
The real effect of Coenzyme Q10, the most detailed introduction
In fact, whether it is an IQ tax depends on how high your expectations are for this product. Most of these products exist in the form of health products. Existing in the form of health products means that there cannot be any treatment for certain diseases or related effects in the official propaganda. Most of them are to improve immunity or resist fatigue. However, Japan has developed coenzyme Q10 as a prescription drug and successfully launched it on the market. Its advertised effects are: myocardial ischemia, high cholesterol, slow blood circulation, prevention of cerebral acid, cerebral infarction, blood viscosity caused by greasy food, slow circulation, and regulating blood flow.
Is coenzyme Q10 a waste of money?
It can also improve the effects of those who have failed to lose weight, have low metabolism, have dull skin, have swollen faces in the morning, have more wrinkles, cannot get up in the morning, feel tired early in the morning, have a strong sense of fatigue, and are out of breath when climbing stairs.
As early as 1940, the ingredient Coenzyme Q10 was discovered in the mitochondria of bovine heart cells. Since then, various studies have been continuously carried out around it, so simply talking about the ingredient Coenzyme Q10 itself is definitely not an IQ tax. Moreover, Coenzyme Q10 itself is a natural ingredient in our own cells. Our human body can naturally synthesize this ingredient, and our cells also use this ingredient to grow and maintain the stability of the cell’s own microenvironment.
Not only that, even the food we eat every day (such as
red meat , fish, nuts, etc.) also contains Coenzyme Q10, but the intake from food cannot significantly increase the level of Coenzyme Q10 in our body, which is why there are Coenzyme Q10 supplements. If someone tells you that Coenzyme Q10 can cure a certain disease with a 100% chance, that is just a waste of money. Although it is a waste of money, it is better to supplement your brain, because there is no disease in this world that can be cured with a 100% chance, not even a cold, let alone other immune system diseases or cancer.
What exactly is Coenzyme Q10?
Since we are going to evaluate it, we also need to understand what this ingredient is. In terms of professional terminology, coenzyme Q10, also known as
ubiquinone or coenzyme Q, is an organic small molecule that exists in all eukaryotic organisms that perform aerobic respiration. The Q in coenzyme Q10 represents the quinone group, and 10 represents the number of isoprene attached to its tail.
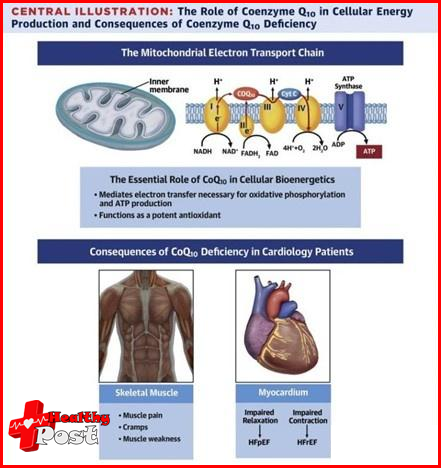
Coenzyme Q10 is one of the substances involved in the electron transport chain and aerobic respiration in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells, and it is also the only non-protein member in the electron transport chain. To put it simply, the core function of Coenzyme Q10 is to help cells convert carbohydrates obtained from food into an important energy molecule, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which involves a series of complex reactions. This also shows that Coenzyme Q10 is crucial to the production of energy. Without it, ATP cannot be produced. Therefore, any organ that requires energy metabolism has it, and ~95% of the energy in the human body is generated by this process.
Organs
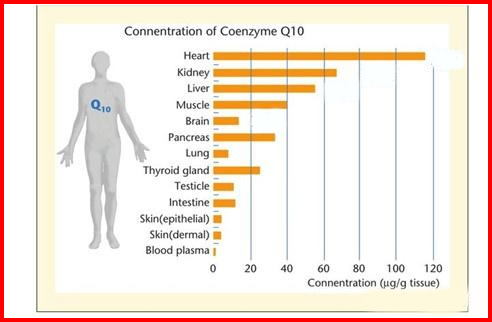
This is why more Coenzyme Q10 can be found in organs with higher energy demands (such as the heart, liver, kidneys, etc.). At the same time, it should not be difficult for us to understand that when the level of Coenzyme Q10 in our body is insufficient, it will definitely have a certain impact on various organs of the body.
