What is Exophthalmos, Symptoms, cause, treatment and prevention
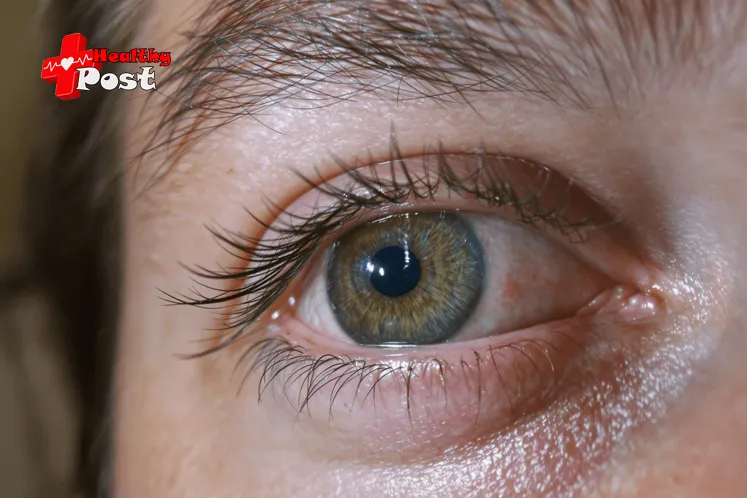
Have you ever looked in the mirror and noticed that your eyes look unusually bulging or sticking out? This condition is called Exophthalmos, and it can be quite alarming for anyone who experiences it.
Exophthalmos is a medical condition where one or both eyeballs protrude forward, going beyond their normal position in the eye socket. This bulging can cause discomfort and affect your daily life in several ways:
- Difficulty fully closing your eyes
- Increased dryness and irritation in the eyes
- Possible changes in vision
- Altered appearance of your face
Your eyes are essential for seeing and contribute to your overall well-being. It’s crucial to understand Exophthalmos because early detection can prevent severe complications. This condition often indicates underlying health problems, especially thyroid-related issues like Graves’ disease.
By recognizing the signs of Exophthalmos early on, you can seek appropriate medical attention before the condition worsens. With proper diagnosis and treatment, many patients can effectively manage their symptoms and protect their vision. The key is to stay informed about the symptoms, causes, and available treatment options for this condition.
In this guide, we will cover everything you need to know about Exophthalmos. From its definition to prevention strategies, this resource aims to help you make informed decisions about your eye health.
What is Exophthalmos?
Exophthalmos, also known as proptosis, is a medical condition where your eyeballs protrude or bulge abnormally from their natural position in the eye socket. This displacement occurs when the tissues, muscles, and fat behind your eyes become inflamed and swollen, pushing the eyeball forward.
The condition has a strong connection to thyroid disorders, particularly Graves’ disease – an autoimmune condition affecting your thyroid gland. In Graves’ disease, your immune system mistakenly attacks the tissues around your eyes, causing inflammation and swelling that leads to eye protrusion.
While Graves’ disease accounts for approximately 80% of exophthalmos cases, other conditions can trigger this eye socket disorder:
- Orbital inflammatory conditions
- Space-occupying lesions (tumors or cysts)
- Orbital infections
- Vascular malformations
The degree of eye protrusion varies among patients:
- Mild cases: Subtle changes in eye appearance
- Moderate cases: Noticeable bulging and discomfort
- Severe cases: Significant protrusion affecting vision and eye closure
Your eye specialist measures the extent of protrusion using a specialized tool called an exophthalmometer, which helps track the progression of the condition and determine appropriate treatment options.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Exophthalmos
The symptoms of exophthalmos present distinct visual and physical changes that affect your daily life. You’ll notice these key indicators:
Primary Visual Changes:
- Noticeable bulging of one or both eyes
- Double vision (diplopia)
- Blurred or reduced vision
- Light sensitivity (photophobia)
Physical Discomfort:
- Pressure sensation behind the eyes
- Eye pain or irritation
- Excessive tearing
- Dry, gritty feeling in eyes
- Difficulty closing eyelids completely
Additional Signs:
- Redness in the whites of eyes
- Swelling around the eyelids
- Visible white area above or below iris
- Eye movement restrictions
- Corneal exposure
These symptoms can range from mild to severe, impacting your vision and comfort levels. A single symptom might not indicate exophthalmos, but experiencing multiple signs warrants immediate medical attention. Early recognition plays a crucial role in preventing potential complications like corneal damage or vision loss.
Your eye doctor can measure the degree of eye protrusion using specialized tools, helping determine the severity of your condition. Regular monitoring of these symptoms helps track disease progression and treatment effectiveness.
