Septate Hymen Explained: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
A septate hymen is a rare congenital condition where an extra band of tissue divides the vaginal opening into two separate holes. This anatomical variation affects approximately 1 in 1,000 females and is present from birth.
The hymen is a thin, elastic membrane that partially covers the vaginal opening. In its typical form, the hymen has a single opening allowing for menstrual flow and tampon use. The normal hymenal tissue can vary in shape and size, with common variations including:
- Crescentic (half-moon shaped)
- Annular (ring-shaped)
- Redundant (extra tissue folds)
In cases of septate hymen, the membrane develops with a vertical band of tissue creating a distinctive double opening. This anatomical difference can impact various aspects of reproductive health and daily activities.
Understanding septate hymen is crucial for several reasons:
- Early Detection: Recognition of symptoms enables timely medical intervention
- Reproductive Health: The condition can affect menstruation and sexual activity
- Medical Management: Proper diagnosis leads to appropriate treatment options
- Quality of Life: Addressing the condition helps prevent physical and emotional complications
If you experience persistent discomfort during menstruation or tampon use, consulting a healthcare provider can help determine if a septate hymen is the underlying cause.
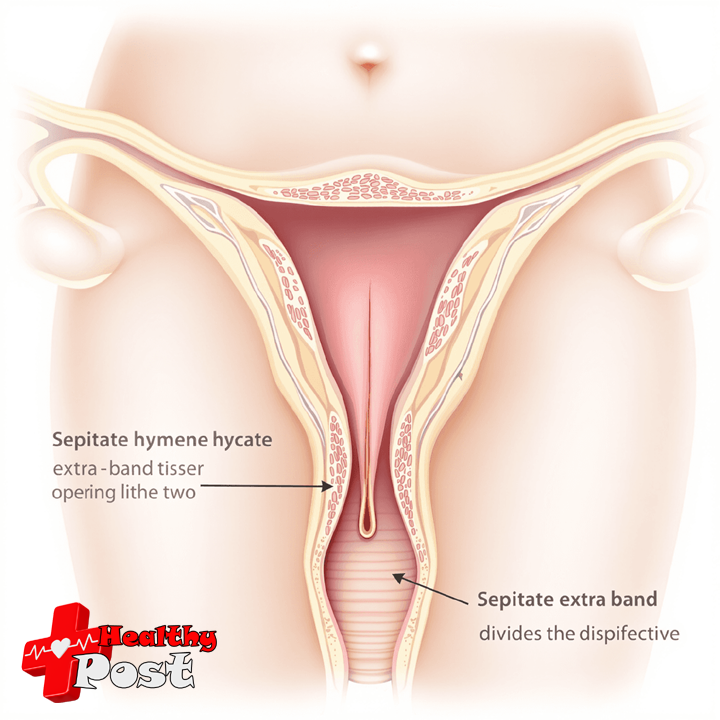
What Causes a Septate Hymen?
A septate hymen develops during the early stages of fetal development, specifically between weeks 8 and 12 of pregnancy. During this critical period, the reproductive system undergoes significant changes and formation. The condition occurs when the hymenal tissue fails to dissolve properly, leaving an extra band of tissue that divides the vaginal opening.
This developmental variation belongs to a group of congenital anomalies that can affect the female reproductive tract. These anomalies include:
- Müllerian duct abnormalities – affecting the formation of the uterus and vagina
- Vaginal septa – similar tissue bands that can form higher in the vaginal canal
- Other hymenal variations – including imperforate, microperforate, or cribriform hymens
It’s essential to understand that a septate hymen is not caused by:
- External injuries
- Physical trauma
- Infections
- Environmental factors
- Lifestyle choices
The presence of a septate hymen is purely a result of natural developmental processes during fetal growth. This understanding helps dispel common misconceptions and ensures proper medical attention. Genetic factors might play a role in its development, though research in this area remains limited.
The condition often goes unnoticed until puberty or the onset of menstruation, when physical symptoms typically begin to manifest.
Recognizing the Symptoms of a Septate Hymen
A septate hymen often goes unnoticed until puberty or the onset of menstruation. The symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, impacting daily activities and overall well-being.
