, and for high-risk individuals, medications or surgical options may be recommended to minimize disease risk.


2 thoughts on “5 Shocking Truths About Mammary Gland Health You Shouldn’t Ignore”