
what cbc blood test indicate cancer
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) test is a crucial tool for assessing your overall health. It provides important information that can indicate the presence of various medical conditions, including cancer. This simple blood test analyzes three key components of your blood: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. In this informative article you can know, what cbc blood test indicate cancer ?
Many people mistakenly believe that cancer detection requires complex imaging tests or invasive procedures. However, a CBC test can actually serve as an early warning system for certain types of cancer, especially those affecting the blood. By examining the results of this test, healthcare providers can identify unusual patterns in your blood that may suggest the presence of cancer cells.
Key Health Indicators from CBC Tests:
- Changes in white blood cell counts
- Variations in red blood cell levels
- Abnormal platelet numbers
- Unusual cell shapes or sizes
Understanding your CBC results empowers you to take an active role in managing your health. This knowledge becomes particularly valuable when discussing potential health concerns with your healthcare provider, particularly in relation to cancer detection and monitoring.

Understanding the Complete Blood Count (CBC) Test
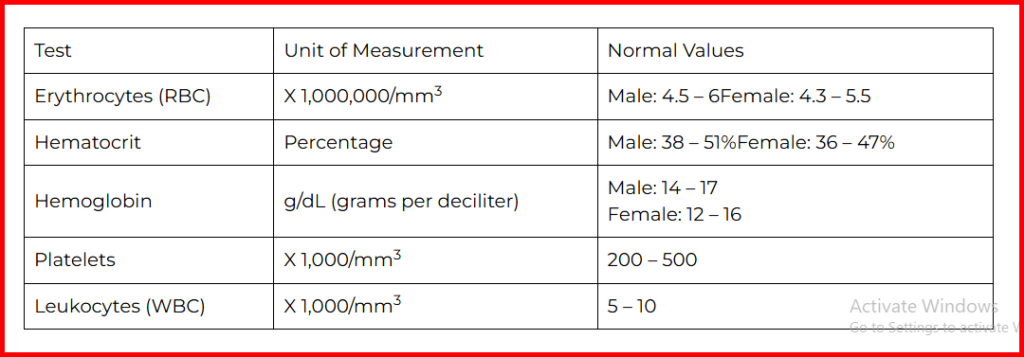
A Complete Blood Count test serves as a comprehensive health screening tool, examining the three main components of your blood: red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets. This vital diagnostic test provides doctors with crucial information about your body’s blood composition and potential health concerns.
Key Components Measured in CBC:
1. Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
- Transport oxygen throughout your body
- Measured through hemoglobin levels and hematocrit percentages
- Indicate potential anemia or blood disorders
2. White Blood Cells (WBCs)
- Act as your body’s defense system
- Include different types: neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils
- Higher or lower counts may signal infection, inflammation, or blood disorders
3. Platelets
- Essential for blood clotting
- Help prevent excessive bleeding
- Abnormal counts can indicate bleeding disorders or bone marrow problems
The CBC test measures specific values for each component:
- RBC count: 4.5 to 5.5 million cells/mcL
- WBC count: 4,500 to 11,000 cells/mcL
- Platelet count: 150,000 to 450,000/mcL
These numbers create a baseline for your health status. Any significant deviation from these ranges triggers further investigation. Medical professionals use CBC results to diagnose conditions, track disease progression, and monitor treatment effectiveness. The test’s ability to measure multiple blood components makes it an invaluable tool in medical assessments.
How CBC Results Can Indicate Cancer Presence
CBC test results can reveal specific patterns that raise red flags for certain types of cancer, particularly blood-related malignancies. These patterns emerge through distinct abnormalities in blood cell counts and characteristics.
Blood Cancer Indicators in CBC Results:
Leukemia Signs
- Extremely high white blood cell counts (>100,000 cells/mcL)
- Presence of immature or abnormal white blood cells
- Unexplained anemia (low red blood cell count)
- Decreased platelet counts
These are some of the common signs and symptoms of leukemia that can be detected through a CBC test.
