Does appendicitis require surgery? Can I do it without surgery?
Many people have heard of appendicitis, which is very painful when it attacks. In people’s minds, appendicitis surgery is just a minor surgery and not a big deal.
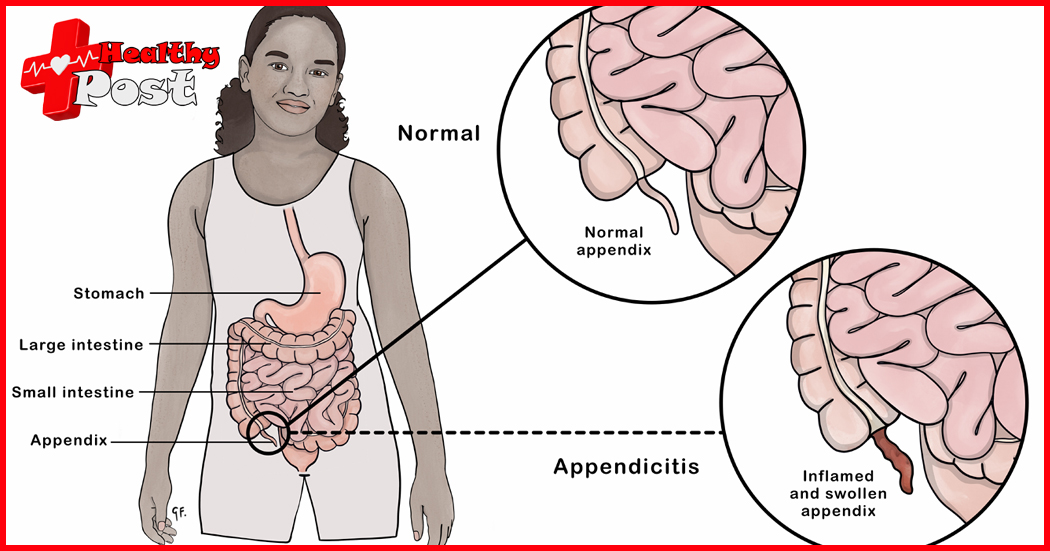
Does appendicitis require surgery?
The answer of course is that it depends.
The appendix is a blind tube, about 6~8cm long and 0.6cm~0.8cm in diameter. It is connected to the cecum. It is as easy to twist as a small tail of the cecum. Because it is a blind tube, it is easy for bacteria to breed, and feces cannot go in and out, causing obstruction. This can lead to appendicitis.
We have not performed simple appendicitis surgery for many years, mainly because we do not admit patients with appendicitis. When we encounter appendicitis in the emergency department at night, we send the patients to other hospitals for surgery. We can’t even deal with gastrointestinal tumors. How can we have the energy to deal with such small things? Operation. But it is not absolute. In some cases, such as appendiceal perforation, unstable vital signs and other emergencies, emergency surgery will be performed.
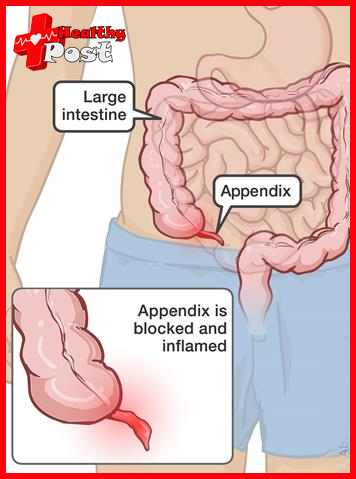
There are four main types of appendicitis:
1. Acute simple appendicitis has mild abdominal pain, no fever or low fever, W BC<15*10^9/L; it is the early stage of the disease, obstruction factors appear in the appendix lumen, and there is edema and neutrophil infiltration of the mucosal surface in all layers of the appendix There are small ulcers and bleeding spots.
2. Acute suppurative appendicitis, severe abdominal pain, fever, WBC >16*10^9/L; at this time, the inflammation worsens, the appendix is obviously swollen, the serosa is highly congested, and purulent exudate is attached.
