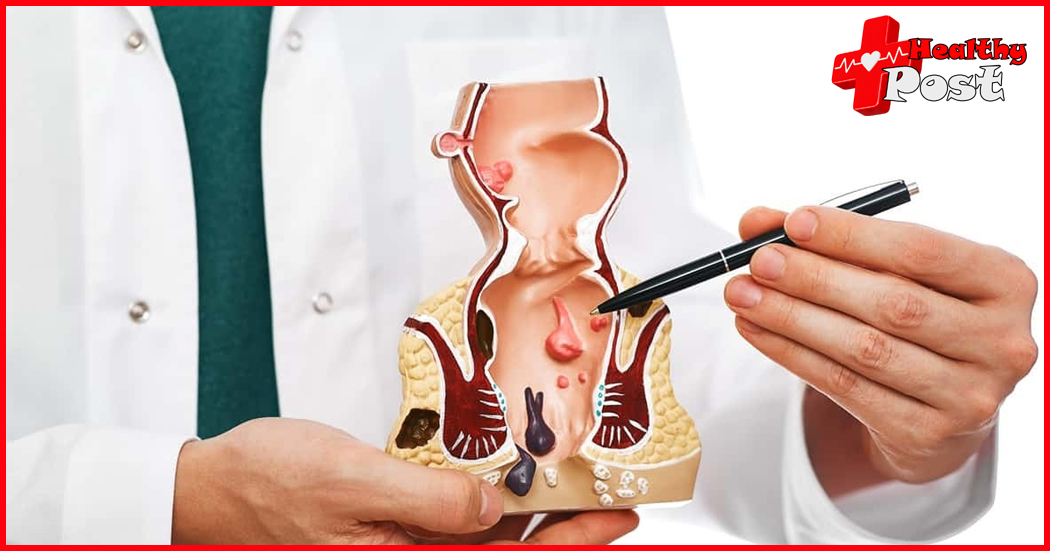
Understanding Anal Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Anal cancer is a serious medical condition that affects the anal canal, a short tube located at the end of the rectum. While it may not be widely discussed or well-known, anal cancer can have a significant impact on individuals’ lives. Understanding this disease and its potential consequences is crucial for early detection and successful treatment.
Early detection plays a pivotal role in improving outcomes for anal cancer patients. By recognizing the signs and symptoms, individuals can seek prompt medical help and receive appropriate treatment. This can greatly increase their chances of successful recovery and long-term survival.
In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for anal cancer. Our goal is to provide readers with valuable information to help them better understand this condition and empower them to take control of their health.
What We Will Cover
- Development of anal cancer
- Risk factors such as HPV infection, smoking, and weakened immune system
- Common symptoms that may indicate the presence of anal cancer
- Various treatment options available to manage this disease
Through knowledge and understanding, we can make a difference in improving outcomes for those affected by this disease.
Understanding Anal Cancer: From Cell Growth to Malignancy
Anal cancer is a type of cancer that originates from the growth of abnormal cells in the anal canal, which is a short tube located at the end of the rectum. These cells multiply rapidly and form tumors, leading to the development of anal cancer. To understand this process better, let’s dive into the details:
The Anal Canal
The anal canal plays a crucial role in the elimination of waste from the body. It is lined with specialized cells that are constantly renewing themselves to maintain its function.
Cell Growth
The growth and renewal of cells in the anal canal are tightly regulated by the body’s natural processes. However, sometimes these processes can go awry, leading to uncontrolled cell growth.
Development of Abnormal Cells
In anal cancer, certain genetic mutations occur within the cells lining the anal canal. These mutations disrupt the normal cell growth and division, causing them to grow uncontrollably.
Tumor Formation
As these abnormal cells continue to divide and accumulate, they form a mass or tumor. This tumor can be either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
Malignancy
In the case of anal cancer, the tumor becomes malignant. When it invades nearby tissues or spreads to other parts of the body. This process, known as metastasis, can occur through lymphatic vessels or blood vessels.
To help visualize this complex process, think of normal cell growth as a well-orchestrated dance where each step is controlled and coordinated. However, in anal cancer, certain factors disrupt this dance, causing chaos and an uncontrolled frenzy of cell division.
