The results of pelvic ultrasound and POP-Q inconsistent?
Pelvic ultrasound is an examination that many mothers have done, but many people cannot understand the content above. Let me first briefly introduce the division of the three chambers of pelvic color ultrasound.
The female pelvic floor is composed of pelvic organs, pelvic floor muscles , fascia, ligaments and other soft tissue structures. In order to better judge and describe pelvic floor injuries, the concept of “three chambers” was proposed. The “three chambers” refers to dividing the pelvic floor into three chambers in the vertical direction: the anterior pelvic cavity. The middle pelvic cavity, and the posterior pelvic cavity.
Anterior chamber – anterior vaginal wall, urethra, bladder Middle chamber – vagina, cervix, uterus
Posterior chamber – perineum, posterior vaginal wall, anal canal and rectal ampulla
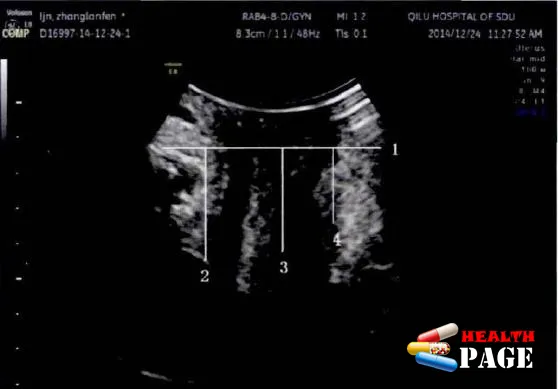
These are the results of two examinations done by the same women. The first one is the data of the POP-Q examination. The second one is the conclusion of the pelvic floor color ultrasound. Both examined the degree of protrusion and sagging, but the conclusions are inconsistent. Why is this so? This is a question that many women have.
Why are there inconsistent conclusions?
01. Different reference lines
The reference line selected by the clinical POP-Q quantitative evaluation system is the hymen edge. That is easily identifiable from external observation . The hymen edge is made of soft tissue. When negative pressure is increase or the anus is lifted, the position of the hymen will change slightly. Especially when the organ is prolapsed, the prolapsed organ will cause a greater change in the position of the hymen.
The reference line selected for pelvic floor ultrasound is the lower edge of the pubic symphysis. Which will not shift due to changes in abdominal pressure or pelvic floor muscle status. Slight shifts of the hymen edge and anatomical differences between different people can cause differences between the two measurement results.
02. Different landmarks
In the quantitative evaluation of POP-Q, Ba, C, and Bp represent the most obvious locations of prolapse of the anterior vaginal wall, cervix, and posterior vaginal wall. In the pelvic floor ultrasound system, the bladder neck, external cervical opening, and rectal ampulla are selected to represent the landmarks of the anterior, middle, and posterior pelvic cavities. From an anatomical point of view, the bladder neck, external cervical opening, and rectal ampulla are close to the locations of Ba, C, and Bp points.
By default, the bladder neck is equivalent to Ba, the external cervical opening is equivalent to C, and the rectal ampulla is equivalent to Bp. In fact, the landmarks used in POP-Q are not always well correlated with the actual position of the organs. Moreover, due to the anatomical differences between different subjects, the above landmarks may not be completely equivalent, which leads to the gap between POP-Q quantification and pelvic floor ultrasound measurement.
03. Limitations of POP-Q assessment
The POP-Q quantitative assessment system can only quantitatively assess the type and degree of prolapse, but cannot clearly and specifically determine the type of pelvic prolapse . Only uterine prolapse in the middle pelvis can be directly manifested, while prolapse of other organs such as the bladder and rectum is indirectly manifested through prolapse of the anterior and posterior walls of the vagina.
The sagittal plane of pelvic floor ultrasound can clearly display the sonograms of each anatomical position, provide anatomical information of each cavity , clarify the type of prolapse, and evaluate the degree of prolapse, providing richer information.
For patients with early pelvic floor muscle relaxation but no obvious rectal prolapse, clinical POP-Q cannot make a diagnosis and classification. However, pelvic floor ultrasound can show that the tension position of organs with increased mobility but not yet prolapse has become slightly depressed.
