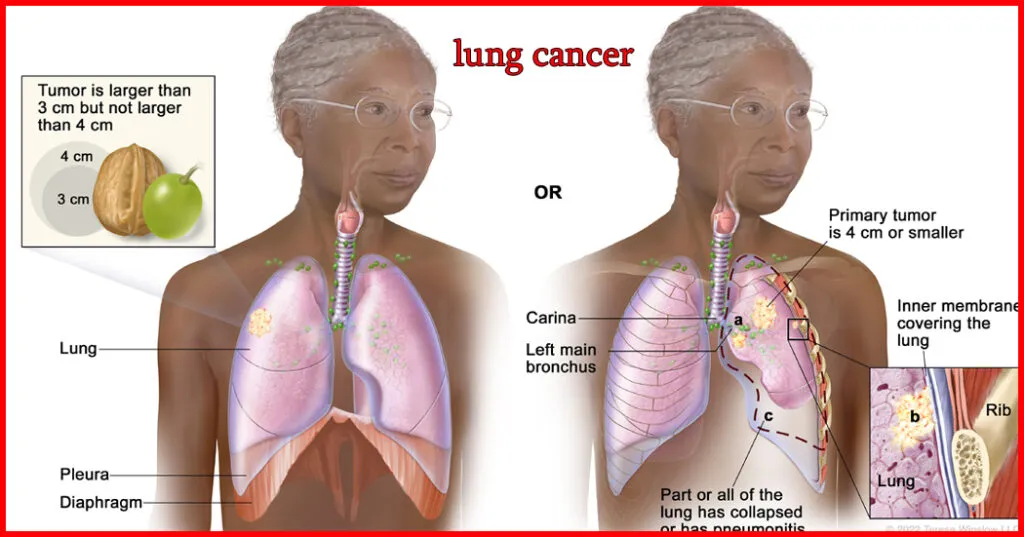
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer ICD-10: The Ultimate Guide for 2024
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a prevalent and significant condition in the medical field, accounting for the majority of lung cancer cases. Proper coding and documentation for NSCLC ICD-10 are crucial as they directly impact patient care and reimbursement processes. In this ultimate guide for 2024, we will delve into everything healthcare professionals need to know about accurately coding NSCLC with ICD-10-CM.
Consider this scenario: A dedicated oncology coder faces the challenge of accurately documenting a patient’s NSCLC diagnosis to ensure appropriate reimbursement and optimal patient care. The complexity of coding NSCLC reflects its multifaceted nature and the critical role it plays in a patient’s healthcare journey.
By understanding the intricacies of NSCLC coding, healthcare professionals can streamline the billing process and contribute to comprehensive patient care. Throughout this guide, we will explore the details of NSCLC ICD-10 coding, highlighting its importance in the constantly changing world of healthcare documentation and reimbursement.
Understanding Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a term used to describe several different types of lung cancers. Each type has its own unique features and impacts how it is diagnosed and treated. It is essential for healthcare providers who work with NSCLC patients to have a good understanding of these subtypes:
Types of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Adenocarcinoma: This is the most common type of NSCLC, especially among people who don’t smoke. It usually starts in the outer parts of the lungs and looks like glandular cells under a microscope. Adenocarcinoma tends to spread to nearby lymph nodes and other organs early on. Using visual aids can help in identifying the specific characteristics of this type of cancer.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Squamous cell carcinoma often develops in the central chest area in bronchi lined with squamous cells. It is strongly associated with smoking and exposure to harmful substances. This highlights the importance of targeted screening for individuals with a history of tobacco use. Additionally, emphasizing potential complications, such as obstructive pneumonia or hemoptysis, can underscore the significance of early detection and intervention. Supporting these points with relevant images can enhance healthcare professionals’ understanding of this subtype.
- Large Cell Carcinoma: Large cell carcinoma is less common than adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma but tends to grow quickly and spread early on. Its aggressive nature makes treatment planning challenging, so palliative care options and symptom management become more important. Highlighting the limited treatment options available for large cell carcinoma can provide insights into the complexities associated with managing this form of NSCLC.
Understanding the different characteristics of these NSCLC subtypes helps healthcare providers personalize their approach to diagnosis, treatment, and patient education based on each patient’s unique situation. By thoroughly studying the features, prevalence, and implications of each subtype, healthcare professionals can better navigate the complexities of NSCLC management.
The Significance of TNM Staging and Clinical Information
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a type of cancer that starts in the lungs. There are different types of NSCLC, including adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. It’s important to accurately classify NSCLC in order to plan the best treatment.
