Atrial Fibrillation—10 Key Facts You Must Know
When it comes to a rapid heartbeat, many people’s first reaction is fear: “Is there something wrong with my heart?”
In fact, not all rapid heartbeats require panic.
Stress, anxiety, or even a few extra cups of coffee or wine can increase your heart rate.
But if your racing heartbeat is caused by atrial fibrillation (AFib), it’s something to take seriously.
Atrial fibrillation is a heart disease that affects millions of people and can have serious consequences if not controlled.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), one in seven strokes is related it.
Below, we will answer your frequently asked questions about atrial fibrillation in detail to help you fully understand this controllable heart disease.
1. Why is atrial fibrillation so dangerous?
It can cause the heart to lose its normal pumping function, which can cause two major problems.
On the one hand, it may cause symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, chest tightness and even difficulty breathing; on the other hand, the greater risk is that it will significantly increase the risk of stroke.
When the upper chambers of the heart (atria) lose their ability to contract normally due to fibrillation, blood can easily accumulate in the atria and form blood clots.
If these blood clots break off and travel to the brain, they can cause a severe stroke.
According to data, more than 450,000 people are hospitalized due to atrial fibrillation and 158,000 die from it in the United States alone each year.
2. How serious are the dangers of stroke?
According to research published in The Lancet, stroke is the second leading cause of death worldwide.
Strokes caused by atrial fibrillation are generally more severe and more likely to result in permanent disability or death.
3. What causes atrial fibrillation?
It is usually caused by damage or abnormalities in the heart muscle, which causes the heart’s electrical signals to become distorted, leading to an irregular heartbeat.
The following factors may be to blame:
hypertension
Coronary artery disease or heart attack
Heart valve abnormalities
Hyperthyroidism
Chronic exposure to stimulants, such as caffeine, tobacco, or alcohol
Sick sinus syndrome (heart “pacemaker” malfunction)
Sleep apnea
High-intensity physical activities, such as long-distance running, cycling, etc.
It is important to note that in some cases, the cause of atrial fibrillation may not be clear.
4. Does an accelerated heartbeat necessarily mean atrial fibrillation?
uncertain.
While it is one of the most common causes of an abnormal heartbeat, other arrhythmias can also cause your heart to beat faster, such as atrial flutter, supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), or ventricular tachycardia (VT).
If you often feel abnormal heartbeat, be sure to seek medical attention in time for an accurate diagnosis.
5. Can atrial fibrillation lead to heart failure?
The answer is yes.
It can cause the heart to work overloaded for a long time, eventually leading to heart failure.
Symptoms of heart failure include shortness of breath, fatigue, and leg edema.
If left untreated, heart failure can worsen and seriously affect your quality of life.
Doctors warn that controlling atrial fibrillation is the key to preventing heart failure.
6. How to diagnose atrial fibrillation?
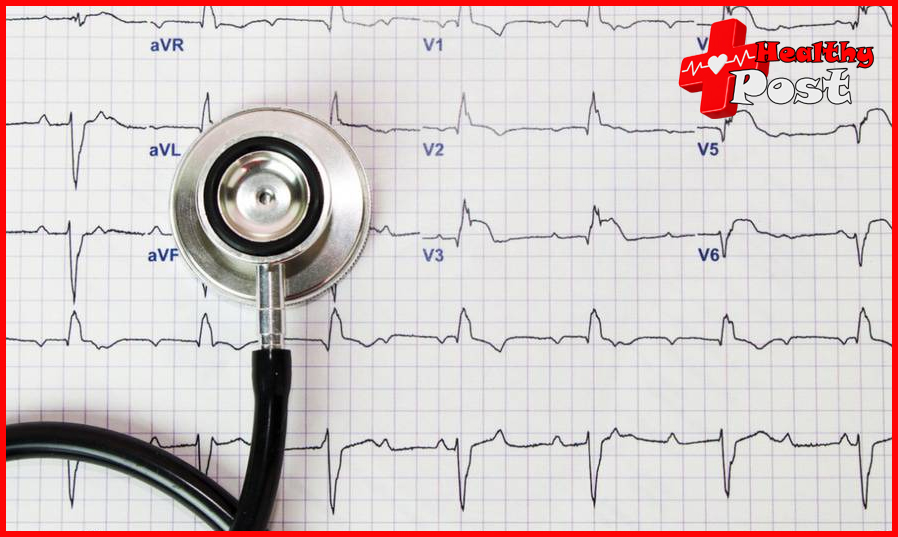
The most common method for diagnosing atrial fibrillation is an electrocardiogram (ECG).
An electrocardiogram (ECG) monitors the heart’s electrical activity through electrodes on the chest and can quickly detect abnormal heart rhythms.
To further confirm the diagnosis, some patients may need to wear a portable heart monitor to track their heart rhythm for 24 hours or longer.
7. Do female patients have a higher risk of stroke?
Yes.
Several studies have shown that women with atrial fibrillation have a higher risk of stroke than men.
This risk increases significantly, especially when women have other stroke risk factors such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
8. How to assess stroke risk?
Doctors typically use the CHA2DS2-VASc scoring system to assess stroke risk in patients with atrial fibrillation.
The system is scored based on the following factors:
Congestive heart failure
hypertension
Age (65 years and over get more points)
diabetes
History of stroke or transient ischemic attack
Vascular disease
Gender (female plus points)
The higher the score, the greater the patient’s stroke risk, and the doctor will develop a personalized prevention plan based on the score.
9. What is the best treatment for atrial fibrillation?
The goals of treating atrial fibrillation are to control symptoms and prevent stroke, and the specific plan varies from person to person.
Drug treatment
Medicines to control heart rate and rhythm
Anticoagulant drugs to reduce the risk of blood clots
Lifestyle Adjustments
Reduce weight
Control high blood pressure and blood sugar
Treating sleep apnea
Quit smoking and drinking
Surgery
Catheter ablation : A minimally invasive procedure that removes abnormal electrical signals and restores normal heart rhythm.
Watchman device implantation: For patients who cannot take anticoagulants long-term, this device can be implanted to prevent thrombosis.
10. How effective is catheter ablation?
Catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure for atrial fibrillation that restores the heart’s normal rhythm by removing the heart muscle tissue that triggers abnormal electrical signals.
Studies have shown that this surgery is effective in controlling atrial fibrillation, especially for patients who do not respond well to drug treatment.
What is a Watchman device?
The Watchman device is an implantable medical device specifically designed to reduce the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation.
It is placed in a small pouch-like structure in the atrium to prevent blood clots from forming and is suitable for people who are not suitable for long-term anticoagulant medication.
Summarize
Although it is dangerous, it is a controllable disease.
Through early diagnosis, scientific treatment and health management, most patients can effectively reduce the risk of stroke and heart failure.
If you or your family members have symptoms of atrial fibrillation, be sure to seek medical attention promptly and choose the appropriate treatment plan.

2 thoughts on “Atrial Fibrillation—10 Key Facts You Must Know”