Lymphoma Markers
- Abnormal lymphocyte counts
- Unexpected drops in all blood cell types
- Presence of atypical lymphocytes
- Unexplained anemia with normal iron levels
Other Cancer-Related CBC Changes:
Bone marrow cancers often show:
- Pancytopenia (reduction in all blood cell types)
- Unusual cell shapes or sizes
- Presence of blast cells (immature blood cells)
Blood cancers can disrupt normal blood cell production in unique ways. For example, leukemia cells crowd out healthy blood-forming cells in bone marrow, leading to decreased production of normal blood cells. This disruption creates distinctive patterns visible in CBC results.

Key CBC Measurements That May Signal Cancer:
- White Blood Cell Count
- Extremely high or low counts
- Presence of abnormal cell forms
- Red Blood Cell Parameters
- Unexplained low hemoglobin levels
- Unusual cell sizes or shapes
- Platelet Count
- Significantly low numbers
- Abnormal platelet size
These changes often appear gradually and may be detected before physical symptoms develop. A single abnormal result doesn’t automatically indicate cancer, but persistent abnormalities warrant further investigation through specialized testing.
Furthermore, specific types of leukemia such as acute promyelocytic leukemia also present unique indicators in CBC results that should not be overlooked.
The Role of Abnormal White Blood Cell Counts in Cancer Diagnosis
White blood cell (WBC) counts are important in diagnosing cancer, especially blood-related cancers. A normal WBC range is usually between 4,000 and 11,000 cells per microliter. If there is a significant difference from these numbers, it is important to seek medical attention.
High WBC Counts and Cancer
- Counts above 11,000 cells/microliter indicate an elevated WBC level
- Persistent elevation might signal chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) often presents with extremely high WBC counts
- Some patients show counts exceeding 50,000 cells/microliter
Common Signs Accompanying Elevated WBCs
- Unexplained fever or night sweats
- Frequent infections
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Bone pain
- Unusual fatigue
A detailed analysis of WBC subtypes provides additional diagnostic insights:
- Neutrophils: Elevation suggests acute myeloid leukemia
- Lymphocytes: High counts indicate chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- Blast cells: Presence signals acute leukemia
Medical professionals examine WBC patterns alongside other symptoms. Sudden spikes in WBC counts require immediate medical evaluation, as early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes. Regular monitoring helps track disease progression and treatment effectiveness in diagnosed patients.
Other non-cancerous conditions can cause elevated WBC counts:
- Infections
- Inflammatory diseases
- Stress
- Certain medications
This complexity highlights the need for healthcare providers to conduct thorough evaluations in order to determine the specific reason behind abnormal WBC counts.
Understanding Low Platelet Counts: A Possible Sign of Cancer
A decrease in platelet count, known as thrombocytopenia, can be a potential warning sign for certain types of cancer. Platelets are essential for blood clotting, and when their levels drop below 150,000 per microliter of blood, it raises concerns among healthcare providers.
Types of Cancer That Can Cause Low Platelet Counts
Several types of cancer can lead to low platelet counts:
1. Blood Cancers
- Leukemia
- Multiple myeloma
- Lymphoma
2. Solid Tumors
- Advanced-stage breast cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Lung cancer
How Cancer Affects Platelet Counts
Cancer can impact platelet counts through various mechanisms:
- Direct Bone Marrow Impact: Cancer cells invading the bone marrow can disrupt platelet production
- Immune System Response: The body might destroy platelets as part of its reaction to cancer
- Cancer Treatment Effects: Chemotherapy and radiation can temporarily lower platelet counts, leading to low blood cell counts
Common Signs of Low Platelets
Here are some common signs that may indicate low platelet levels:
- Easy bruising
- Prolonged bleeding from minor cuts
- Tiny red spots under the skin
- Frequent nosebleeds
- Blood in urine or stool
What Low Platelet Counts Mean
A complete blood count (CBC) test showing low platelet counts doesn’t automatically mean cancer is present. Other factors such as viral infections, certain medications, or autoimmune disorders can also cause thrombocytopenia. To determine if cancer might be the underlying cause, doctors look at the pattern and severity of platelet reduction along with other blood count changes.