So what is the normal range of Coenzyme Q10 in the human body? Studies have shown that the level of Coenzyme Q10 in human blood is considered to be in the normal range of 0.3-3.8 µg/mL. About 25% of Coenzyme Q10 in a person’s blood comes from the diet, and the rest is produced by the body itself. As we mentioned earlier, many of the foods we consume daily contain Coenzyme Q10, such as fish, beef, chicken, nuts, soybeans and other foods. Although the proportion is not large, it can be regarded as an external supplement. Therefore, for most healthy people (especially young people), the amount of Coenzyme Q10 synthesized by themselves plus daily dietary intake is already large enough, so even if there is no additional supplement, there will basically be no problem of Coenzyme Q10 deficiency.

Since the body’s ability to synthesize coenzyme Q10 decreases with age, the need for coenzyme Q10 supplementation is relatively highest among the elderly. At the same time, coenzyme Q10 levels have also been found to be lower in people with certain diseases, such as heart disease patients and people taking cholesterol-lowering
statins . Therefore, for this group of people, coenzyme Q10 supplementation is indeed necessary.
Disease-related research on Coenzyme Q10
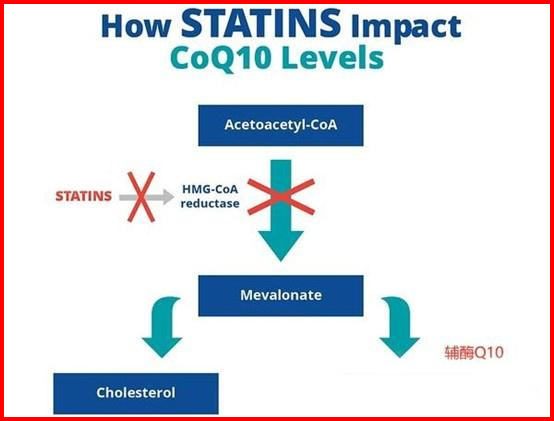
As we mentioned earlier, when taking cholesterol-lowering statins, the concentration of CoQ10 in the body will also be affected. This is because statins block the production of an intermediate in the
mevalonate pathway, which is one of the important pathways for the production of CoQ10. Therefore, researchers believe that taking statins may further reduce the concentration of CoQ10 in the body. Common side effects of statins include muscle pain and cramps, which are also likely cause by the consumption of CoQ10.
In general, in many diseases related to increased reactive oxygen species, the concentration of coenzyme Q10 in the human body will decrease. After a certain level, it may lead to
respiratory chain dysfunction , thereby reducing cell metabolic efficiency. In addition, for other manifestations of the body, such as immunity and athletic performance, because the related cells are all high-energy-consuming, they are more or less related to the concentration of coenzyme Q10 in the body. Therefore, for special groups, coenzyme Q10 supplementation can be consider.
How to choose related products
In fact, there are two types of coenzyme Q10 now, one is health care products and the other is prescription drugs. Health care products are available in many countries, mainly in the United States, Germany, Australia, etc., and the only prescription drug currently available is the water-soluble coenzyme Q10 develop by Japan’s Sawai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Many fans have asked [Medical Companion] whether health care products or prescription drugs are better, and whether prescription drugs have side effects. According to customer feedback, prescription water-soluble coenzyme Q10
There are no side effects. Its main advantages are:
①The absorption rate of fat-soluble coenzyme Q10 in health supplements is only 2-3%
②The absorption rate of prescription water-soluble coenzyme Q10 reaches 22%-28%, and its effect is extremely strong.
Coenzyme is a nutrient that is easily oxidize and very unstable. Once oxidize, the absorption effect will be greatly weakened. Therefore, water-soluble coenzyme Q10 is more recommended in the selection of coenzymes. This process can reduce the probability of oxidation of the product exponentially, and the absorption rate is naturally high.
About price: As we all know, many health products are high-end and targeted at the rich, so the price of health products such as coenzyme is very high, while prescription drugs are more affordable. When many people come to [Medical Companion] to ask about coenzyme, I will recommend prescription coenzyme Q10, and the purpose of writing this article is to let everyone know the coenzyme correctly, which can indeed play a certain role. If you have any questions or needs, you can kick me in the background.
The next question is: What is the use of coenzyme Q10 and why do we need to supplement it?
