What Is Sonography and Its Benefits: The Ultimate Guide
Sonography, also known as ultrasonography, is a valuable imaging technique used in the medical field to diagnose and monitor various conditions. By using high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound), sonography allows healthcare professionals to see moving pictures of organs, tissues, and blood flow inside the body without surgery.
In this article, we will explore the many benefits of sonography and understand why it is considered an essential tool in healthcare. Accurate and timely diagnosis is crucial in medical treatment, and sonography plays a significant role in achieving this by providing detailed information about the body’s internal structures.
Advantages of Sonography
Sonography offers several advantages over other imaging techniques, making it a preferred choice for many medical professionals:
- Noninvasive: Sonography does not require any incisions or punctures, minimizing the risk of complications or infections.
- Safe: Unlike X-rays or CT scans that use ionizing radiation, sonography uses harmless sound waves, making it safe for repeated use.
- No radiation exposure: It does not involve exposure to ionizing radiation like X-rays or CT scans.
- Suitable for pregnancy: Sonography is particularly suitable for monitoring fetal development during pregnancy without posing any harm to the mother or the baby.
These advantages make sonography a versatile and widely used imaging technique in various medical scenarios.
Importance of Sonography in Medical Diagnosis

By capturing real-time images, sonography allows doctors to identify problem areas and detect abnormalities in different parts of the body. This helps in diagnosing diseases such as liver diseases or detecting anomalies during pregnancy. Sonography can also be used to assess organ function and guide biopsy procedures accurately.
Overall, sonography has revolutionized medical diagnosis and has become an essential tool for healthcare professionals worldwide. In the following sections, we will explore:
- How sonography works
- The process of conducting a sonography exam
- Its applications in various medical fields
- Advancements in ultrasound technology
- Why sonography continues to play a crucial role in modern medical practice.
How Does Sonography Work?
Sonography, also known as ultrasonography, uses high-frequency sound waves called ultrasound or ultrasonic waves to create images inside the body. Here’s how it works:
- Transmission: The sound waves are emitted from a device called a transducer and directed into the body.
- Reflection: As the sound waves travel through the body, they bounce off different tissues and organs.
- Reception: The transducer detects the reflected waves and converts them into electrical signals.
- Processing: These electrical signals are processed by a computer to generate visual images on a screen.
To better understand this concept, think of ultrasound waves like echoes bouncing off walls. Just as echoes help you perceive the layout of a room without seeing it, ultrasound waves provide valuable information about the internal structures of the body.
Key components of a sonography machine include:
- The diagnostic ultrasound unit: This unit generates and receives ultrasound waves.
- The transducer: It acts as both a transmitter and receiver of these waves.
These two components work together to perform sonography exams.
Understanding how sonography works is essential in recognizing its significance in modern medicine. It offers healthcare professionals:
- Non-invasive imaging: Unlike procedures such as surgery or X-rays, sonography doesn’t require any incisions or exposure to radiation.
- Real-time visualization: Sonography provides immediate images, allowing doctors to observe dynamic processes in the body as they happen.
- Diagnostic accuracy: By providing detailed images of internal structures, sonography helps in identifying various medical conditions accurately.
With its many advantages, sonography plays a vital role in enhancing patient care and improving outcomes across different medical specialties.
The Process of Conducting a Sonography Exam
Sonography is a collaborative process that involves different medical professionals working together to ensure accurate diagnosis and interpretation of sonographic images. Let’s explore the roles and responsibilities of these professionals and the step-by-step process of conducting a sonography exam.
Roles and Responsibilities
- Sonographers: Sonographers are highly trained healthcare professionals who specialize in performing sonography exams. They are responsible for preparing the patient, operating the sonography equipment, and capturing high-quality images. Sonographers play a crucial role in ensuring patient comfort and safety during the exam. [^1^]
- Radiologists: Radiologists are medical doctors who specialize in interpreting medical images, including sonographic images. They work closely with sonographers to analyze the captured images and provide accurate diagnoses. Collaboration between sonographers and radiologists is essential for effective communication and optimal patient care. [^2^]
Teamwork and Communication
Teamwork and communication are vital in the field of sonography to ensure accurate interpretation of sonographic images. Close collaboration between sonographers and radiologists allows for comprehensive evaluation of the images, leading to precise diagnoses. Effective communication between team members helps streamline the diagnostic process and ensures timely reporting of results to patients and referring physicians. [^3^]
Step-by-Step Guide
Here is a general outline of how a typical sonography exam is conducted:
- Patient Preparation: The patient is positioned appropriately, depending on the area of the body being examined. Gel is applied to the skin to help transmit ultrasound waves.
- Transducer Placement: The sonographer places a handheld device called a transducer on the patient’s skin, which emits ultrasound waves into the body.