When platelet levels drop significantly (below 50,000 per microliter), doctors usually recommend further tests like bone marrow biopsies or imaging studies to check for potential cancer presence.
Why CBC Alone Cannot Confirm or Rule Out Cancer
A CBC test provides valuable health insights, yet it has specific limitations when it comes to cancer diagnosis. Understanding these constraints helps patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about additional testing needs.
Key Limitations of CBC Testing:
- CBC tests primarily detect blood-related cancers
- Solid tumors often show no CBC abnormalities
- Many non-cancerous conditions can cause similar CBC changes
The test’s inability to detect solid tumors presents a significant limitation. Breast, lung, prostate, and colon cancers might progress without causing any noticeable changes in blood cell counts. These types of cancers require specific screening methods such as imaging studies, biopsies, or specialized blood markers.
Common Scenarios Where CBC Falls Short:
- Early-stage cancers might show normal blood counts
- Some aggressive cancers can develop without affecting blood values
- CBC changes can be subtle or masked by other health conditions
A normal CBC result doesn’t guarantee the absence of cancer. Many patients with early-stage malignancies maintain normal blood counts until their disease reaches advanced stages. This reality underscores the importance of comprehensive medical evaluations that include multiple diagnostic tools.
Medical professionals view CBC results as one piece of a larger diagnostic puzzle. They combine these findings with physical examinations, patient history, specific cancer markers, and imaging studies to form accurate diagnoses.

Using CBC to Monitor Cancer Treatment Progress and Detect Complications Early On
CBC tests serve as a vital tool during cancer treatment, providing real-time insights into a patient’s response to therapy. These regular blood tests create a detailed picture of how the body reacts to different treatments.
Treatment Response Monitoring:
CBC tests are used to monitor the effectiveness of cancer treatments in several ways:
- Tracks changes in blood cell counts after chemotherapy sessions
- Indicates bone marrow function and recovery between treatments
- Shows effectiveness of targeted therapies on blood cell production
- Helps doctors adjust medication dosages based on patient response
Early Detection of Treatment Complications:
Blood count changes can signal various treatment-related issues:
- Low white blood cell counts – risk of infection
- Decreased red blood cells – anemia development
- Reduced platelet levels – bleeding risks
- Abnormal cell patterns – potential disease progression
In some cases, these blood count changes can lead to conditions such as pancytopenia, which requires immediate medical attention.
Medical teams use CBC results to make critical decisions:
- Timing of next treatment sessions
- Need for supportive medications
- Adjustments to current therapy protocols
- Prevention of serious complications
Regular CBC monitoring allows healthcare providers to maintain a delicate balance between aggressive treatment and patient safety. This proactive approach helps medical teams identify and address potential complications before they become severe, ensuring optimal treatment outcomes while maintaining patient quality of life.
