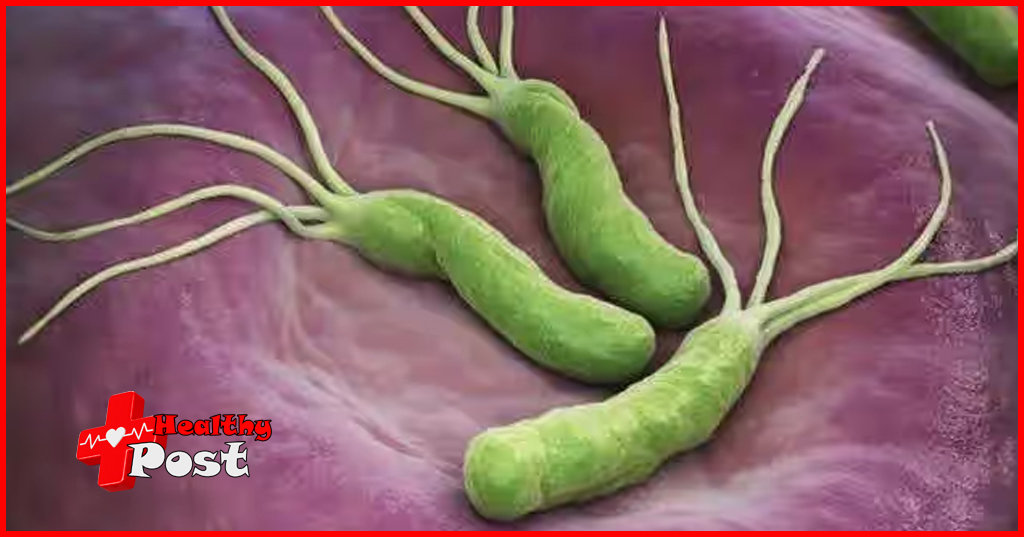
What are the symptoms of Helicobacter pylori, how to check and treat it
Helicobacter pylori (Hp), also known as Helicobacter pylori, is a type of bacteria and the only bacteria that can survive in the stomach. Because our stomach secretes gastric acid, the stomach is a highly acidic environment. Ordinary bacteria cannot grow in the stomach, but Helicobacter pylori can.
What are the dangers of Helicobacter pylori
It mainly lives in the stomach. Almost all people infected with it have chronic active gastritis , also known as Helicobacter pylori gastritis. About 15% to 20% of infected people develop peptic ulcers (gastric ulcers and duodenal ulcers), 5% to 10% develop indigestion, and about 1% develop gastric malignant tumors [including gastric cancer and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma.

That is to say, if patients infected with Helicobacter pylori do not receive treatment, 1% of them will develop gastric malignant tumors. Therefore, it is a type of carcinogen and has a very close relationship with gastric cancer.
How does Helicobacter pylori infect humans?
It mainly infects humans through the fecal-oral route and the oral-oral route. What does the fecal-oral route mean? Patients infected with it also have Helicobacter pylori in their feces. If the feces contaminate the water source, healthy people who drink water containing Helicobacter pylori can be infect.
Also, if the patient does not wash his hands after going to the toilet, his hands may carry bacteria. If his hands touch fruits, vegetables and other foods, the food may be contaminate, and other people may be infect if they eat these fruits. This is the classic fecal-oral route.

Bacteria may also exist in the mouths of people infected with it, and eating together, kissing, using unclean tableware, etc. can all transmit Helicobacter pylori. In particular, when adults chew food with their own mouths and feed it to children, it is easy to transmit to children.
What discomfort does being infect with Helicobacter pylori cause?
Most people do not feel any discomfort, but gastritis or gastric ulcer may cause discomfort, such as upper abdominal pain or discomfort, a feeling of fullness without eating much; nausea or vomiting; acid reflux or heartburn; darker or black stools; increased fatigue, bad breath and other symptoms.
How is Helicobacter pylori infection diagnose?
1. Breath test
This is the most commonly use test method, and blowing a breath can determine whether or not you are infected with it, because Helicobacter pylori can produce highly active urease.

