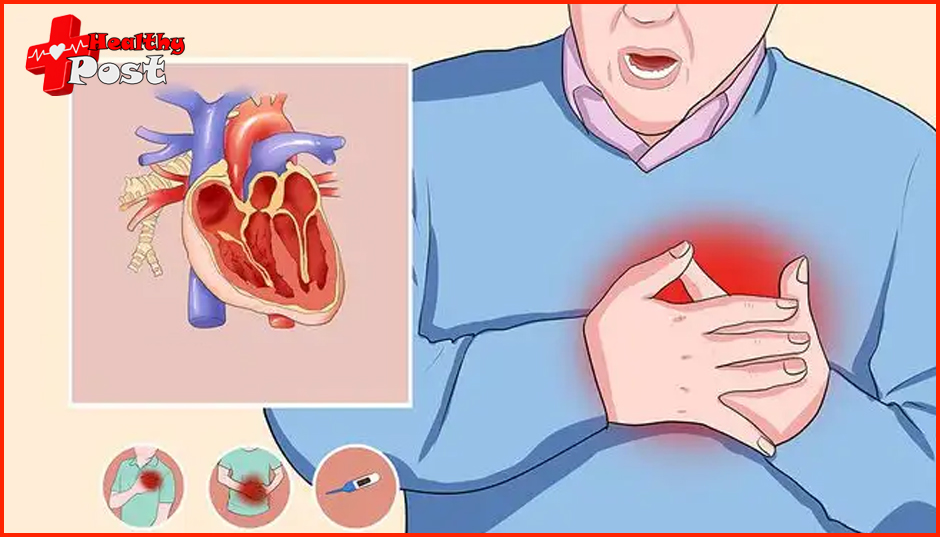
What is the most obvious sign of myocardial ischemia?
Myocardial ischemia is a pathophysiological state cause by insufficient blood and oxygen supply to the heart due to coronary artery stenosis, spasm or embolism.
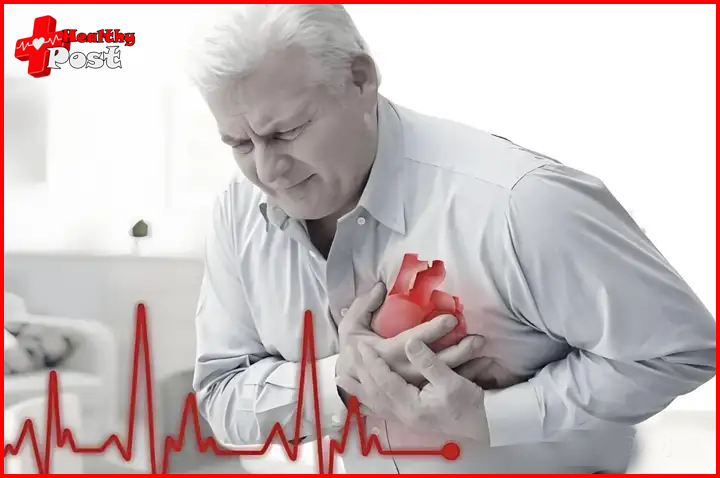
When the coronary arteries are diseased, the blood supply to the myocardium may be drastically reduced, or when the heart beats faster, causing the myocardial oxygen consumption to increase, if the coronary arteries cannot provide enough blood to the myocardium for oxygen supply, myocardial ischemia will occur.The root cause of myocardial ischemia is that
The blood and oxygen supply to the myocardium by the coronary arteries cannot meet the myocardial demand for oxygen. The specific causes can be divide into two categories:
insufficient coronary blood supply and abnormal increase in myocardial oxygen consumption, generally the main cause is insufficient blood supply. Common causes include
coronary heart disease, syndrome X, coronary artery spasm, myocardial bridge, arrhythmia, etc.