3. Acute gangrenous appendicitis accompanied by appendiceal perforation may cause widespread and severe abdominal pain, diffuse peritonitis, fever, WBC >16*10^9/L, and pneumoperitoneum during perforation; necrosis or partial necrosis of the appendiceal wall can be seen grossly and pathologically. It is purple-black or black and may be perforated.
4. Periappendiceal abscess: Acute appendicitis lasts for more than 3 days (or as short as 8 hours) with persistent high fever and persistent abdominal pain, but often not severe. A tender mass can be palpable in the right lower abdomen, and WBC remains high. When acute appendicitis leads to pus and gangrene, the greater omentum can move to the right lower abdomen, wrap the appendix and form adhesions, resulting in inflammatory masses or peri-appendiceal abscess.
Conservative treatment
When many people hear about surgery, they are afraid and do not want to do it.
Non-surgical treatment of acute appendicitis is only suitable for the following situations:
① Early simple appendicitis can be temporarily observed, in principle, no more than 24 hours
②Abscess around the appendix
③ If the duration of the disease is >3 days, in principle, surgery is not recommended because most abscesses have formed and are wrapped around the area.
④Those with other serious organic diseases and contraindications to surgery
It should be reminded that the above are not hard indicators for conservative treatment, and should be decided according to the actual situation of the patient.
For example, if a young man is diagnosed with appendicitis, but his abdominal pain is not severe and is limited to the right lower abdomen, and he has no fever or only low-grade fever, then conservative treatment is enough.
If a patient is diagnosed with an abscess around the appendicitis, develops chills and high fever, cannot control the infection with antibiotics, and even develops shock symptoms such as fast heart rate, low blood pressure, cold limbs, etc., this situation requires emergency surgery. Only surgery to clear the abscess can Prevents more toxins from entering the bloodstream.
The main measures of conservative treatment are: bed rest, fasting, intravenous nutrition, and symptomatic treatment. Antibiotic treatment is broad-spectrum plus antibacterial. Most people need to take medication for 4 to 5 days before their symptoms are significantly relieved. Some people even take a week, so they don’t want to suffer. Friends who have suffered for such a long time can choose surgery directly. One thing that needs to be kept in mind is that there is a possibility of recurring attacks after conservative treatment, and the intervals between attacks will become shorter and shorter.
Surgical treatment
As long as there are no contraindications to surgery, acute appendicitis should be treated with early surgery after a clear diagnosis, which is both safe and prevents complications. Early surgery refers to surgical removal when the appendix is still blocked in the lumen or only has congestion and edema.
Surgical treatment
(1) Acute simple appendicitis:
This is the simplest case. Just remove the appendix and suture it. You can be discharged from the hospital soon after the operation.
(2) Acute suppurative or gangrenous appendicitis:
This is a little complicated. In addition to removing the appendix, the pus in the abdominal cavity must be cleaned, and then a drainage tube and sometimes an irrigation tube must be placed. After the operation, continuous flushing and drainage are required to cure the disease. Rinse any newly produced pus.
(3) Abscess around the appendix:
If the abdominal pain is not localized, incision and drainage are performed. Whether the appendix can be removed depends on the specific conditions during the operation; if the appendix has fallen off, try to remove it and close the cecal wall to prevent intestinal fistula. If the abscess has been limited to the right lower abdomen and the condition is stable, appendectomy cannot be performed forcibly, because opening the abscess can easily lead to the spread of infection, which is very dangerous. Postoperative antibiotics were given and systemic supportive treatment was strengthened to promote the absorption and resolution of pus.
(4) Appendiceal fecal stone obstruction
It will almost perforate later without surgery. Of course, this does not mean that surgery is absolutely safe and hassle-free. Surgery is still risky and complications may occur.
1. Incision infection
It is the most common postoperative complication. The incidence rate in the non-perforated group is less than 10%,. In the perforated group it can reach more than 20%. It is mostly cause by contamination of the incision during surgery, retaine hematoma and foreign bodies, and poor drainage. Clinical manifestations include elevate body temperature 2 to 3 days after surgery, local swelling or throbbing pain at the incision, and local redness, swelling, and tenderness. Treatment consists of cutting off sutures, enlarging the incision, draining pus, removing foreign bodies and providing adequate drainage.