Urease can decompose urea to produce carbon dioxide. We label urea with radioactive isotopes and then swallow the urea. If it is in the stomach, the radioactive isotope can be detect when the patient exhales, which can determine whether the patient is infect with Helicobacter pylori.
2. Gastroscopy
When doing a gastroscopy, a small piece of gastric mucosal tissue can be take for testing, which can also confirm Helicobacter pylori. However, it is not evenly distribute throughout the stomach. If the tissue take does not contain Helicobacter pylori, then the diagnosis may be miss.
3. Blood test
Blood tests can be do to check for antibodies, and if infect with Helicobacter pylori, the antibodies are positive. However, this antibody is not a neutralizing antibody and cannot kill Helicobacter pylori, and it cannot distinguish whether the patient is infect with Helicobacter pylori.
If you are currently infect with Helicobacter pylori, or have been infect and are now cured, the antibodies may be positive and there is no way to distinguish them.
4. Stool test
It is also possible to test stool to see whether it contains Helicobacter pylori antigens. If so, the diagnosis can be confirm.
Currently, the most commonly used methods in clinical practice are breath tests and gastroscopy. If the patient cannot cooperate with the breath test, stool testing is another option.
Who needs treatment?
Routine testing for Helicobacter pylori is not recommend for children under 18 years of age because, compared with adults, children are less likely to develop serious illness after infection; have fewer drug options and lower tolerance to adverse drug reactions; and have a high rate of reinfection after eradication.
Testing and treatment should only be consider if a child develops peptic ulcer, stubborn iron deficiency anemia after excluding other causes, and chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Therefore, if a child is to be treat for Helicobacter pylori, the doctor must be extremely cautious and consult a doctor in a regular hospital.
For adults, the recommendations are completely different. As long as there are no contraindications to taking the medicine, radical cure is recommend for adults, especially for patients with peptic ulcers and gastric lymphoma, for whom eradication is strongly recommend.
How to cure it?
The recommended quadruple therapy is to cure Helicobacter pylori, which includes four drugs: a proton pump inhibitor, which inhibits gastric acid secretion and promotes ulcer healing; a bismuth agent, which can protect the gastric mucosa; and two antibiotics, which kill Helicobacter pylori. The course of treatment is 14 days, and the medication needs to be take continuously for 14 days.
Proton pump inhibitors include omeprazole, pantoprazole, esomeprazole, etc., you can choose any one of them; bismuth agents include potassium citrate bismuth or pectin. Antibiotics include amoxicillin, clarithromycin, levofloxacin, metronidazole, tetracycline, etc., you can choose two antibiotics from them.
As can be see from the table below, there are 7 antibiotic combinations, and you can choose any one of them, such as amoxicillin + clarithromycin. If you are allergic to amoxicillin, you should choose an antibiotic regimen that does not contain amoxicillin.
For example, the commonly used quadruple therapy is: amoxicillin + clarithromycin + rabeprazole + potassium citrate bismuth, or amoxicillin + levofloxacin + omeprazole + bismuth pectin.
Everyone should never buy medicine by themselves. You should find a regular doctor to prescribe medicine. The doctor will choose the most appropriate plan based on your condition, local drug sensitivity conditions, and whether you have a history of drug allergies.
According to current data, the eradication rate of Helicobacter pylori can reach 80% to 90% for patients receiving first-time treatment.
How to take medicine?
These four drugs are not take at the same time, there are some rules. Antibiotics usually have a certain degree of gastrointestinal irritation, and when the stomach acid is low, the antibacterial effect of antibiotics is the best. Therefore, it is generally recommend to take antibiotics half an hour after a meal.
Acid-suppressive drugs and bismuth should be take about half an hour before meals. Acid-suppressive drugs can only take effect quickly when taken on an empty stomach, and bismuth can only form a good gastric mucosal protective layer in an acidic environment. Therefore, you can choose to take acid-suppressive drugs + bismuth half an hour before meals.
Don’t stop taking medicine casually
During the medication process, some side effects may occur, such as bitter taste in the mouth, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and some complications include rash, insomnia, headache, black stools, constipation, etc.
Most of them are not serious and can generally recover quickly after stopping the medication. Never stop the medication casually. If you stop taking the medication after a few days, it will not only fail to completely kill the bacteria, but may also cause drug resistance and lead to treatment failure. The next time you want to treat it, it will be even more difficult.
If more serious side effects occur, be sure to consult a doctor and never stop taking the medicine casually!
When to follow up after treatment.
After finishing the medicine, you need to wait at least one month for a follow-up check. The first choice for follow-up check is also a breath test. If the breath test is negative, then congratulations, you have been cured.
However, everyone should also note that after being cured, you do not have lasting immunity to Helicobacter pylori and there is a possibility of reinfection. The probability of reinfection is about 5%.
How to prevent infectaion?
When eating, separate meals should be adopted, or serving chopsticks should be used. Do not share bowls and chopsticks, do not use your own chopsticks to pick up food for others, and do not feed people mouth to mouth. Before the infected person is cured, they must use separate tableware, wash it separately after use, and disinfect it at high temperature.
In summary, Helicobacter pylori is a type of carcinogen. For adults infect with Helicobacter pylori, it is recommend to eradicate the bacteria. Quadruple therapy is the main means of treating Helicobacter pylori.

4 thoughts on “What are the symptoms of Helicobacter pylori, how to check and treat it”