Understanding NSCLC and Its Subtypes
- NSCLC Definition: NSCLC is a type of cancer where abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the lung tissue. Each subtype has its own characteristics and may need different treatments.
- Clinical Signs and Distinguishing from Small Cell Lung Cancer: Symptoms of NSCLC include ongoing cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. Differentiating it from small cell lung cancer is like telling apart a slow-growing tree (NSCLC) from a rapidly spreading vine (small cell lung cancer).
- How Neoplasms Form in the Lungs: Lung tumors can develop due to various reasons such as smoking, exposure to harmful substances, or genetic factors.
- Importance of Diagnostic Methods: Tests like CT scans and biopsies are crucial for confirming NSCLC. For example, a case study can show how a patient’s CT scan revealed a suspicious mass in the lung, leading to further tests for confirmation.
TNM Staging: Assessing NSCLC Extent
TNM staging helps determine how far NSCLC has spread:
- Tumor size (T): It measures the size and reach of the main tumor.
- Lymph Node involvement (N): It shows if cancer has reached nearby lymph nodes.
- Metastasis (M): It checks for any spread of cancer to distant organs or tissues.
Gathering Clinical Information
When dealing with NSCLC cases, it’s important to gather relevant clinical details:
- Patient history
- Symptoms experienced
- Laboratory test results
These details are crucial for proper coding, billing, treatment decisions, and reimbursement processes.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer ICD-10-CM Code: Understanding and Updates for 2024
The ICD-10-CM coding system is crucial for accurately classifying diseases and procedures in healthcare. For non-small cell lung cancer, the specific ICD-10-CM code C34.90 is vital for precise documentation and billing. This code allows healthcare professionals to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes, ensuring proper financial coverage for the provided care.
Key Components and Coding Guidelines
The ICD-10-CM code C34.90 covers malignant neoplasm of the unspecified part of the unspecified bronchus or lung. It provides a standardized way to record diagnoses and simplifies the billing process. Understanding its key components and coding guidelines is crucial for healthcare professionals to accurately document non-small cell lung cancer cases.
Updates in the 2024 Edition
The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM will take effect on October 1, 2023. It’s important for healthcare professionals to stay updated on the recent changes, especially those related to non-small cell lung cancer. These updates may affect claims submission and reimbursement processes, highlighting the importance of being familiar with the changes to ensure compliance and accuracy in coding practices.
By fully understanding the role of ICD-10-CM in disease classification, learning about the specifics of the C34.90 code, and staying updated on the 2024 edition changes, healthcare professionals can improve their ability to document and code non-small cell lung cancer cases effectively.
The Relationship Between Tissue Analysis and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment
Tissue analysis plays a crucial role in diagnosing different types of non-small cell lung cancer, which helps determine the most effective targeted therapies. Pathologists examine tissue samples under a microscope to identify the specific subtype of non-small cell lung cancer, such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, or large cell carcinoma. This information is vital for oncologists to create personalized treatment plans based on the subtype, maximizing effectiveness while minimizing side effects.
The Importance of Quality Tissue Samples
To accurately analyze the tissue, it’s essential to obtain high-quality samples. Interventional pulmonology procedures like bronchoscopy and transthoracic needle biopsy are used to collect tissue specimens from the lungs. These techniques allow healthcare providers to gather enough material for thorough analysis, leading to precise diagnosis and tailored treatment approaches for non-small cell lung cancer patients.
Collaboration for Optimal Care
Recognizing how tissue analysis influences treatment highlights the importance of involving pathology experts in the comprehensive management of non-small cell lung cancer. It underscores the significance of collaborative decision-making among pathologists, pulmonologists, medical oncologists, and other specialists to optimize patient care and outcomes for this complex disease.
Conclusion
Staying updated on the latest coding guidelines and advancements in non-small cell lung cancer management is crucial for healthcare professionals. This article has provided a comprehensive understanding of non-small cell lung cancer ICD-10-CM coding and its updates.
To further enhance your knowledge in oncology practice, it is essential to explore additional resources. That address coding challenges associated with metastatic cancers and treatment-related complications. By continually educating yourself, you can ensure accurate coding and billing for non-small cell lung cancer cases. Ultimately improving patient care and reimbursement.
Remember, proper documentation and precise coding are essential components in the fight against non-small cell lung cancer. Let’s work together to stay ahead of the curve and provide optimal care for patients.

2 thoughts on “Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer ICD-10: The Ultimate Guide for 2024”