- Image Acquisition: The transducer is moved over the area of interest, capturing real-time images on a monitor. The sonographer adjusts settings such as depth, gain, and focus to optimize image quality.
- Image Evaluation: While performing the exam, the sonographer evaluates the images in real-time to ensure all necessary anatomical structures are adequately visualized.
- Documentation: The sonographer may document relevant findings and measurements for future reference and collaboration with the radiologist.
- Radiologist Interpretation: The sonographic images are then reviewed by a radiologist, who provides an expert analysis and diagnosis based on the findings. [^2^]
Contrast-Enhanced Sonography
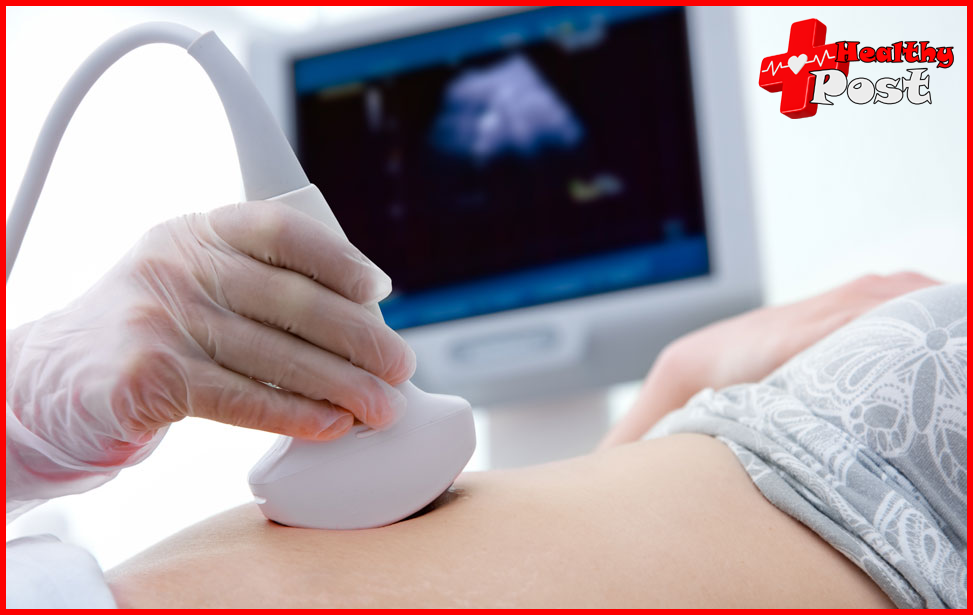
In certain cases, contrast agents may be used during a sonography exam to enhance visualization of blood flow or specific tissues. Contrast-enhanced sonography involves the injection of a contrast agent into a vein, which helps differentiate between normal and abnormal structures. This technique is particularly useful in assessing liver lesions, evaluating organ perfusion, and detecting tumors. [^4^]
By following this step-by-step process and utilizing contrast-enhanced techniques when necessary, sonographers and radiologists can work together effectively to provide accurate diagnoses and contribute to optimal patient care.
[^1^]: Professional Practice Standards Online [^2^]: Collaborative practice in diagnostic imaging: a joint guideline of the Canadian Association of Radiologists and Canadian Association of Radiology Technologists [^3^]: [Teamwork in healthcare: Key discoveries enabling safer,
Applications of Sonography in Medical Field
Sonography has a wide range of applications in the medical field, making it an invaluable tool for healthcare professionals. In this section, we will explore some of the specific areas where sonography is commonly used:
Obstetrics and Gynecology
One of the most well-known applications of sonography is in monitoring fetal development during pregnancy. Sonograms, or ultrasound images, allow healthcare providers to visualize the growth and well-being of the fetus. Some specific uses of sonography in obstetrics and gynecology include:
- Confirming Pregnancy: Sonography can confirm the presence of a viable pregnancy by detecting a gestational sac or fetal heartbeat.
- Determining Gestational Age: By measuring specific fetal structures, such as the crown-rump length, sonography can accurately estimate gestational age.
- Monitoring Fetal Growth: Regular ultrasound exams throughout pregnancy help assess the growth and development of the fetus. This is especially important in identifying any potential abnormalities or growth restrictions.
- Identifying Birth Defects: Sonography plays a crucial role in detecting various birth defects, such as heart abnormalities, neural tube defects, and cleft lip/palate. Early detection allows for appropriate medical interventions and treatment planning.
- Assessing Placental Health: Sonography helps evaluate the position and health of the placenta, which is essential for monitoring maternal-fetal well-being.
One significant advantage of ultrasonography in obstetrics and gynecology is that it is non-invasive and safe for both the mother and the baby. Unlike other imaging techniques that use ionizing radiation, such as X-rays or CT scans, ultrasound relies on harmless sound waves to create images.