Understanding the Causes Behind Exophthalmos
The primary cause of exophthalmos is dysfunction of the thyroid gland, with Graves’ disease being the leading cause. This autoimmune condition causes the body’s immune system to attack its own tissues, resulting in:
- Inflammation of orbital tissues
- Swelling of eye muscles
- Accumulation of fat behind the eyes
In hyperthyroidism, the overproduction of hormones by the thyroid creates a chain reaction, causing the soft tissues around the eyes to swell and push the eyeballs forward.
Other Medical Conditions That Can Cause Exophthalmos
Several other medical conditions can also trigger exophthalmos:
Inflammatory Conditions
- Orbital pseudotumor
- Orbital cellulitis
- Wegener’s granulomatosis
Space-Occupying Lesions
- Orbital tumors
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis
- Metastatic cancer
Developmental Issues
- Shallow eye sockets
- Craniosynostosis
- Orbital bone abnormalities
Special Considerations for Children
Children with exophthalmos require special attention, as their causes often differ from adults. Pediatric cases might stem from:
- Neuroblastoma
- Orbital hemangioma
- Congenital orbital cysts
Importance of Identifying the Underlying Cause
Identifying the exact cause is crucial for proper treatment, as each underlying condition requires specific medical approaches. Your healthcare provider will conduct targeted tests based on your symptoms and medical history to determine the root cause.
Diagnosing Exophthalmos: Tests and Procedures Used
Accurate diagnosis of exophthalmos requires a comprehensive series of medical tests and specialized procedures. Your healthcare provider will typically start with a physical examination to assess the degree of eye protrusion and related symptoms.
Blood Tests
Your doctor may order the following blood tests:
- Thyroid Function Tests (TFT) measure levels of T3, T4, and TSH hormones
- Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulin (TSI) detects specific antibodies
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) helps identify underlying infections
- Inflammatory markers assessment reveals active inflammation
Specialized Eye Measurements
The exophthalmometer plays a crucial role in diagnosis. This precision instrument:
- Measures the forward displacement of your eyes from the orbital rim
- Provides numerical values to track progression
- Helps determine the severity of the condition
- Creates baseline measurements for future comparisons
Advanced Imaging Studies
Your doctor might recommend additional tests:
- CT scans reveal orbital tissue changes and muscle inflammation
- MRI shows detailed soft tissue involvement
- Ultrasound helps evaluate eye muscle thickness
These diagnostic tools create a detailed picture of your condition, enabling healthcare providers to develop targeted treatment strategies. The combination of test results helps determine the underlying cause and extent of exophthalmos, guiding appropriate medical interventions.
Exploring Treatment Options for Exophthalmos
Treatment for exophthalmos targets both the underlying causes and immediate symptom relief. Your healthcare provider will create a personalized treatment plan based on the severity of your condition and its root cause.
Medical Treatments
- Antithyroid medications to regulate thyroid hormone production
- Corticosteroids administered orally or intravenously to reduce orbital inflammation
- Immunosuppressive drugs for severe cases resistant to standard treatments
Supportive Care Measures
- Artificial tears and lubricating ointments to combat dry eyes
- Prism glasses to correct double vision
- Protective shields during sleep to prevent corneal exposure
- Selenium supplements under medical supervision
- Elevation of the head during sleep to reduce fluid accumulation
Advanced Treatment Options
- Orbital radiotherapy to decrease inflammation in active thyroid eye disease
- Rituximab therapy for patients unresponsive to conventional treatments
- Teprotumumab, a targeted antibody therapy specifically designed for thyroid eye disease
Surgical Interventions
- Orbital decompression surgery to create more space in the eye socket
- Strabismus surgery to realign eye muscles
- Eyelid surgery to improve eye closure and protection
Your treatment success depends on consistent adherence to prescribed medications and regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare team. Smoking cessation plays a crucial role in treatment effectiveness, particularly for patients with thyroid-related exophthalmos.
Taking Preventive Measures Against Exophthalmos
Preventing Exophthalmos starts with understanding your risk factors and taking proactive steps to minimize them. Smoking cessation stands as the most crucial preventive measure you can take. Research shows that smokers face a significantly higher risk of developing severe eye complications related to thyroid disorders.