An analogy that might help is to imagine a peaceful garden with carefully pruned plants. Under normal circumstances, each plant grows at a steady pace and maintains its shape. But if there’s an issue with the garden’s caretaker or an infestation of pests, the plants might grow wildly and invade each other’s space, leading to a disorganized and chaotic garden.
Understanding how anal cancer develops from normal cell growth to malignancy is crucial in recognizing the importance of early detection and treatment. By catching the abnormal cell growth in its early stages, individuals have a higher chance of successful treatment and improved outcomes.
What Causes Anal Cancer? Unraveling the Role of HPV and Other Risk Factors
Anal cancer is a complex disease with multiple contributing factors. While there are several risk factors involved. The primary focus lies on the link between human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and anal cancer development. Let’s explore this connection further and delve into other significant risk factors. That can contribute to the development of anal cancer.
The Link with HPV
HPV is a common sexually transmitted infection that affects both men and women. It is estimated that around 90% of anal cancers are caused by HPV, particularly the high-risk types like HPV-16. This virus can infect the cells in the anus and lead to abnormal cell growth, which can eventually progress into cancer.
The transmission of HPV occurs through skin-to-skin contact during sexual activities, including anal intercourse. Receptive anal intercourse increases the risk of HPV transmission, making it an important factor in the development of anal cancer. Other sexual behaviors, such as having multiple partners or engaging in unprotected sex, also increase the likelihood of contracting HPV and developing anal cancer.
Additional Risk Factors
While HPV is a major contributor to anal cancer, there are other risk factors that can increase the chances of developing this disease:
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains carcinogens that can damage DNA and increase the risk of various cancers, including anal cancer. Smokers have a higher likelihood of developing anal cancer compared to non-smokers.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those living with HIV/AIDS or taking immunosuppressive medications after organ transplantation, are more susceptible to HPV infection and subsequent development of anal cancer. A compromised immune system reduces the body’s ability to fight off infections and control abnormal cell growth.
Real-Life Examples
To better understand how these factors contribute to the disease process, let’s consider a few real-life examples:
- Sarah, a 35-year-old woman, was diagnosed with anal cancer after years of smoking and engaging in unprotected anal intercourse. Her history of HPV infection further increased her risk, leading to the development of cancerous cells in her anus.
- John, a gay man in his 40s, had been living with HIV for over a decade. His weakened immune system combined with his history of receptive anal intercourse and HPV infection made him more susceptible to anal cancer. Regular screening helped detect the disease at an early stage.
These examples highlight how the interplay between risk factors like HPV infection, smoking, and weakened immune system can contribute to the development of anal cancer. It is crucial to understand these connections to raise awareness about preventive measures and early detection.
Recognizing the Signs: Common Symptoms and When to Seek Help
Anal cancer can present with a variety of signs and symptoms, which can vary from person to person. It is important to be aware of these potential indicators and take action if you notice any concerning changes. By recognizing the signs early on, you can seek medical help promptly and improve your chances of successful treatment.
- Bleeding from the rectum: One of the most common symptoms of anal cancer is rectal bleeding, which may occur during bowel movements or persistently throughout the day. The blood may appear bright red or dark in color, depending on the location and severity of the cancerous growth. It is essential not to dismiss rectal bleeding as hemorrhoids without proper evaluation by a healthcare professional.
- Itching and pain around the anus: Anal itching (pruritus ani) and discomfort or pain in the anal area are common symptoms of anal cancer. These symptoms may be persistent or intermittent, worsening over time as the cancer progresses. It is important to note that itching and pain can also be caused by other conditions such as hemorrhoids or infections, so a thorough evaluation is necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
- Changes in bowel habits: Anal cancer can lead to changes in bowel habits, including diarrhea or constipation that lasts for an extended period. You may also experience a feeling of incomplete bowel movement even after passing stools. These changes should not be ignored, especially if they are unrelated to dietary changes or other identifiable causes.
- Lumps or masses near the anus: In some cases, anal cancer may cause the development of lumps or masses near the anus. These can be felt as growths, bumps, or hard nodules during self-examination or physical examination by a healthcare professional. Any new growths should be investigated promptly to determine their cause.
These symptoms
It is important to remember that these symptoms can have various causes, and experiencing them does not necessarily mean you have anal cancer. However, if you notice any of these signs persisting for more than a few weeks or if they are accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as unexplained weight loss or fatigue, it is crucial to seek medical attention.