Diagnostic Medicine
Sonography is widely used as a diagnostic tool in various medical specialties. It provides valuable information about different organs and tissues, aiding in the diagnosis and management of diseases. Some common diagnostic applications of sonography include:
- Liver Disease Detection: Sonography is highly effective in assessing liver health, detecting conditions such as fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, and liver tumors. It is often used as an initial imaging modality when evaluating patients with suspected liver abnormalities.
- Guiding Biopsy Procedures: Sonography-guided biopsies enable precise targeting of suspicious areas within organs. This minimally invasive technique allows for accurate tissue sampling, aiding in the diagnosis of cancers and other diseases.
- Evaluation of Kidney Function: Sonography plays a crucial role in assessing kidney health and function. It can detect kidney stones, cysts, tumors, and other abnormalities that may affect renal function.
- Thyroid Imaging: Sonography is commonly used to evaluate thyroid nodules and other thyroid disorders. It helps determine the size, characteristics, and vascularity of the nodules, assisting in the diagnosis and management of thyroid diseases.
One notable advantage of sonography in diagnostic medicine is its patient-friendly nature. It is a painless procedure that does not require any injections or exposure to ionizing radiation. This makes sonography suitable for patients of all ages, including children and pregnant women.
Organ Function Assessment
Sonography offers unique advantages when it comes to assessing organ function in real-time. While other imaging modalities like MRI scans provide detailed anatomical images, sonography provides dynamic images that show organ movement and blood flow. Some examples include:
- Cardiac Ultrasound (Echocardiography): Sonography is used to evaluate heart structure and function. Echocardiograms provide valuable information about heart chambers, valves, and blood flow patterns. This helps diagnose various cardiac conditions like heart failure, valve disorders, and congenital heart defects.
- Vascular Ultrasound: Sonography is used to assess blood flow within blood vessels and identify any abnormalities or blockages. It plays a vital role in diagnosing conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), peripheral artery disease (PAD), and carotid artery stenosis.
- Musculoskeletal Imaging: Sonography is often used to evaluate soft tissue structures like tendons, ligaments, and muscles. It helps diagnose conditions such as tendonitis, muscle tears, and joint abnormalities.
In comparison to other imaging modalities like MRI scans, sonography offers the advantage of real-time imaging. This allows healthcare providers to observe organ function and make immediate assessments during procedures or interventions.
Sonography’s versatility and non-invasive nature make it an invaluable tool in various medical specialties. Its ability to provide detailed images and real-time assessments contributes to accurate diagnosis, effective treatment planning, and improved patient outcomes. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in ultrasound technology, expanding its role in modern medical practice.
Diagnostic Medicine
Sonography plays a crucial role in diagnostic medicine beyond its applications in obstetrics and gynecology. It is commonly used across various medical specialties for diagnosis and evaluation. Some key points to consider in this section include:
1. Detection of Liver Diseases
Sonography is widely used to detect liver diseases, such as fatty liver, cirrhosis, and liver tumors. The non-invasive nature of ultrasound exams makes it a preferred choice for evaluating liver health without the need for invasive procedures.
2. Guiding Biopsy Procedures
Sonography is also utilized to guide biopsy procedures. By using real-time ultrasound imaging, medical professionals can precisely target the area for biopsy, ensuring accurate and effective tissue sampling.
3. Painless Ultrasound Techniques
Unlike certain diagnostic methods that may cause discomfort or require sedation, sonography offers painless techniques for patients. This patient-friendly approach enhances the overall experience and compliance with diagnostic procedures.
In addition to these applications, sonography continues to evolve in the field of diagnostic medicine, offering innovative solutions for accurate and non-invasive diagnosis across diverse medical conditions.
Assessing Organ Function with Sonography
Sonography, also known as ultrasound imaging, is a versatile diagnostic tool used in various medical fields to assess organ function. Unlike other imaging techniques like MRI scans, sonography offers unique advantages that make it particularly useful for evaluating how organs are working.
How Sonography Compares to MRI Scans
To understand why sonography is preferred for organ function assessment, let’s compare it to MRI scans:
- Real-time Assessment: Sonography provides immediate feedback on organ function in real time, allowing doctors to monitor changes as they happen. This is especially beneficial for dynamic organs like the heart or digestive system. In contrast, MRI scans produce detailed images but lack the ability to show ongoing activity.
- Wide Application: Sonography is widely used across different medical specialties due to its versatility and accessibility. It can be performed at the bedside or in outpatient settings, making it convenient for both patients and healthcare providers. On the other hand, MRI scans are typically conducted in specialized radiology departments, which may limit their availability.
