
What is gout , symptoms and cause
Many people may not know much about gout. In fact, gout is a very harmful disease, and in severe cases it will affect people’s normal activities. Therefore, we need to find the cause in time and prevent gout from the cause. So first of all, we need to understand what gout is and what causes gout.
There is a substance called purine in the human body, which can cause gout after metabolic disorders. After a series of metabolic changes, purine finally forms uric acid. Uric acid has no physiological function in the human body. Under normal circumstances, 2/3 of the uric acid produced in the body is excreted from the kidneys and 1/3 is excreted from the large intestine.
Uric acid is constantly produced and excreted in the human body, so it maintains a certain concentration in the blood.
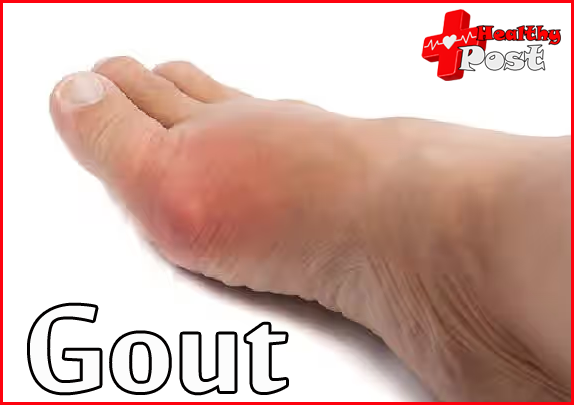
The uric acid content in 100 ml of blood of a normal person does not exceed 6 mg, while that of a woman does not exceed 5 mg. In the process of decomposition and synthesis of purine, due to congenital abnormalities of enzymes or some unclear factors, metabolic disorders, increased synthesis or decreased excretion of uric acid lead to hyperuricemia. When the blood uric acid concentration is too high, uric acid is deposited in the joints, soft tissues, cartilage and kidneys in the form of sodium salts, causing foreign body inflammatory reactions in tissues and becoming the root cause of gout.
What other symptoms does gout have besides joint pain?
There are about 355 million arthritis patients in the world. There are more than 100 million arthritis patients in my country, with an incidence rate of about 13%. Arthritis is the world’s number one disabling disease. Please take care of your joint health and prevent disease-induced disability!
Many people think that gout is just joint pain, so they take a few painkillers when the joints hurt, and ignore the disease when it doesn’t hurt. However, as a metabolic disease, it is only the most easily discovered symptom of joint pain, and there are many other hazards that are “hidden”!
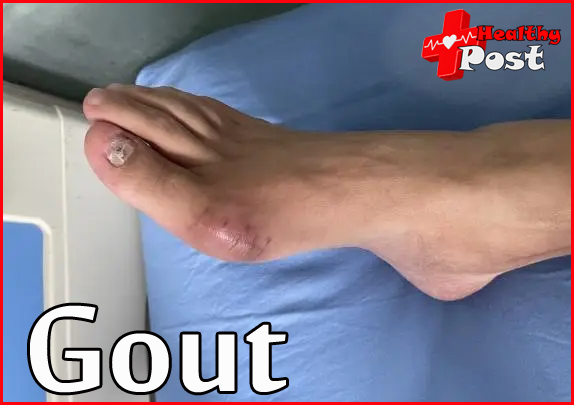
1. The harm of gout – tophi
It is based on high uric acid. Long-term high uric acid levels will cause uric acid to deposit in the form of monosodium urate crystals in cartilage, joint cavities, tendons and other soft tissues, forming tophi over time. Tophi mainly appear in affected joints, cartilage, bursae, tendons, ligaments and soft tissues, and can cause persistent joint swelling and pain, toothache, deformity and dysfunction. Severe subcutaneous tophi can lead to skin ulceration, infection and even sepsis. Severe joint tophi can lead to joint bone destruction, loss of function and disability.
2. The harm of gout – gouty nephropathy
Hyperuricemia is closely related to kidney damage, because the kidney is the main channel for uric acid to be excreted from the body. When uric acid is high, the corresponding uric acid concentration in the kidney is also high, which naturally easily causes kidney damage. A major manifestation of kidney damage in patients with hyperuricemia is uric acid kidney stones, which can cause low back pain and hematuria. Stone blockage can also cause fever, oliguria, anuria, hydronephrosis, etc. Many gout patients already have uric acid kidney stones before gout attacks. In addition, hyperuricemia can also lead to acute and chronic kidney damage. For every 60 micromoles per liter increase in blood uric acid, the risk of kidney disease increases by 7% to 11%.

3. The harm of gout – metabolic syndrome
Hyperuricemia, hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and hyperlipidemia belong to the same metabolic syndrome and share a common basis – insulin resistance. These metabolic diseases are “in cahoots” with each other, and suffering from one will increase the incidence of the others. Therefore, patients with hyperuricemia are more likely to suffer from the “three highs” than the average person.
4. The harm of gout – cardiovascular disease
In addition to increasing the risk of metabolic diseases, hyperuricemia and gout also increase the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Excessively high blood uric acid levels will aggravate oxidative stress, damage endothelial function, and accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis. For every 60 micromoles per liter increase in blood uric acid levels, the mortality rate of coronary heart disease increases by 30% in women and 17% in men. In addition, hyperuricemia can also promote the occurrence of cerebral infarction, increase the mortality and recurrence rate of cerebral infarction, and is an independent risk factor for stroke.
After reading this, will you still ignore the harm of gout? For those with it, even if your joints don’t hurt, you should pay attention to it, manage the disease well, and keep uric acid within the target range, so as to minimize the damage of high uric acid to the body!
What causes gout?
The current mainstream theory holds that gout is mainly caused by urate accumulation in the joints, and the related influencing factors can generally be divided into two types: controllable and uncontrollable: Controllable factors: Drinking: Alcoholic beverages contain purine, which increases the risk of gout. Among them, the purine content of beer and rice wine is much higher than that of other alcoholic beverages, and has a higher risk of disease than other alcoholic beverages. Eating habits: High-purine foods will increase the risk of gout, including animal offal, seafood, fish eggs, thick soup and gravy. Recent studies have also pointed out that high sugar (such as carbonated drinks and fructose) can also cause gout.
Vitamin C, coffee and dairy products may help prevent the occurrence of gout. Obesity: Obesity can cause an increase in uric acid concentration and induce gout. Exercise: Exercise can promote uric acid excretion, but strenuous exercise can cause an increase in uric acid concentration, increasing the risk of gout. Uric acid concentration: Lack of water in the body can lead to excessive uric acid concentration, increasing the risk of gout. Mental factors: Increased mental stress and excessive fatigue can also lead to endocrine disorders, abnormal uric acid metabolism, increased uric acid concentration, and gout. Low temperature environment: Urate is more likely to precipitate into crystals in a low temperature environment, deposit around the joints, and cause arthritis attacks.
This is also one of the reasons why gout is prone to attack at night. Uncontrollable factors: Age: It usually occurs after the age of 40, and the risk of gout increases with age. Gender: Women generally do not develop gout before the age of 50 because estrogen inhibits the formation of uric acid; but the incidence rate increases after menopause.
Family history
People with a family history of gout have a higher incidence rate. Other diseases: Reduced uric acid excretion caused by kidney disease or certain drugs, increased uric acid production caused by myeloproliferative diseases and tumor chemotherapy, etc., may induce it. However, the above are only possible influencing factors. A warrior who drinks a beer at a night snack stall does not necessarily get it, and a fish farmer who is keen on health preservation may not be able to pass the test safely.

2 thoughts on “What is gout , symptoms and cause”