If you notice any of the aforementioned symptoms or have concerns about your health, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. Early detection and diagnosis are key to successful treatment outcomes. Remember, it’s always better to be proactive when it comes to your health.
“When I first noticed rectal bleeding, I assumed it was just hemorrhoids. But when it persisted for several weeks, I knew something wasn’t right. I reached out to my doctor who referred me to a specialist. It turned out to be anal cancer, and thanks to early intervention, I am now cancer-free. Don’t ignore your body’s warning signs – they could save your life.” – Sarah, anal cancer survivor
By listening to your body and seeking medical help when needed, you can play an active role in safeguarding your health.
From Diagnosis to Survivorship: A Multimodal Approach to Anal Cancer Management
Anal cancer is a complex disease that requires a comprehensive and multimodal approach to management. In this section, we will explore the various methods used for diagnosing anal cancer. And delve into the main treatment modalities available. We will also hear from a survivor who will share their real-life treatment journey. Highlighting the importance of integrative care and emotional support throughout the process.
Anal Cancer Diagnosis: Confirming the Disease
Diagnosing anal cancer involves a series of tests and procedures aimed at confirming the presence of malignant cells in the anal canal. Here are some common diagnostic methods:
- Physical Examination: During a physical examination, a healthcare provider may visually inspect the anus and surrounding areas for any visible abnormalities or lesions. They may also perform a digital rectal exam to assess the size and location of tumors.
- Imaging Techniques: Imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or positron emission tomography (PET) scans may be used to obtain detailed images of the anal canal and nearby lymph nodes. These imaging tests help determine the extent of the disease and if it has spread to other parts of the body.
- Biopsy: A biopsy is crucial for confirming an anal cancer diagnosis. During this procedure, a small tissue sample is taken from the suspicious area in the anal canal and sent to a laboratory for analysis. The biopsy results will reveal whether cancerous cells are present, as well as provide information on the specific type and stage of anal cancer.
Treatment Modalities: Surgery, Chemotherapy, and Radiation Therapy
The management of anal cancer typically involves a combination of treatment modalities tailored to each individual’s specific case. The main treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
- Surgery: Surgery plays a central role in treating anal cancer, especially in early-stage cases. The goal of surgery is to remove the cancerous tumor along with a margin of healthy tissue to ensure complete eradication. Depending on the size and location of the tumor, different surgical techniques may be employed, such as local excision, wide local excision, or abdominoperineal resection. In some cases, a colostomy may be necessary to divert stool temporarily or permanently.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. It can be administered before surgery (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) to shrink tumors and increase the chances of successful surgical removal. It can also be given after surgery (adjuvant chemotherapy) to destroy any remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence. Additionally, chemotherapy may be used as the primary treatment for advanced or metastatic anal cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy involves the use of high-energy X-rays or other forms of radiation to target and destroy cancer cells. It is often combined with chemotherapy (chemoradiation) as the primary treatment for anal cancer. This combination approach has been shown to improve outcomes by increasing tumor response rates and reducing the risk of recurrence. Radiation therapy may also be used after surgery to eliminate any residual cancer cells.
Real-Life Treatment Journey: The Importance of Integrative Care and Emotional Support
To truly understand the impact of anal cancer treatment on patients’ lives, we turn to a survivor who shares their personal journey. [Survivor’s Name], diagnosed with anal cancer [number] years ago, underwent a multimodal treatment plan that included surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Throughout their treatment journey, emphasizes the importance of integrative care and emotional support. They found solace in joining support groups where they could connect with others facing similar challenges. Additionally, complementary therapies such as acupuncture and meditation helped alleviate treatment side effects and improve overall well-being.
[Survivor’s Name]’s story highlights the need for a holistic approach to anal cancer management. It underscores the value of emotional support, both from healthcare providers and fellow survivors, in navigating the physical and emotional toll of treatment.
In the next section, we will explore the role of palliative care in enhancing. The quality of life for individuals with advanced-stage anal cancer. We will also discuss complementary therapies and lifestyle strategies that can complement medical interventions.
Palliative Care: Enhancing Quality of Life for Advanced Anal Cancer Patients
Palliative care is crucial for individuals dealing with advanced-stage anal cancer. Its primary focus is on relieving symptoms and improving overall well-being, with the goal of enhancing the quality of life for patients facing the challenges of this condition. This specialized form of care provides comprehensive support to both patients and their families, addressing their physical, emotional, and psychological needs.