- Patient Comfort: Sonography is a non-invasive procedure that involves no radiation or injections, making it comfortable and safe for patients of all ages. In comparison, some MRI scans may require the use of contrast agents or even invasive techniques like biopsies.
- Cost Considerations: Sonography is generally more cost-effective than MRI scans, making it a practical choice for routine monitoring and assessment of organ function. This affordability factor can be crucial, especially when repeated examinations are necessary.
Applications of Sonography in Medicine
Sonography finds extensive use in various medical specialties for diagnosing conditions and evaluating organ health:
1. Gastroenterology
In gastroenterology practice, ultrasonography helps with:
- Assessing liver and gallbladder function
- Detecting abnormalities or masses in the abdomen
- Guiding biopsy procedures for accurate diagnosis
2. Cardiology
Cardiologists rely on a specialized form of sonography called echocardiography to:
- Evaluate heart function and structure
- Detect abnormalities such as valve defects or fluid accumulation around the heart
- Monitor the effectiveness of treatments like medication or surgery
3. Urology
Sonography plays a crucial role in urology by assisting in:
- Assessing kidney function and identifying any signs of damage or blockage
- Detecting urinary tract abnormalities or stones
- Guiding minimally invasive procedures like nephrostomy tube placement or kidney stone removal
4. Obstetrics and Gynecology
In women’s health, ultrasonography is invaluable for:
- Monitoring fetal growth and development during pregnancy
- Detecting any complications or abnormalities in the uterus or ovaries, such as cysts or fibroids
- Guiding procedures like amniocentesis or fetal blood sampling when needed
The Benefits of Sonography for Organ Function Assessment
When compared to MRI scans, sonography stands out as a valuable tool for assessing organ function due to its specific advantages:
- Real-time Imaging: Sonography allows for dynamic visualization of organ function in real time, enabling immediate assessment and diagnosis. 2
The Advantages and Benefits of Choosing Sonography
Advancements in Ultrasound Technology
Technology is constantly improving, and this applies to the field of sonography as well. There are several exciting developments happening in ultrasound technology that are shaping the future of healthcare:
- Portable and Wearable Devices:
- Portable ultrasound devices have completely changed the game in healthcare. They allow medical professionals to perform ultrasonography exams right where the patient is, whether it’s in a remote location, an ambulance, or even at someone’s home. These portable devices not only make medical imaging more accessible but also help with faster diagnoses and treatments.
- Point-of-Care Devices:
- Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) devices are becoming more and more popular because they are versatile and easy to use. These handheld devices empower healthcare providers in different fields to see inside the body during physical exams, which leads to quicker decisions and better outcomes for patients.
- Future Trends:
- There are exciting possibilities for ultrasound technology in the future. Ongoing research is focused on improving image quality, expanding what we can diagnose using ultrasound, and using artificial intelligence to analyze images automatically. Additionally, scientists are also working on creating new types of ultrasound probes and better ultrasound gel to make the whole process even better for patients.
- According to an article exploring the future of ultrasound, there are five key trends to watch out for in the coming years. These trends include further advancements in image quality, expanded diagnostic capabilities, increased use of artificial intelligence in analysis, development of new ultrasound probes, and improvements in ultrasound gel.
In summary, ultrasound technology is constantly evolving and changing how medicine is practiced. It’s making medical imaging more accessible, faster, and more accurate than ever before. As these advancements continue, it’s important for healthcare professionals to stay updated with the latest trends and take advantage of the potential benefits.
Continued Relevance of Sonography in Modern Medical Practice
The continued evolution of ultrasonography in modern medical practice is a testament to its enduring significance. As technology advances, ultrasonography continues to play a pivotal role in various medical specialties, ensuring accurate diagnosis and effective patient care. To remain abreast of the latest developments in this field, it is crucial for healthcare professionals to stay informed and engaged.
Key Factors Contributing to the Continued Relevance of Sonography
Here are some key factors that contribute to the continued relevance of sonography in modern medical practice:
- Ultrasound Gel: The use of specialized gels enhances the quality of sonographic images, ensuring better accuracy in diagnosis. These gels facilitate the transmission of ultrasound waves, resulting in clearer and more detailed images for interpretation.
- Point-of-Care Devices: The emergence of point-of-care ultrasound devices has revolutionized medical practice by providing immediate insights at the patient’s bedside. This expedites decision-making processes and enhances the overall quality of patient care.
- Future Trends: The future holds promising trends for ultrasonography, including advancements in portable and wearable ultrasound devices. These innovations are poised to further expand the reach of ultrasonography, enabling remote healthcare delivery and improving accessibility to diagnostic imaging.
The sustained relevance of ultrasonography underscores its indispensable role in modern medical practice. By embracing ongoing advancements and innovations, healthcare professionals can harness the full potential of ultrasonography for delivering exceptional patient care across diverse medical specialties.