Here’s what you can do to reduce your risk:
- Stop smoking immediately – Smoking accelerates eye damage and reduces treatment effectiveness
- Regular thyroid screenings – Early detection of thyroid abnormalities helps prevent eye complications
- Monitor eye changes – Track any changes in your vision or eye appearance
- Protect your eyes – Use UV-protective sunglasses to minimize eye strain
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle – Regular exercise and balanced nutrition support thyroid function
For individuals with existing thyroid conditions, these additional steps can help prevent Exophthalmos:
- Track thyroid medication compliance
- Attend scheduled endocrinologist appointments
- Document any eye-related symptoms
- Avoid exposure to secondhand smoke
- Stay hydrated to maintain eye moisture
Early intervention plays a vital role in preventing severe complications. When you notice subtle changes in your eyes or vision, seeking immediate medical attention can prevent the progression of Exophthalmos and protect your long-term eye health.
The Role of a Multidisciplinary Approach in Managing Exophthalmos Effectively
Managing Exophthalmos requires a coordinated effort from multiple healthcare specialists working together to create comprehensive treatment strategies. Your medical team typically includes:
- Ophthalmologists – These eye specialists monitor vision changes, assess eye muscle function, and perform necessary surgical interventions.
- Endocrinologists – They manage thyroid hormone levels and underlying autoimmune conditions.
- Orbital Specialists – These experts focus on the anatomy around the eyes and perform specialized procedures when needed.
- Primary Care Physicians – They coordinate care between specialists and manage overall health.
Each patient experiences Exophthalmos differently, requiring personalized treatment plans. Your healthcare team considers several factors:
- Disease severity and progression
- Presence of vision-threatening complications
- Individual response to treatments
- Quality of life impact
- Coexisting medical conditions
Regular communication between specialists ensures coordinated care delivery. Your treatment plan adapts as your condition changes, with specialists working together to:
- Adjust medication dosages
- Schedule timely interventions
- Monitor treatment effectiveness
- Address emerging complications
- Provide comprehensive follow-up care
This integrated approach maximizes treatment outcomes while minimizing potential complications. Your active participation in the treatment process helps your medical team make informed decisions about your care. Incorporating patient support strategies can further enhance this multidisciplinary approach by empowering you with knowledge and tools to manage your condition effectively.
Conclusion
Exophthalmos requires immediate attention and proactive management to prevent serious complications that can affect your vision and quality of life. The success of treatment depends on:
- Early Recognition: Quickly identifying symptoms like bulging eyes or vision changes
- Prompt Medical Care: Immediately consulting with healthcare providers
- Consistent Monitoring: Regular check-ups to track disease progression
- Active Patient Participation: Following prescribed treatments and lifestyle changes
Your dedication to treatment, along with expert medical guidance, forms the basis for successfully managing exophthalmos. The collaboration between specialists ensures you receive targeted care for both the underlying condition and its eye-related effects.
Remember: Each case of exophthalmos presents unique challenges, requiring personalized treatment approaches. By staying informed about your condition and maintaining open communication with your healthcare team, you increase your chances of achieving the best outcomes and preserving your eye health.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is Exophthalmos and how does it affect eye health?
Exophthalmos is a condition characterized by the abnormal protrusion or bulging of the eyes, commonly associated with thyroid-related diseases such as Graves’ disease. It impacts eye health by causing symptoms like eye discomfort, dryness, and potential vision problems, making early diagnosis and treatment crucial.
What are the common symptoms of Exophthalmos to watch for?
Common symptoms of Exophthalmos include noticeable bulging of the eyes, sensitivity to light (photophobia), double vision, and eye irritation. Recognizing these signs early is important for timely medical evaluation and management.
What causes Exophthalmos and which conditions are most commonly involved?
Exophthalmos primarily results from thyroid gland problems, especially autoimmune disorders like Graves’ disease that lead to inflammation around the eyes. Less frequently, tumors or infections near the eye socket can also cause eye bulging.
How is Exophthalmos diagnosed by healthcare professionals?
Diagnosis of Exophthalmos involves blood tests to assess thyroid hormone levels and detect autoantibodies, along with imaging studies. An exophthalmometer, a specialized tool, is used to measure the degree of eye protrusion accurately.
What treatment options are available for managing Exophthalmos?
Treatment focuses on controlling underlying thyroid issues using antithyroid medications or corticosteroids to reduce inflammation. Supportive care such as lubricating eye drops and prism glasses can alleviate symptoms. In some cases, individualized multidisciplinary care plans are developed for optimal outcomes.
How can one prevent Exophthalmos or reduce its risk?
Preventive measures include lifestyle modifications like quitting smoking, which lowers the risk of developing Exophthalmos. Early detection and timely treatment of thyroid disorders also play a vital role in preventing complications associated with severe eye bulging.