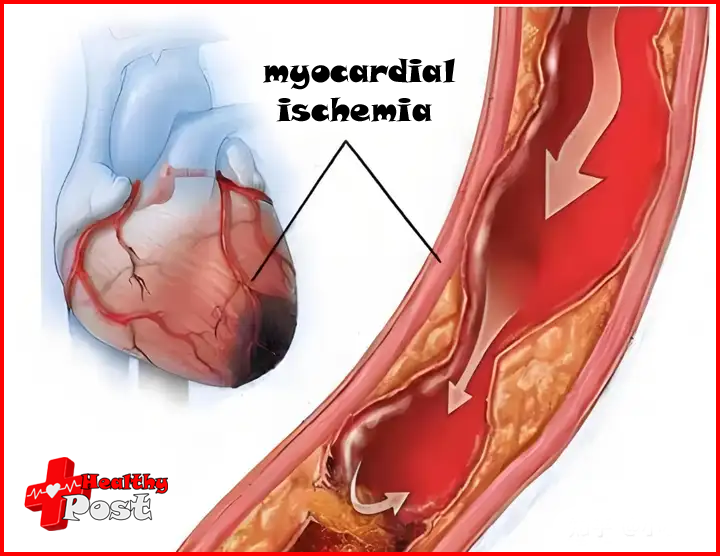
The clinical symptoms of myocardial ischemia are varied and may vary from individual to individual.
1. Chest pain: The most common symptom of myocardial ischemia is chest pain, which usually manifests as squeezing, tightening or stuffy pain, located behind the sternum or in the precordial area. The pain may radiate to the left shoulder and left upper arm, sometimes affecting most of the precordial area, and even the ring finger and little finger may have radiating pain. The pain usually lasts for 3-5 minutes and can be relieve after resting or taking nitroglycerin tablets. Chest pain may be accompanied by sweating and sometimes a fear of dying.
2. Chest tightness and shortness of breath: Patients with myocardial ischemia may feel chest tightness, palpitations, and shortness of breath, especially during physical activity or fatigue. These symptoms usually resolve on their own after rest.
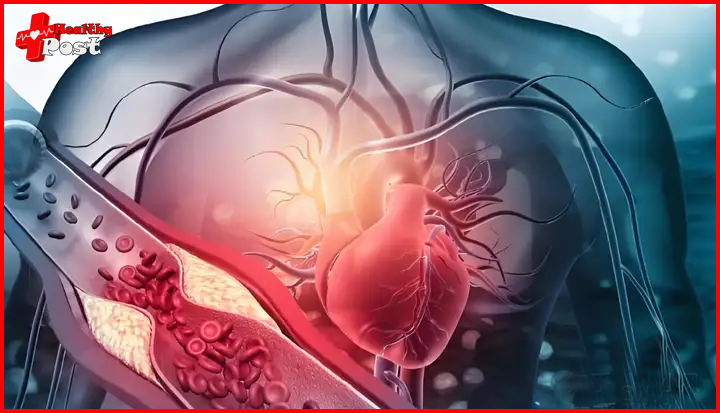
3. Pain in other parts of the body: Patients with myocardial ischemia may experience exercise-related headaches, toothaches, leg pains, etc., or pain in other parts of the body, such as the lower sternum, left precordial area, or upper abdomen.
4. Other symptoms: Patients with myocardial ischemia may also experience other symptoms, such as sudden bradycardia, low blood pressure or syncope .
The main goal of myocardial ischemia treatment is to improve myocardial blood supply and reduce myocardial oxygen consumption. Drug therapy is usually adopted, such as drugs to improve myocardial ischemia, relieve angina pectoris , and prevent myocardial infarction and death . For myocardial ischemia of different causes, interventional treatment or surgical treatment can be performed if the condition is serious. Prevention of myocardial ischemia is mainly to avoid the risk factors that cause myocardial ischemia, such as cold, excessive exercise, etc., improve bad living habits, and actively control the progression of coronary heart disease and related chronic diseases.
Drug recommendations for myocardial ischemia mainly include the following categories:
- Antiplatelet drugs : such as aspirin, ticagrelor, clopidogrel, etc. These drugs can inhibit platelet aggregation, prevent thrombosis, and thus relieve myocardial ischemia.
- Anti-myocardial ischemia drugs : such as nitroglycerin, isosorbide mononitrate, metoprolol, diltiazem , etc. These drugs can dilate coronary arteries, increase myocardial blood supply, reduce myocardial oxygen consumption, and thus improve myocardial ischemia symptoms.
- Lipid-lowering drugs : such as statins, atorvastatin, rosuvastatin , etc. These drugs can lower blood lipids, stabilize plaques, prevent plaque detachment and formation of blood clots, thereby delaying the progression of myocardial ischemia.
- Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB): such as benazepril, enalapril, telmisartan, valsartan , etc. These drugs can dilate blood vessels, lower blood pressure, reduce the burden on the heart, and thus improve myocardial ischemia.
The above drug recommendations are for reference only. Specific drug use should be based on the patient’s specific situation and the doctor’s advice.

