How to diagnose asthma in children, 5 tests can help you confirm
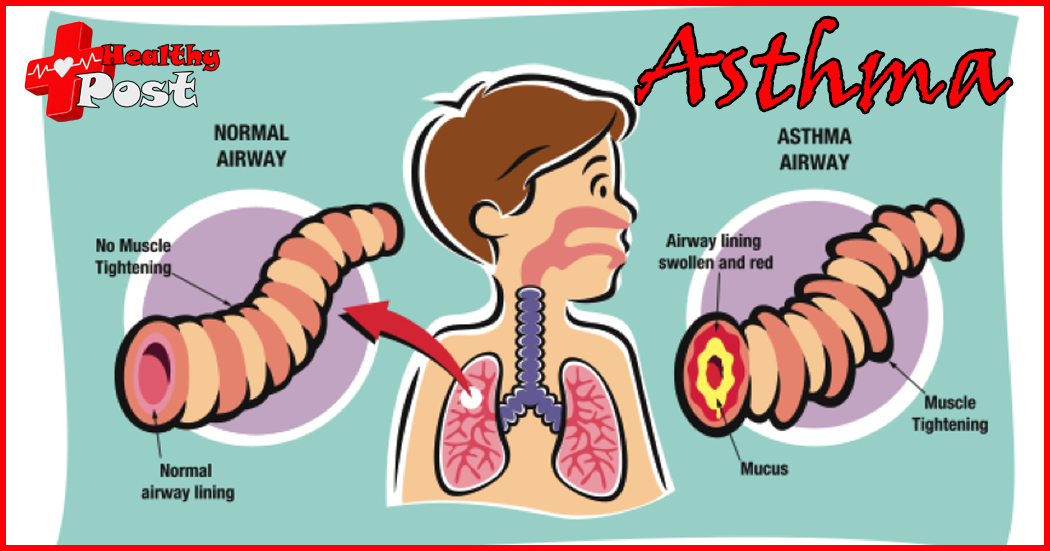
Asthma is a wheezing lung disease that is prone to recurring attacks. Asthma is mostly cause by colds in children, or it may be cause by exposure to other foreign objects. In general, frequent asthma attacks in children are very easy to identify. However, some children’s symptoms are not very obvious, or the condition is hidden to a certain extent, making it difficult to diagnose. So, how to diagnose asthma in children?
01 Chest X-ray
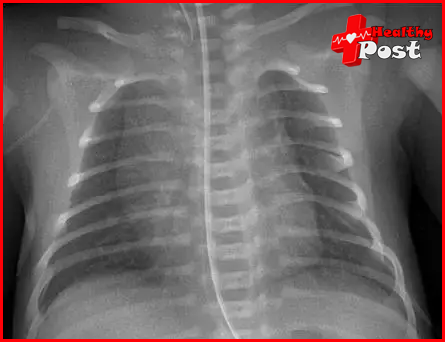
Chest X-rays should be taken to rule out lung parenchymal lesions, congenital anomalies, foreign body signs, etc. During an acute asthma attack, chest radiographs may be normal, or there may be emphysema, peribronchial interstitial infiltrates, and atelectasis. Pneumothorax and mediastinal emphysema are occasionally seen. During it attack in children, wheezing sounds, mainly expiration, can be heard in both lungs.
02 Perform lung function testing
The expiratory volume in 1 second can be measured. If the FEV1 is measured to be greater than or equal to 70% of the normal predicted value in a child with suspected asthma, the bronchial provocation test can also be used to measure airway reactivity.
For children with suspect it whose FEV1 is less than or equal to 70% of the predicted normal value, there are certain limitations and reversibility in choosing a bronchodilation test to evaluate airflow. Therefore, during the measurement process, if the bronchial provocation test is positive and the bronchodilation test is positive greater than or equal to 20%, it will help to diagnose it in children.
03 Allergen testing
For all children with repeated wheezing and suspect it, especially preschool children who are unable to cooperate with lung function testing. It is recommend to conduct allergen skin prick testing or serum allergen-specific IgE measurement to understand the patient’s allergic status and assist it.
Reminder: When a child repeatedly suffers from bronchitis, pneumonia or coughs repeatedly, accompanied by wheezing. Also has a family history and a personal history of allergies (eczema, allergic rhinitis, urticaria, etc.). Asthma should be highly suspected and he should go to a children’s asthma specialist for further treatment. Check and confirm.
04 Blood test
Routine blood tests can also detect whether children have it. Generally, a routine blood test shows an increase in eosinophils and neutrophils. If co-infection occurs, white blood cells and neutrophils will be significantly elevated.
05 Non-invasive airway inflammation index detection
Eosinophils and exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) levels in sputum or induced sputum can be use as indicators of airway inflammation in asthma. Although there are currently no prospective studies to confirm the exact value of these non-invasive inflammatory markers in the diagnosis of childhood asthma. It monitoring of these markers can help assess the level of asthma control and develop optimal asthma treatment plans.

6 thoughts on “How to diagnose asthma in children, 5 tests can help you confirm”