04. Check for interference from equipment
When evaluating with the POP-Q system, a speculum is needed to expose the vagina in order to clearly identify the position and changes of various organs. The speculum can cause deformation of the soft tissue to a certain extent . Discomfort may affect the quality of the subject’s Valsalva maneuver, which may fail to reflect the most natural state of the organs and may even stimulate the contraction of the levator ani muscles, resulting in a false negative.
During pelvic floor ultrasound examination, the probe needs to be close to the perineum to reduce the impact of bubbles between the two. But the force needs to be controlled. Excessive pressure on the perineum by the probe will affect the descent of the organs. Therefore, whether it is clinical examination or pelvic floor ultrasound examination, there will be influence caused by human factors.
After a long discussion, we can draw the following conclusion:POP-Q has its limitations. It only evaluates the degree of pelvic organ prolapse, but cannot evaluate in detail whether the pelvic floor muscles are loose and torn , whether
the fascia and primary band structures are intact, and there is a lack of corresponding evaluation standards and systems for the patient’s pelvic floor function. In addition, POP-Q evaluation also has a certain false negative rate.Pelvic color ultrasound can clearly and intuitively display the location of pelvic organs and the structure of the support system, making up for the shortcomings of the POP-Q system. Therefore,
when the conclusions of the two reports conflict, it is best to use pelvic color ultrasound as the standard.
In fact, in most cases, the conclusions of pelvic floor color ultrasound and POP-Q assessment are basically consistent, and the two have a good correlation. When any report shows abnormalities, it should attract everyone’s attention.
Several issues regarding common pelvic ultrasound problems
01. How to determine the specific degree of sagging through pelvic ultrasound data?
At present, there is no clear standard for pelvic floor ultrasound diagnosis in my country. Ruchu has checked a lot of information and compared the color Doppler ultrasound data of many mothers. It is found that even if the sagging organs are located at the same position of the pubic symphysis reference line, the conclusion of sagging may still be inconsistent. I hope that the standard can be unified and improved as soon as possible.
02. What does the area of the levator ani hiatus represent?
The pelvic floor muscles play a very important role in maintaining the pelvic organs, and the most important of the pelvic floor support structures is the levator ani muscles . The levator ani muscles are a complex muscle group, including three main muscle bundles: the pubococcygeus muscle , the iliococcygeus muscle, and the ischiococcygeus muscle.
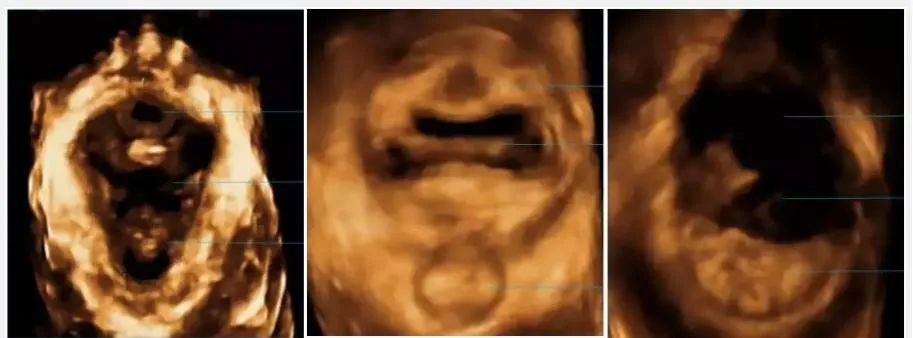
When the anal levator muscle is abnormal, the pelvic organs will be out of their normal anatomical position, and pelvic organ prolapse will occur. Studies have shown that the severity of pelvic organ prolapse is positively correlated with the area of the anal levator muscle hiatus. The anal levator muscle hiatus is an important indicator for measuring the state of the pelvic floor.
03. Why choose the lower edge of the pubic symphysis reference line as the reference value?
① The pubic symphysis is a bony structure with a fixed position. It will not change position during the tension period and anal contraction period. It can help locate the position of the pelvic floor organs and measure their mobility.
② The pubic symphysis is easy to identify in ultrasound. With obvious visualization and strong echoes accompanied by acoustic shadows at the back. Making it easier to make an accurate judgment.
Do you understand all the above? The examination results are important, but after bulging and sagging. The most important thing is to stick to Kegel exercises and pelvic floor repair treatment . Your health is in your hands~
Recover as before, I wish all postpartum mothers to recover as before~