Supportive Treatments
Alongside traditional medical treatments, palliative care also includes various complementary therapies and lifestyle strategies that can greatly contribute to managing symptoms and promoting emotional wellness. Some examples are:
- Pain Management: Using medications, physical therapy, and alternative treatments to reduce pain and discomfort.
- Emotional Support: Offering counseling, support groups, and other mental health services to help individuals cope with the psychological effects of the disease.
- Nutritional Guidance: Providing dietary advice to ensure proper nutrition and overall health during treatment.
Managing Side Effects
Patients undergoing treatment for advanced anal cancer often experience a range of side effects. Palliative care professionals are committed to assisting these individuals in navigating these challenges by offering personalized approaches for managing side effects like nausea, fatigue, and loss of appetite. By addressing these issues proactively, palliative care aims to minimize the impact of treatment-related symptoms on patients’ daily lives.
Personal Stories
Real-life stories from individuals who have benefited from palliative care can offer valuable insights into its positive effects. These accounts demonstrate how comprehensive support approaches have made a significant difference in the lives of patients dealing with advanced-stage anal cancer. By sharing these experiences, readers can develop a deeper understanding of the practical benefits. Also emotional importance of palliative care in this particular situation.
Beyond Treatment: Navigating Survivorship with Vigilance and Hope
Surviving anal cancer is a significant milestone, but it does not mark the end of the journey. As a survivor, it is important to navigate the path of survivorship with vigilance and hope. Here are some key points to consider:
Guidance on long-term follow-up care strategies for anal cancer survivors
After completing treatment for anal cancer, regular follow-up care is essential to monitor your health. Detect any signs of recurrence or late effects. Your healthcare team will develop a personalized surveillance plan based on your individual needs. Some important aspects of long-term follow-up care include:
- Regular check-ups: These appointments will typically involve physical examinations, discussions about any symptoms or concerns, and an opportunity to address any emotional or psychological challenges you may be facing.
- Surveillance tests: Depending on your specific situation, your healthcare provider may recommend periodic imaging tests (such as CT scans or MRIs) or blood tests to monitor for any signs of recurrence.
- Psychosocial adjustment support: Surviving anal cancer can bring about a range of emotions and challenges. It is crucial to seek support from counselors, therapists, or support groups who specialize in helping cancer survivors navigate the emotional and psychological aspects of their journey.
Embracing the new normal while staying vigilant
As you move forward in your life post-treatment, it is important to embrace your “new normal” while remaining vigilant about potential signs of disease recurrence or late effects. Here are some tips to help you strike this balance:
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to any changes or symptoms that may arise. This includes persistent pain, unexplained weight loss, bowel changes, or any other unusual symptoms. If anything seems concerning, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare team.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Adopting a healthy lifestyle’ As suggested by the Mayo Clinic, can help reduce the risk of cancer recurrence and improve overall well-being. This includes eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol use, and managing stress.
Effective communication with healthcare providers
Establishing open and effective communication with your healthcare team is crucial for ongoing care. Here are some tips to facilitate clear communication:
- Ask questions: Don’t hesitate to ask your healthcare provider any questions or voice any concerns you may have. Understanding your follow-up care plan and being informed about potential risks or warning signs will empower you to take an active role in your own health.
- Keep a record: Maintain a record of your treatments, tests, and appointments. This will help you stay organized and ensure. That you have all the necessary information readily available when discussing your care with healthcare providers.
- Seek clarification: If anything is unclear during conversations with your healthcare team, politely ask for further explanation or clarification. It’s important to fully understand the information provided to make informed decisions about your ongoing care.
Navigating survivorship after anal
Conclusion
Raising public awareness about anal cancer is crucial for ensuring timely diagnosis and improved outcomes. By being advocates for their own health and that of others. Readers can share accurate information and destigmatize discussions around anal cancer.
Those affected by the disease are encouraged to seek support from reputable patient organizations and online communities. Embracing the new normal post-treatment while staying vigilant about potential signs of disease recurrence or late effects is essential for navigating survivorship with hope.
Remember, early detection and exploring treatment options are key in the fight against anal cancer.


One thought on “Understanding Anal Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment”