Bradyarrhythmia symptoms, causes, and treatment
Bradyarrhythmia is a heart rate that is slower than your typical heart rate due to an irregular heartbeat . Do you know Bradyarrhythmia symptoms ? Let’s know and discuss it.
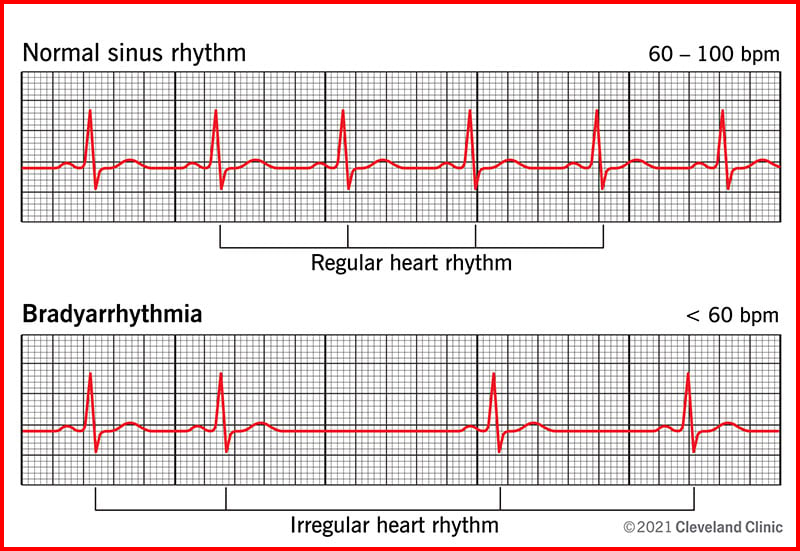
People with bradyarrhythmias have a resting heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute.
For most adults, a resting heart rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute is considered normal.
Sometimes, healthy people naturally slow their heart rate.
But people with bradyarrhythmia have a slow heart rate due to a medical condition, heart disease, or a defect that affects the heart rhythm.
What is the difference between bradyarrhythmia and bradycardia ?
Both terms mean a slower than average heart rate.
Bradycardia is a resting heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute.
Bradyarrhythmia is a slow heart rate caused by an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia).
Healthy young people and athletes usually have a resting heart rate below 60 beats per minute.
For them, bradycardia does not indicate illness.
In fact, a slow heart rate is a sign that they are healthy and have a strong heart.
It is also normal for your heart rate to drop below 60 beats per minute while you sleep.
What are the types of bradyarrhythmias?
There are several different types of bradyarrhythmias.
Each type has its own causes, but they all result in a lower-than-typical heart rate.
Types of bradyarrhythmias include:
(1) Sinus node dysfunction :
Sinus node dysfunction is also called sick sinus syndrome .
The sinoatrial (or sinus) node is often referred to as the heart’s natural pacemaker.
It is an important part of the heart’s electrical system.
The sinoatrial node sends out electrical impulses that trigger the heart to beat.
An underactive thyroid gland ( hypothyroidism ) can cause sinus node dysfunction.
Alternatively, diseases or defects that affect the sinus node can cause sick sinus syndrome.
It is more common as we age, but in many cases there is no known cause.
(2) Heart block :
Heart block is something that blocks the heart’s electrical signals.
The block prevents the electrical impulses in your heart from traveling as they should.
May cause a slow heart rate or skipped heartbeats.
(3) Bradycardia/tachycardia syndrome:
In some cases, sinus node dysfunction can cause alternating slow and fast heart rates .
Atrial fibrillation+ (Afib) is one of these syndromes.
What causes bradyarrhythmias?
Most arrhythmias, including bradyarrhythmias, are caused by heart disease or heart damage.
Some causes of bradyarrhythmias include:
(1) Age-related changes in the cardiac electrical system.
(2) Coronary artery disease .
(3) Heart defects.
(4) Cardiac medications, such as beta-blockers .
(5) Metabolic imbalance (such as hypothyroidism).
(6) Cardiac trauma or injury (e.g., heart attack).
What are the signs and symptoms of bradyarrhythmia?
When your heart pumps too slowly, your brain may not get enough blood and oxygen.
Symptoms of bradyarrhythmia may include:
(1) Dizziness.
(2) Fainting.
(3) Fatigue.
(4) Shortness of breath.
(5) Weakness.
How are bradyarrhythmias diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will perform a thorough physical examination and ask about any symptoms you are experiencing.
To accurately diagnose arrhythmia, your provider will measure and track your heart rate. Diagnostic tests may include:
(1) Electrocardiogram:
An electrocardiogram (also called an EKG) records the heart’s electrical impulses.
(2) Portable electrocardiogram equipment:
Your heart may not develop an abnormal rhythm while you are in the doctor’s office.
To help diagnose arrhythmias, you may need to wear a portable ( holter ) monitor, such as a Holter monitor, for 24 to 48 hours.
(3) Exercise stress test :
During an exercise stress test, increasing your heart rate while walking on a treadmill can help identify abnormal heart rhythms.
(4) Echocardiography :
An echocardiogram provides pictures of the heart’s valves and chambers as they pump blood.
(5) Electrophysiological examination:
Electrophysiology studies provide detailed information about how the heart’s electrical system works.
How are bradyarrhythmias managed or treated?
In some cases, an underlying medical condition can cause a bradyarrhythmia.
For example, treating an underactive thyroid gland can help improve a slow heart rate.
When bradyarrhythmias are caused by changes in the heart’s electrical system, your provider may recommend inserting a pacemaker.
This electronic device generates electrical pulses to help you maintain a steady, healthy heart rate.
How to prevent bradyarrhythmias?
One preventive measure is to treat underlying health conditions, such as hypothyroidism .
You can also reduce your risk of bradyarrhythmia by taking good care of your heart.
To keep your heart healthy, you should:
(1) Eat a heart-healthy diet.
(2) Limit alcohol intake.
(3) Maintain a healthy weight.
(4) Maintain physical activity.
(5) Quit smoking and using tobacco products.
What is the prognosis (outlook) for people with bradyarrhythmias?
If left untreated, bradyarrhythmias can lead to serious health problems and may cause dizziness and fainting.
Getting the right treatment can restore your heart’s normal rhythm and reduce your risk of complications.
When should I call my doctor?
You should call your healthcare provider if you experience:
(1) Chest pain.
(2) Difficulty breathing.
(3) Dizziness or lightheadedness.
(4) Fainting.
(5) Severe fatigue.
What should I ask my doctor about bradyarrhythmias?
You may want to ask your healthcare provider:
(1) How do I know if my heart rate is too slow?
(2) Is my heart rate low enough to cause health problems?
(3) Do I need medication to control my arrhythmia?
(4) Do I need a pacemaker to restore normal heart rhythm?
Bradyarrhythmia is an abnormally slow resting heart rate, usually less than 60 beats per minute.
A slow heart rate may be caused by changes in the heart’s electrical system, heart defects, or other medical conditions.
Your healthcare provider can treat bradyarrhythmias with medicine or a pacemaker.
Restoring a normal heart rhythm helps your heart function properly and reduces your risk of complications.