Common Physical Symptoms:
- Difficulty inserting or removing tampons due to the divided opening
- Painful menstruation with slow or incomplete flow
- Pain during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Bleeding after sexual activity from tissue tearing
- Challenges with complete bladder emptying
- Constipation or straining during bowel movements
Menstrual-Related Signs:
- Menstrual blood accumulation behind the septum
- Extended periods lasting longer than usual
- Dark or brown discharge between periods
- Spotting throughout the menstrual cycle
Additional Health Concerns:
- Frequent urinary tract infections
- Vaginal irritation and discomfort
- Persistent pelvic pain
- Unusual discharge or odor
Many individuals with a septate hymen experience a combination of these symptoms, varying in severity. The presence of these signs doesn’t automatically indicate a septate hymen – similar symptoms can occur with other gynecological conditions. A proper medical evaluation helps determine the exact cause and appropriate treatment plan.
Diagnosing a Septate Hymen: What to Expect?
The diagnosis of a septate hymen involves a systematic medical evaluation process. Your healthcare provider will start with a detailed medical history review, focusing on:
- Menstrual patterns and irregularities
- Pain or discomfort during daily activities
- Sexual health concerns
- Previous gynecological issues
- Family history of reproductive tract anomalies
A physical examination follows the medical history review. During this examination, your healthcare provider will:
- Perform a gentle external genital examination
- Identify the presence of the extra tissue band dividing the hymenal opening
- Assess the size and location of the septum
- Check for other potential anatomical variations
In some cases, additional diagnostic tools might be necessary:
- Pelvic ultrasound: Creates detailed images of reproductive organs
- MRI scan: Provides comprehensive views of the reproductive tract
- Vaginoscopy: Allows direct visualization of the vaginal canal
Your healthcare provider might recommend these imaging tests to:
- Rule out other reproductive tract anomalies
- Determine the exact thickness and length of the septum
- Plan the most appropriate treatment approach
The diagnostic process typically takes place in a private medical setting, with a nurse present during the examination. You can request a female healthcare provider if it makes you more comfortable.
Treatment Options for a Septate Hymen: What You Need to Know?
The primary treatment for a septate hymen is a surgical procedure called hymenectomy. This minor operation removes the extra band of tissue dividing the vaginal opening, creating a single, normal-sized opening.
The Surgical Process
The surgical process includes:
- Local or general anesthesia administration for patient comfort
- Careful removal of the extra tissue band
- Creation of a single vaginal opening
- Placement of dissolvable stitches when needed
Duration and Recovery
The hymenectomy procedure typically takes 15-30 minutes and can be performed as an outpatient surgery. You can return home the same day, with most patients resuming normal activities within 24-48 hours.
Post-Surgical Care Instructions
Post-surgical care instructions include:
- Keeping the area clean and dry
- Using prescribed pain medication if needed
- Avoiding tampons or sexual activity for 4-6 weeks
- Wearing loose, comfortable clothing
- Taking sitz baths to promote healing
Success Rate and Complications
The success rate for hymenectomy is high, with most patients experiencing complete resolution of their symptoms. Physical discomfort during recovery is minimal, and complications are rare when performed by an experienced healthcare provider.
Your doctor might prescribe antibiotics to prevent infection and recommend follow-up appointments to monitor healing progress.
Risks and Complications Without Treatment for a Septate Hymen
Leaving a septate hymen untreated can lead to significant health complications. The extra tissue band creates physical barriers that affect multiple aspects of reproductive health and daily comfort.
Physical Pain and Discomfort
- Chronic pelvic pain that intensifies during physical activities
- Sharp pain during menstruation as blood struggles to exit
- Persistent discomfort during intimate activities
- Muscle tension from compensating for ongoing pain
Menstrual Complications
- Blood accumulation behind the septum creates pressure
- Irregular or incomplete menstrual flow
- Risk of toxic shock syndrome from retained menstrual blood
- Severe cramping from blocked menstrual flow
Infection Risks
- Bacterial growth in trapped menstrual fluid
- Recurring vaginal infections from poor drainage
- Higher susceptibility to urinary tract infections
- Difficulty maintaining proper hygiene due to anatomical obstruction
Long-term Health Impact
The presence of these complications often creates a cycle where each issue compounds the others. The obstruction leads to trapped fluids, which increases infection risks, leading to more pain and potential tissue damage. These physical symptoms can worsen with time if left unaddressed. In some cases, the untreated septate hymen may even necessitate surgical intervention, such as a hymenectomy, to alleviate these complications.
