
Fish Oil vs Krill Oil: Which is Better for You?
There is a lot of confusion regarding the health benefits of fish oil and krill oil. Many people want to know if there are significant differences between the two and whether one is more beneficial than the other. In this article we are going to compare fish Oil vs Krill Oil.
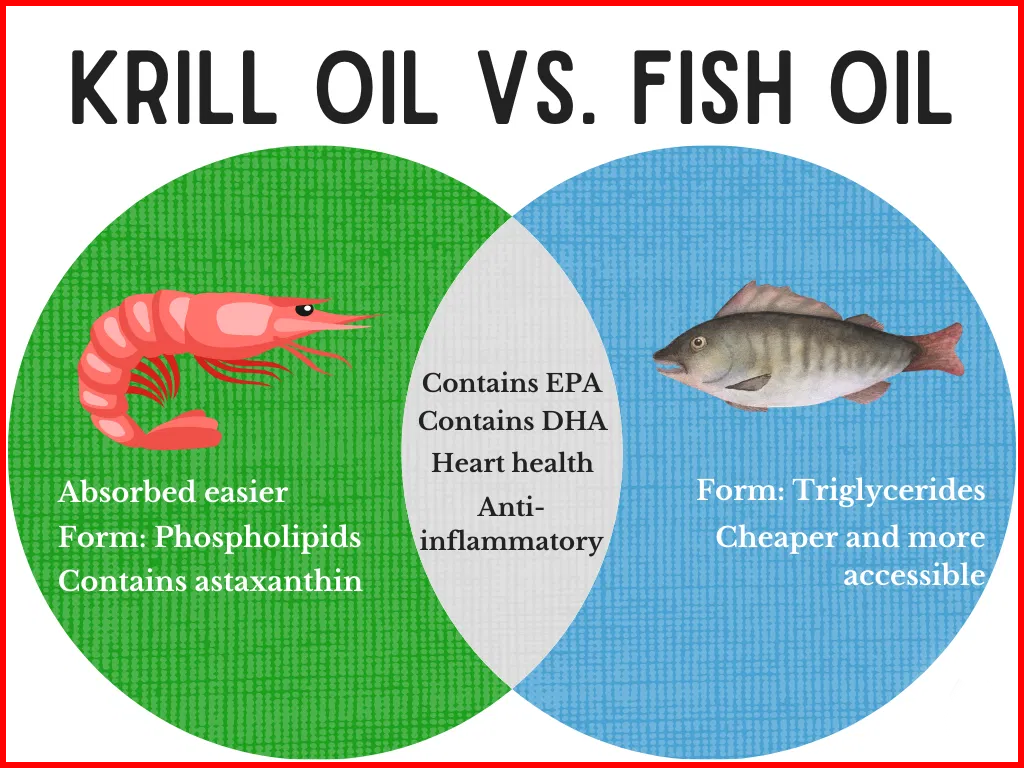
Both fish oil and krill oil contain omega-3 fatty acids, specifically docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). These essential fatty acids may help lower triglycerides and reduce pain and inflammation in people with joint problems.
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid that is an important component of the human brain, skin, and eyes. Although important, it is not considered “essential” because it can be synthesized in the body if alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is consumed in the diet.
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; or eicosapentaenoic acid) is commonly found in fish oil, krill oil, and eggs (assuming the chickens were fed EPA).
A 2016 study showed similar increases in blood DHA/EPA levels when subjects took equal amounts of fish oil and krill oil over a 4-week period.
Sources of DHA and EPA
Fish oil obviously comes from fish. Typically, commercial fish oil comes from tuna, herring, and sardines. When extracted, fish oil is usually white or yellow. When extracted, fish oil is usually white or yellow. Overall, it has low antioxidant properties, which means it may not be a very good antioxidant. When consumed, it is delivered to the body in the form of triacylglycerides (TAGs). Commercial-quality fish oil goes through an additional purification process to eliminate any heavy metals that may be present.
Likewise, krill oil comes from krill, a crustacean found in the Antarctic region. Krill feed on phytoplankton and algae and are at the bottom of the food chain. Therefore, in their natural habitat, krill are virtually exposed to heavy metals, eliminating the need for additional purification.
Krill is a small, red, lobster-like creature found in the South Atlantic Ocean. Krill oil is an essential fatty acid that has a distinctive red color. It tends to be more expensive than fish oil. When consumed, it is delivered to the body in the form of phospholipids.
Krill tends to be more abundant than fish worldwide, so extracting adequate DHA from krill has greater long-term sustainability potential than extracting these oils from fish.
Is eating seafood a good choice?
Ideally, people should get all of their vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids from food. This is what I advise my patients, but I know it’s not always possible. The American Heart Association recommends eating fish regularly, at least twice a week, for a healthy heart. For those who prefer vegetarian alternatives, consuming certain foods may be a good source of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which can be convert to DHA. ALA is found in foods such as flaxseeds , walnuts , soybeans , chia seeds , and hemp seeds .
Due to ocean pollution, getting enough DHA and EPA from animal sources can be a challenge if you rely solely on food. For example, fish such as mackerel, swordfish, bass, shark, and tuna tend to have higher than average levels of mercury and should be consume sparingly. Fish such as salmon, catfish, anchovies, sardines, herring, trout, and tilapia are lower in mercury, but levels can add up if consumed more than two to three times per week.