2. Peritonitis and abdominal abscess
Mostly caused by the appendix stump being ligate poorly and the sutures falling off. The clinical manifestations include continued increase in body temperature, abdominal pain, bloating, and worsening of systemic poisoning symptoms after surgery. It needs to be treat according to the principles of treating peritonitis.
3. Bleeding:
Looseness of the mesoappendiceal ligature can cause massive intra-abdominal bleeding, with symptoms such as abdominal pain, abdominal distension, and hemorrhagic shock. When the appendix stump ligature is loose and the purse-string suture is tight, bleeding can flow into the cecum and cause massive bleeding in the lower gastrointestinal tract. In both cases, immediate blood transfusion and fluid replenishment are require, and if necessary, another operation is require to stop the bleeding.
4. Fecal fistula :
There are many reasons for postoperative fecal fistula, such as fragile ends and falling off of ligatures; damage to the cecal wall; original tuberculosis, cancer and other lesions in the cecum; hard drainage materials that compress the cecal wall and cause necrosis, etc. Most fistulas can self-close after non-surgical treatment, but if the fistula does not close for a long time, a fistula biopsy can be perform to rule out the possibility of other underlying diseases, and treatment can be select according to the situation.
5. Appendiceal stump inflammation
It can occur when the stump is too long and exceeds 1cm during appendectomy. The symptoms are similar to appendicitis. If the diagnosis is clear and the symptoms are severe, the appendix stump should be surgically remove again.
6. The incidence of adhesive intestinal obstruction
Especially when complicated by perforation, can reach about 5%.
The longer these complications are delay before surgery, the greater the chance of them appearing. Some people are hesitant when they are first diagnosed. After returning home, they feel unbearable and come back to ask for surgery the next day. We need to understand a truth: the diseases of our human body It’s progressing every moment, especially with this acute illness, and waiting half an hour makes a big difference.
Epecial treatment
There are some special patients who require special treatment, such as the elderly, pregnant women, and children.
The appendix cavity in the elderly has a narrow and thin wall, coupled with arteriosclerosis, it is prone to embolism and perforation. In addition, the elderly are associate with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, diabetes, renal insufficiency, etc., making the condition more complicate and serious. In addition, the organs of the elderly may feel degenerated, and the disease may progress to a very serious stage, but the patient’s clinical manifestations are very mild, and tenderness and abdominal muscle tension are not obvious.
We often receive emergency reports of elderly patients with perforated appendicitis. Who already have signs of shock when they arrive. They may be fine at first but then their condition quickly deteriorates. Many of them have to be transfer to the intensive care unit for monitoring and treatment after surgery. Just because the abdominal pain is not obvious, they think it is just ordinary enteritis. Some people know it is appendicitis but think it is nothing and put it off until the feeling becomes unbearable and then it becomes serious.
Pregnancy makes the pelvic cavity congested, and infection develops quickly and gangrene and perforation may easily occur. During pregnancy, the omentum is push and block by the uterus, making it difficult for it to move down and wrap up localized infections, making the infection difficult to control and easy to spread. Infectious stimulation can lead to premature delivery and miscarriage, as well as fetal hypoxia and death.
Troublesome
What’s even more troublesome is that most antibiotics cannot be use during pregnancy. Even those antibiotics that are not specifically prohibit during pregnancy are not dare to be prescribed by doctors in the current medical environment. If a malform fetus appears, no one can tell whether it is cause by this drug. , if the patients and their families cause trouble, then the blame will be too big.
The impact of surgery is also great. Pregnancy of <3 months and >7 months of pregnancy is very prone to miscarriage or premature birth if surgery is performed during this period. Whether an anesthesiologist dares to anesthetize is another matter. In the end, if you are lucky, the appendicitis will heal on its own. Otherwise the doctor will secretly ask you to have an abortion and then perform appendicitis surgery. Therefore, for female friends who are planning to become pregnant, if appendicitis occurs before preparing for pregnancy, try to have it surgically removed. If it is not remove, it will easily relapse due to the squeezing of the uterus during pregnancy, and you will be in a dilemma.
Children’s symptoms are similar to those of the elderly due to imperfect physical development. However, children’s disease develops very rapidly and their body resistance is weak, which can easily lead to death. As parents, we should not take it lightly. I won’t go into details here.