The Importance of Follow-Up Testing After Abnormal CBC Results are Found
Abnormal CBC results require immediate attention and a structured approach to diagnosis. Your healthcare provider will typically recommend specific follow-up tests based on the type of abnormality detected:
For Low Red Blood Cell Counts:
- Iron studies to check for anemia
- Vitamin B12 and folate level tests
- Bone marrow biopsy in certain cases
Elevated White Blood Cell Counts:
- Blood smear examination
- Flow cytometry
- Genetic testing
- Bone marrow analysis
For Abnormal Platelet Counts:
- Coagulation tests
- Bone marrow examination
- Additional blood tests to check for autoimmune conditions
Your doctor might also request imaging studies such as:
- CT scans
- MRI
- PET scans
- X-rays
The timing of these follow-up tests is crucial. Some tests need immediate attention within 24-48 hours, while others can be scheduled within a few weeks. Your healthcare provider will prioritize these tests based on:
- Severity of the abnormality
- Your current symptoms
- Medical history
- Risk factors
- Age and general health condition
Remember: Abnormal CBC results don’t automatically indicate cancer. Many non-cancerous conditions can cause similar blood count changes. The follow-up testing process helps establish an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Beyond Cancer Detection: Other Health Insights Provided by a Complete Blood Count Test
A CBC test is a powerful diagnostic tool that can do more than just detect cancer. It provides valuable information about different aspects of your health. This comprehensive blood analysis can reveal:
- Infection Status: Elevated white blood cell counts might indicate bacterial or viral infections
- Anemia Detection: Low red blood cell counts or hemoglobin levels point to different types of anemia
- Bleeding Disorders: Abnormal platelet counts can signal clotting issues or bleeding risks
- Nutritional Status: CBC results help identify deficiencies in iron, vitamin B12, or folate
- Bone Marrow Function: The test evaluates how well your body produces blood cells
- Autoimmune Conditions: Certain patterns in blood cell counts can suggest autoimmune disorders
- Allergic Reactions: Specific white blood cell variations might indicate allergic responses
Your CBC results create a detailed snapshot of your body’s internal functioning. These insights enable healthcare providers to detect and monitor various health conditions, from minor infections to chronic diseases, making it an invaluable tool in preventive healthcare and disease management.
Regular Health Check-Ups: Your Best Defense Against Late-Stage Cancer Diagnosis
Regular health screenings, including CBC tests, are your first line of defense against late-stage cancer diagnosis. Making these check-ups a priority can literally save your life.
Here’s why routine CBC tests matter:
- They establish your baseline health markers
- They detect subtle changes before symptoms appear
- They enable early intervention when treatment is most effective
- They provide peace of mind about your health status
Take charge of your health with these simple steps:
- Schedule annual physical exams with your healthcare provider
- Keep track of your CBC test results
- Report any unusual symptoms promptly
- Follow up on abnormal test results without delay
Remember: Early detection through regular screening dramatically improves cancer survival rates. Your CBC test results tell a story about your health – make sure you’re listening to that story by maintaining consistent check-ups.
Don’t wait for symptoms to appear. Book your next health screening today and take control of your well-being. A simple blood test could make all the difference in catching potential health issues at their most treatable stage.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What does a CBC blood test indicate about cancer?
A CBC blood test can provide important insights into your health and may indicate the presence of certain types of cancer. Abnormalities in the levels of red blood cells (RBC), white blood cells (WBC), or platelets can suggest further investigation is needed, particularly for cancers such as leukemia or lymphoma.
How can elevated white blood cell counts relate to cancer diagnosis?
An elevated white blood cell (WBC) count may be a sign of leukemia or other types of cancer. This condition indicates that the body is responding to an underlying issue, which could include a malignancy, and warrants further evaluation by a healthcare professional.
What does low platelet count mean in the context of cancer?
Low platelet counts, known as thrombocytopenia, can be associated with various cancers. This condition may indicate bone marrow involvement or other malignancies that affect platelet production, making it an important factor in cancer detection.
Why can’t a CBC test alone confirm or rule out cancer?
While a CBC test provides valuable information regarding blood components, it cannot definitively confirm or rule out cancer, especially solid tumors. Additional diagnostic tests and evaluations are necessary to arrive at a conclusive diagnosis.
How can CBC tests be used during cancer treatment?
Regular CBC tests are beneficial during cancer treatment as they help monitor the response to therapy and detect any complications early on. These tests provide crucial information about how well the body is coping with treatment and whether adjustments are needed.
What should I do if my CBC results are abnormal?
If your CBC results show abnormalities, it is essential to follow up with your healthcare provider for further testing. Additional diagnostic evaluations will help confirm or rule out serious conditions like cancer and guide appropriate treatment options.


One thought on “what cbc blood test indicate cancer”