Fish oil and krill oil may affect the following common health conditions:
1. Joint diseases
Osteoarthritis is often cause by general wear and tear of the joints. It can be cause by damage to the cartilage, which acts as a cushion around the bones. Early signs of osteoarthritis may begin when an individual is about 40 years old and may progress as they age. Symptoms include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and loss of joint function. Many people seek natural alternatives to help relieve symptoms. Often, doctors prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), such as ibuprofen, naproxen , and indomethacin.
Fish oil: Research suggests that essential fatty acids may help improve joint pain and reduce NSAID use. Research shows that joint stiffness may be relieve when fish oil is take at least 500 mg and up to 2,000 mg daily.
Krill oil: A 2007 study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition showed that 300 mg of krill oil “significantly suppressed inflammation and reduced symptoms of joint disease in short-term treatments of 7 and 14 days.” A 2016 double-blind, placebo-controlled study in patients with mild knee pain showed that a daily dose of 2,000 mg of krill oil may help relieve pain.

2. Blood vessel health
Cardiovascular disease is a leading killer of people worldwide. There are various risk factors that may increase the risk of heart and blood vessel disease. Omega 3 fatty acids may be beneficial to the body.
Fish oil: Regular intake of omega -3 fatty acids is important for heart and vascular health. A 2017 study suggests it may help prevent atherosclerosis, or hardening of the arteries. While a 2013 study in the Journal of the American Heart Association show that higher levels of DHA/EPA in the blood may be associate with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease.
Krill Oil: A 2015 study in the British Medical Journal concluded that “ krill oil may modestly improve cardiovascular risk in people with type 2 diabetes, particularly endothelial dysfunction and high-density lipoprotein (HDL).” However, these benefits also apply to those without diabetes. A 2017 study in Nutrition Reviews show that krill oil may benefit the heart by lowering “bad” (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides, which can be risk factors for heart disease when levels in the blood are elevate.
3. Inflammation
Inflammation occurs when the body is out of balance—in a sense, the body is “on fire” from the inside. During times of stress, the body may produce a steroid hormone called cortisol. When cortisol is elevate, the body may produce inflammatory chemicals call prostaglandins. Inflammation may also be assessed by measuring C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in the blood.
Elevated CRP levels can increase your risk of cancer and heart disease, according to a 2017 study in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition . Cholesterol-lowering statins may reduce inflammation, according to a 2018 study in JUPITER. Krill oil and fish oil may also be helpful.
Fish Oil: It is well know that fish oil may help lower CRP levels. A 2016 study may also confirm this, but also showed that krill oil may be more effective than 2000 mg of fish oil. However, another 2016 study in the Journal of Internal Medicine show that CRP levels may not be reduce when 1400 mg of fish oil was take. Based on this, I recommend at least 2000 mg of omega 3 fish oil twice a day to possibly reduce CRP levels.
Krill oil: A 2016 study showed that 500 mg of krill oil twice daily helped lower CRP levels more than 2,000 mg of fish oil twice daily. A 2017 study in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition showed that 300 mg of krill oil daily may reduce CRP levels by nearly 20%.
4. Memory
As the population ages, memory problems are becoming more common. Alzheimer’s disease, the most common dementia, has no specific treatment and can cause tremendous frustration and challenges for patients and caregivers. Symptoms include forgetting names and confusion in the early stages, while more serious problems such as paranoia and sadistic behavior can occur in later stages of Alzheimer’s disease. One percent of Alzheimer’s cases occur before the age of 65, but scientists predict that after the age of 65, 1 in 9 people may be at risk. Natural remedies, such as turmeric and frankincense, appear to help when used along with DHA and EPA.
Fish oil: A 2016 study of 44 patients with memory problems took 22 of them fish oil and 22 a placebo. The researchers note that those who were given fish oil may have better memory. Other studies may show similar findings.
Krill Oil: A 2017 study in the World Journal of Molecular Sciences suggests that krill oil may help reduce oxidative stress in the brain and reduce beta-amyloid deposits. Which are thought to contribute to Alzheimer’s disease. More research is ongoing.
5. High triglycerides
Triglycerides are a type of fat that circulates in your blood. Ideal levels should be below 150 mg/dL (or less than 1.7 mmol/L). Elevated levels can be a risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Eating a diet low in sugar and simple carbohydrates may help lower them, but sometimes that may not be enough. Consider EPA/DHA supplements.
Fish oil: Pharmaceutical companies say to have realize the benefits of lowering triglycerides and have develop a pharmaceutical grade fish oil. However, due to its high cost, many people may not be able to afford it.
A 2016 study in Lipids in Health and Disease concluded that omega-3 fatty acids may help lower triglycerides. Similarly, a 2017 meta-analysis in the Journal of Atherosclerosis , which looked at 1,378 people, showed that eating fatty fish may help lower triglycerides while increasing HDL (“good”) cholesterol levels, two important biomarkers for cardiovascular disease.
Krill Oil: A 2014 study showed that krill oil may reduce triglyceride levels by 10%. A 2017 study in Nutrition Reviews looked at 662 patients and showed similar results in those who consumed krill oil. Other studies have supported these findings.