1. What is the use of Coenzyme Q10?
Coenzyme Q10, like vitamins, indirectly affects our health through metabolism. It is mainly involve in the body’s energy supply and oxygen metabolism process – studies have show that its content is related to our energy, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular health.
First, let’s talk about energy. Apart from psychological and emotional factors, the quality of energy is mainly affect by energy supply. The most important energy supply substance in our body is ATP ; and coenzyme Q10 is an important auxiliary factor in the synthesis of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) in the body , participating in a series of redox reactions in ATP synthesis. In other words, coenzyme Q10 is directly involve in the body’s energy supply process.
In order to supply energy to the body more efficiently, the distribution of coenzyme Q10 in the body is also concentrate in important organs related to “energy”, such as the heart, kidneys, liver, and brain.
2. Adequate supply of coenzyme Q10 and ATP provides physical protection for our energy
Coenzyme Q10 can help the body achieve oxidative balance. We metabolize oxygen every moment to maintain normal metabolism and energy supply, and oxygen free radicals are inevitably produce in the process.
Especially when we encounter the following factors:
- External factors, such as air pollution, sunlight (ultraviolet rays), toxins (pesticides), stress, etc.;
- Internal factors, such as bad living habits (smoking and drinking/fried food/lack of exercise, etc.), and aging.

3. Summary of the effects of coenzyme Q10 (both effective and ineffective):
① Coenzyme Q10 improves fatigue related to physical activity
The most important effects of fatigue include decreased work motivation, increased reaction time, decreased alertness, poor concentration, poor psychometric coordination, memory and information processing problems, and poor judgment.
A double-blind, placebo-controlled study (8 days in 17 healthy subjects) showed that oral coenzyme Q10 helped improve maximum speed change after a fatigue-inducing physical task. In addition, the subjective fatigue sensation and recovery time were lower in subjects give coenzyme Q10 (300 mg) than in the placebo group.
* Conclusion: It is effective in fighting fatigue
② Coenzyme Q10 is beneficial to endothelial function
The vascular endothelium is an active monolayer of cells that covers the vascular lumen and separates the vessel wall from the circulating blood. It is also a highly selective barrier and metabolically active organ that is important for hemostasis and thrombosis, regulation of local vascular tone and redox balance, and coordination of acute and chronic inflammatory responses within the arterial wall.
Accumulating evidence suggests that endothelial dysfunction is the first recognizable sign of the development of atherosclerosis and exists long before the onset of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
A literature meta-analysis (including 5 randomized controlled trials with a total of 194 participants) pointed out that it can significantly improve endothelial function through flow-mediated dilation.
However, a fixed-effects model evaluating endothelial function as assessed by nitrate-mediated arterial dilation did not yield significant improvements.
*Conclusion: Coenzyme Q10 supplementation may have a positive effect on improving endothelial function. But whether it can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease remains to be confirm.
③Can coenzyme Q10 help lose weight?
Obesity is the abnormal accumulation of body fat (usually 20% above normal ideal body weight). Due to the psychological and social stigma associated with being overweight and obese, those affected are also vulnerable to discrimination, low self-esteem and depression in their personal and work lives.
In addition, depending on the degree, duration and distribution of overweight, excess weight can gradually lead to or aggravate a variety of comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, cardiovascular disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, reproductive dysfunction, respiratory abnormalities, mental illness, and even increase the risk of certain cancers.
A systematic literature review and meta-analysis (including 17 randomized controlled clinical trials) pointed out that coenzyme Q10 supplementation had no significant effect on reducing body weight (weighted mean difference WMD: 0.28 kg) and body mass index (weighted mean difference WMD: -0.03).
Additionally, subgroup analyses showed that the dose of Q10 and the duration of the trial did not have any effect on the outcomes of supplementation.
*Conclusion: To date, there is no evidence to prove that supplementing with coenzyme Q10 is helpful for weight loss. But due to the heterogeneity of the includ studies, more research is still need to confirm its clinical benefits.
④ Does Coenzyme Q10 improve disease-related fatigue?
Fatigue is one of the most common complaints see by physicians and is characterize by a decrease in ability or motivation to work, often accompanied by feelings of tiredness and drowsiness. This type of fatigue is a nonspecific symptom associate with many medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism, celiac disease, anemia, influenza, heart failure, acute liver disease, cancer, diabetes, and sleep apnea.