Emotional and Psychological Considerations with a Septate Hymen
Living with a septate hymen creates unique emotional challenges that extend beyond physical symptoms. Many individuals experience significant psychological impacts, particularly during crucial developmental stages.
Common Emotional Responses:
- Self-consciousness about body differences
- Anxiety during intimate relationships
- Fear of medical examinations
- Feelings of isolation or being “different”
- Concerns about future fertility
- Depression linked to chronic pain
- Stress about potential surgical procedures
The diagnosis can be particularly challenging during adolescence – a time when body image and peer relationships hold heightened importance. Young people might feel hesitant to discuss their symptoms with friends or family, leading to feelings of isolation.
Adults facing a septate hymen diagnosis often struggle with relationship dynamics and intimate partnerships. The condition can affect sexual confidence and create anxiety about physical intimacy. Some individuals report feeling frustrated or embarrassed about delayed diagnosis, especially when symptoms have persisted for years.
Support Strategies:
- Connecting with healthcare providers who specialize in reproductive health. It’s essential to find professionals who are not only knowledgeable but also empathetic towards the emotional aspects of such conditions. Talking to older patients may also provide insights into handling sensitive discussions.
- Joining support groups or online communities
- Open communication with trusted friends or family members
- Working with mental health professionals familiar with reproductive health issues
- Educational resources to better understand the condition
The emotional impact varies significantly among individuals, influenced by factors like age at diagnosis, severity of symptoms, and available support systems. Professional counseling can help develop coping strategies and build confidence in managing both physical and emotional aspects of the condition.
When Should You See a Healthcare Provider for a Suspected Septate Hymen?
Knowing when to see a doctor for a suspected septate hymen is important for your health. Here are some signs that mean you should make an appointment with a healthcare provider:
Physical Symptoms
- Difficulty inserting or removing tampons
- Pain or discomfort during sexual activity
- Unusual bleeding after intercourse
- Problems with menstrual flow
- Recurring urinary tract infections
Additional Warning Signs
- Feeling a physical obstruction in the vaginal area
- Unexplained pelvic pain
- Changes in urination patterns
- Difficulty with bowel movements
If you have any combination of these symptoms, it’s important to get a gynecological evaluation. Your healthcare provider can examine you thoroughly to confirm the diagnosis and talk about treatment options.
Don’t wait to get help if you:
- Feel persistent discomfort during daily activities
- Notice changes in your menstrual cycle
- Experience anxiety about intimate relationships due to physical symptoms
Remember: Finding and treating a septate hymen early can stop problems from happening and make your life better. A qualified healthcare provider can diagnose you correctly, give you treatment options, and support you throughout your medical journey.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is a septate hymen and how does it affect vaginal anatomy?
A septate hymen is a congenital hymenal anomaly characterized by an extra band of tissue dividing the vaginal opening. It results from improper formation of the hymenal membrane during fetal development, affecting the normal anatomy of the hymen.
What causes a septate hymen to develop?
A septate hymen originates during fetal development due to anomalies in the formation of the hymenal membrane. It is a congenital condition and is not caused by external factors or injuries.
What are the common symptoms associated with a septate hymen?
Symptoms often appear during puberty or at the onset of menstruation and include difficulty inserting or removing tampons, painful sexual intercourse accompanied by bleeding due to tearing, menstrual difficulties, problems with urination and bowel movements caused by obstruction, and recurrent urinary tract infections linked to septal obstruction.
How is a septate hymen diagnosed by healthcare providers?
Diagnosis involves a thorough medical history review focusing on symptoms and menstrual issues, followed by a physical examination by a healthcare provider to identify the presence of an extra tissue band indicative of a septate hymen.
What treatment options are available for a septate hymen?
The primary treatment for a septate hymen is a minor surgical procedure called hymenectomy, which involves removing the extra tissue band to restore normal vaginal anatomy and alleviate symptoms.
What are the risks and complications if a septate hymen remains untreated?
Without treatment, pain may persist or worsen, menstrual blood accumulation can lead to flow difficulties and possible infections, there is an increased risk for vaginal infections due to obstruction and hygiene challenges, and fertility may potentially be impacted.

One thought on “Septate Hymen Explained: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options”