A 24-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 236 women with breast cancer who were receiving chemotherapy found that oral CoQ10 did not improve self-reported fatigue or quality of life scores.
Another randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (12 weeks, involving 48 patients with multiple sclerosis) showed that oral coenzyme Q10 (daily dose of 500 mg) can improve fatigue and depression.
*Conclusion: The results of using coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) to improve disease-related fatigue are mix and need to be confirm.
⑤ Coenzyme Q10 is beneficial for blood sugar control
Adults with diabetes have a 50% higher risk of death from all causes than adults without diabetes, in addition to the risk of complications including accelerated development of cardiovascular disease, end-stage renal disease, vision loss, and amputation.
A systematic literature review and meta-analysis (including 13 randomized controlled trials with a total of 765 patients with type 2 diabetes) pointed out that oral coenzyme Q10 can improve blood sugar control (lowering glycated hemoglobin and fasting blood sugar) and blood lipids (lowering triglycerides and increasing high-density lipoprotein cholesterol).
*Conclusion: For type 2 diabetes, oral coenzyme Q10 has a positive effect on blood sugar control, but it is limit by possible risk bias and heterogeneity, and more research is still need to confirm it.
⑥ Coenzyme Q10 is beneficial for migraine
Migraine is the second most common headache and is usually describe as moderate to severe unilateral pain with recurring throbbing or pulsating attacks that usually last 4-72 hours and may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting or sensitivity to light, sound or smell. Before a migraine attack, about one-third of patients experience an aura, the most common of which is a visual aura in the form of jagged lines or scattered flashing dark spots (lasting about 5-60 minutes).
A literature meta-analysis (including 5 studies and a total of 346 migraine patients) pointed out that compared with placebo, oral coenzyme Q10 can reduce the number of days and duration of attacks per month, but there is no significant change in the severity and frequency of attacks.
*Conclusion: It has a positive effect on improving migraines, but due to the small sample size, more large-scale trials are still need to further verify it.
⑦ Coenzyme Q10 is beneficial for sarcopenia
Sarcopenia is an age-related geriatric syndrome characterize by skeletal muscle loss, decreased muscle strength, and decreased physical fitness, which increases the risk of osteoporosis, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. The prevalence of sarcopenia in people over 65 years old can reach 5% to 10%. The etiology of sarcopenia is related to reduced calorie intake, insufficient muscle blood flow, mitochondrial dysfunction, decreased anabolic hormones, and increased pro-inflammatory cytokines.
In population observational studies, a lower CoQ10/cholesterol ratio and reduce CoQ10 levels were found to be important indicators of sarcopenia (the subjects had poor upper body muscle strength, muscle mass, and peak expiratory flow).
*Conclusion: Low levels of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) are consider one of the indicators of sarcopenia, but more research is need to confirm whether supplementation can bring benefits.
⑧ Coenzyme Q10 improves inflammatory indicators
Inflammation is a physiological response of biological tissues to injury, pathogen invasion, or irritants, which is mainly manifest by temperature rise, redness, swelling, and pain cause by increased local blood flow. Short-term or acute inflammation is a unique protective response of organisms to eliminate harmful irritants and initiate self-healing mechanisms, but long-term or chronic inflammation is consider to be the main factor leading to many chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, type 2 diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and cancer.
A systematic literature review and meta-analysis (including 17 randomized double-blind controlled studies) pointed out that coenzyme Q10 supplementation has a significant effect on lowering C-type reactive protein, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor.
The underlying mechanism may be related to coenzyme Q10’s ability to capture free radicals and inhibit the activation of nuclear transcription factors.
*Conclusion: Supplementation with coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) has the effect of reducing multiple pro-inflammatory hormones, but it is limited by the high heterogeneity among studies and still needs more evidence to verify.
⑨ Coenzyme Q10 is beneficial for heart failure
Heart failure occurs when the heart chambers are unable to pump blood efficiently (systolic dysfunction) and their ability to relax is impair (diastolic dysfunction). Symptoms may include unusual shortness of breath during exercise or rest, fatigue, or swelling in the ankles.
The causes of heart failure are often related to coronary heart disease, hypertension, cardiomyopathy, aging, and valvular abnormalities, but congenital heart disease is the most common.
A literature meta-analysis (including 14 randomized controlled trials with a total of 2,149 patients with heart failure) pointed out that compared with placebo, the use of coenzyme Q10 not only reduced the mortality rate by 31%, but also improved exercise capacity (but there was no significant difference in left ventricular ejection fraction and New York Heart Association heart function class).
*Comment: It can reduce mortality and improve exercise capacity in patients with heart failure, but it is limit by possible bias and heterogeneity and needs to be confirm by more rigorous, large-sample experiments.
⑩ Coenzyme Q10 is beneficial for male infertility
Currently, most developed countries are facing a serious problem of declining fertility rates, which is related to complex social and environmental factors, including economic development, environmental pollution and climate warming. Age is also one of the causes of infertility. According to a population survey, the probability of a man getting his partner pregnant after the age of 40 will decrease by 30% (compared to 30 years old).
A literature meta-analysis (including 3 studies with a total of 296 participants) pointed out that although oral coenzyme Q10 can increase sperm concentration and motility, its effect on improving live birth or pregnancy rates is still unknown.
*Conclusion: It can improve relevant routine semen parameters, but there is no evidence to prove that it can increase the chance of pregnancy, and other experiments are need to verify it.
⑪ Coenzyme Q10 is beneficial for high blood pressure
Essential hypertension is the most common blood pressure disease (accounting for about 90% to 95%). Although there is no direct cause of the disease, it is related to a variety of lifestyle factors, such as long-term sitting, stress, visceral obesity, overweight, alcohol intake, aging, etc.
It is consider to be beneficial for blood pressure control due to its antioxidant properties, improving endothelial function, reducing peripheral resistance and inhibiting peroxide production.
A Cochrane review (including 2 randomized controlled studies) showed that oral coenzyme Q10 did not produce a clinically significant blood pressure-lowering effect compared with placebo (systolic blood pressure decreased by 3.68 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure decreased by 2.03 mm Hg).
*Conclusion: Although it has a blood pressure lowering effect, it does not meet the clinical significance standard and needs further verification in more large-scale controlled studies.
⑫ Coenzyme Q10 is beneficial for polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome is the most common endocrine disease in women of childbearing age, with a prevalence of approximately 5-21%.
Patients often experience symptoms such as reproductive dysfunction (hyperandrogenism, hirsutism, ovulation arrest, infertility, menstrual disorders), metabolic system abnormalities (obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease) and mood disorders. Clinically, it has also been found that more than half of patients will have hyperinsulinemia and dyslipidemia, which greatly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.
A double-blind controlled study (12 weeks, subjects included 60 women with polycystic ovary syndrome) found that supplementation with coenzyme Q10 (100 mg per day) helped improve blood sugar metabolism (fasting blood sugar and insulin-related values), total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol values, which may have a beneficial effect on patients.
*Conclusion: It may have a positive effect on improving PCOS, but this needs to be further verify by more large-scale control studies.
⑬ Coenzyme Q10 improves Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson’s disease is cause by degeneration of the substantia nigra and striatum associated with the neurotransmitter dopamine, which makes it difficult for the brain to transmit commands, resulting in motor dysfunction, but the brain’s memory and cognitive functions can function normally. Although Parkinson’s disease does not necessarily develop into dementia, 61% of patients will experience mental symptoms, including depression, anxiety, hallucinations and sleep disorders.
Related studies have shown that the probability of Parkinson’s patients lacking coenzyme Q10 is about 4 to 5 times higher than that of normal people. However, so far, a systematic literature review (including 5 randomized controlled trials, with a total of 981 Parkinson’s patients) and meta-analysis have found that supplementing coenzyme Q10 does not bring any benefits to patients or slow down functional degeneration.
5. How big is the coenzyme gap in our body?
The content of Coenzyme in a normal human body is between 500-1500mg. Taking the middle value of 1000mg, even if it is calculate by a 20% decrease, there is still a gap of about 200mg. The content of Coenzyme in most natural foods is between 1-3mg/100g. Even if you consume 1kg of food rich in Q10 every day, you can only supplement about 20-30mg, which is still a big gap from 200mg.

One thought on “The real effect of Coenzyme Q10, the most detailed introduction”